![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
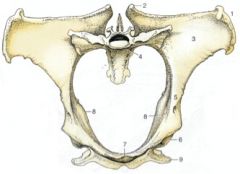
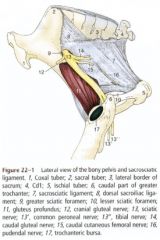
ID this pelvis
|
