![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Arteries of Circle of Willis:
|
Anterior cerebral
ant communicating post communicating posterior cerebral internal carotid artery |
|
|
Which veins run through the skull bones? what runs into them?
|
Diploic veins, supplied by emissary veins
|
|
|
Innervation of eye muscles:
Sensory motor Autonomic |
sens - V1 and V2
Motor: 3 4 and 6 auto - carotic plexus, 3 and V2 |
|
|
Which extra-oc muscle nerve is NOT in lateral wall of cavernous sinus?
|
Abducens
|
|
|
Which extra-oc nerve does not pass thru the tendinous ring?
|
trochlear
|
|
|
Which extra-oc muscles are innervated by which nerves?
|
ciilary/sphincter by oculomotor
lateral rectus- abduc sup oblique - trochlear |
|
|
Branches of the aorta, and their branches
|
1 Braciocephalic trunk - r subclavian and R C. C. Artery
2 Left common carotid 3 Left subclavian |
|
|
What does the vertebral artery arise from? where does it go?
|
From the Subclavian arteries, thru the Foramen magnum becomin BASILAR ARTERY
|
|
|
What are the 5 structurs present in fetal circulation system not present after birth?>
|
umbilical arteries
umbilical veins ductus venosum for ovale (of heart) ductus arteriosum |
|
|
What muscles does the ansa cervicalis innervate?
|
Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, omohyoid
|
|
|
What innervates the trapezius and SCM muscle?
|
Accessory
|
|
|
What nerves make up ansa cervicalis?
|
C1-C3
|
|
|
what 3 veins make up portal vein
|
splenic, sup and inf mesenteric (from the gut)
|
|
|
pharyngeal arch 1
1 - what is the cartilage? 2 - what - bones does it make 3 - what muscles come from it (9) 4 - what nerve is it? 5 - what signal involved 6 - ligament? |
1 - meckels
2- max/mand 3 - 5 mastication muscles, anterior digastric, mylohyoid, 2 tensors 4 - Trigeminal 5 - endothelin 6 - sphenomandibular, anterior malleus |
|
|
Pharyngeal arch 2 -
1 - cartilage? 2 - ligament? 3 - muscles 4 - nerve 5 - signal 6 -bones |
1 - reicharts
2 - stylohyoid 3 - facial expression, post igastric, stapedius, stylohyoid 4 - facial 5 - hoxa2 6 - hyoid, stapes, styloid process |
|
|
Pharyngeal arch 3-
1- bone? 2 - muscle? 3 - nerve? |
1 - lower body of hyoid
2 -stylopharyngeus 3 - glossopharyngeal |
|
|
PA 4 -
1 - cartilage 2 - muscle 3 - nerve |
1 - thyroid
2 - pharyng constrictor, cricothyroid 3 - motor: pharyngeal plexus (vagus, glosso, accesory) (ext of sup laryngeal) sensory - glosso |
|
|
PA 6 -
1 - cartilage 2 - muscle 3 - nerve |
1 - laryngeal
2 - intrinsic larynx muscles 3 - rec. laryngeal of vagus |
|
|
in development, the lateral nasal proces
and the max process form what? |
Intermaxillary segment
|
|
|
2 key components of muscular hydrostat
|
orthogonal muscle orienation
volume preserving |
|
|
4 extrinsinc tongue muscles
|
palatoglossus
hyoglossus genioglossus styloglossus |
|
|
4 intrinsic tongue muscles
|
superior longituntinal
inferior longitudinal verticalis transversus |
|
|
which muscles retract tonue?
|
hyoglossus, styloglossus, maybe palatoglossus
|
|
|
which muscles depress the tongue?
elevate? |
inf longitundinalis? genio and hyoglossus
|
|
|
which muscles elevate the tongue?
|
styloglossus, sup longitud?
|
|
|
Innervation of the tongue muscles: MOTOR:
|
hypoglossal: GG, HG, SG, IL, SL, V, T
vagus: pG |
|
|
innervation of tongue: sensory
1anterior 2/3 taste 2anterior 2/3 sensory 3posterior 1/3 taste 4posterior 1/3 sensory |
1 - facial
2 - v3 lingual 3 - glosso 4 - glosso |
|
|
What are the 3 nerves of taste?
|
facial - ant tongue
Gloss - post tongue Vagus - epiglottis taset |
|
|
What are the 3 branches of lingual artery and what do they supply
|
Dorsal lingual - tonsils, phary consrtrictors, soft palate, epiglottis, post tongue muc membrane
Deep lingual - tongue Sublingual - glands |
|
|
which papililla have taste buds
|
fungiform, circumvallate, foliate in childhood
|
|
|
what goes wrong in the following
1 - unilateral cleft palage 2 - bilateral cleft palage 3 - unilat cleft palage and jaw and lip 4 - bilateral lip, palage, jaw |
1 - intermax segment and max process
2 - intermax segmant and bothe mx processes 3 - no fusion of intermax + max AND no palatine shelves 4 - no intermax and med nasal elevations don't fuse |
|
|
What nerves are in the submandibular region?
|
Mylohyoid, lingual, and hypoglossal
|
|
|
What artery/vein are in submandibular region?
|
mylohyoid, lingual, facial
|
|
|
Innervation of hyoid muscles:
1- post dig? 2 - ant dig? 3 - stylohyoid? 4 - mylohyoid? 5 - geniohyoid? |
1 - facial
2 - V3's mylo 3 - facial 4 - mylo 5 - c1 |
|
|
what openings are in the superior meatus
|
post ethmoidal sinus
|
|
|
what openings are in the middle meatus
|
frontonasal duct into hiatus semilunaris
maxilarry sinus via hiatus semilunaris ant ethmoidal sinus via eth bulla holes |
|
|
what openings in inferior meatus
|
nasolacrimal duct opening
|
|
|
what opnings in sphenoethmoidal recess
|
spenhoid sinus
|
|
|
nasal septum boundaries
|
cartilage, perp plates of ethmoid and hyoid
|
|
|
what nerve supplies the glands of the nasal cavity
|
facial
|
|
|
greater palatine nerve supplies
|
soft palate
|
|
|
lesser palatine nerve supplies
|
hard palate and max teeth
|
|
|
what site can give a full maxillary block?
|
pterygopalatine ganglion in the pterygomaxillary fissure
|
|
|
descriibe PSA block
|
45degrees to both mid sag line and plane of occlusion, just behind zygomatic process
|
|
|
site of problem for PSA block
|
hitting the venous(pterygoid) plexus can giv ehematoma
|
|
|
where is the site of block for ASAN
|
infraorbital
|
|
|
If you go too far in a infraorbital nerve block?
|
blindness, dialation of pupi, loss of sensation in forehead, fixed eye position
|
|
|
primary function of lymph system
|
return lymph to venous system
|
|
|
a lymph node is shaped like a __1___ with __2___ lymph vessels entering at __3___ which have __4__ which consist of densely packed __5___ and some __6__ dispersed throughout. the ___7__ lymph vessels leave through the __8__ area
|
1 - kidney
2 - afferent 3 - cortex 4 - nodules 5 - lymphocytes 6 - germinal centers 7 - effferent 8 - medullary |
|
|
2 superior deep cervical nodes are
|
jugulomohyoid and jugulodigastric, are superior to omohyoid
|
|
|
jugulomohyoid drains
|
ant tongue, submand and submental nodes
|
|
|
jugulomohyoid drains into
|
inf deep cervical node
|
|
|
jugulodigastric drains
|
palatine/lingual tonsils, post palate, post tongue
|
|
|
jugulodigastric into
|
inf deep cervical
|
|
|
inf deep cervical nodes drain
|
ant jug nodes, transverse cerv nodes and sup deep cervical nodes
|
|
|
jugular trunks which drain all lymph from R or L side of head. these are formed by
|
deep cervical nodes
|
|
|
Jugular trunks drain into ___ on left and ___on right
|
left - thoracic
Right - right lymphatic |
|
|
Where is DANGER SPACE 4
|
between alar fascia (ant. projection of) and prevertebral fascia
|
|
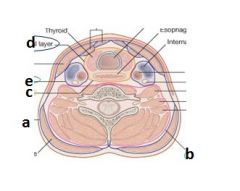
|
a - investing fascia
b - prevertebral fascia c - buccopharyngeal d - pretracheal e - carotid sheath |
|
|
what are the cartilages of the larynx?
|
3 paired: arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform
3 unpaired - epi, thy, cric |
|
|
function of noggin and chordin
|
stimulate neuroectoderm development by inhibiting BMP4
|

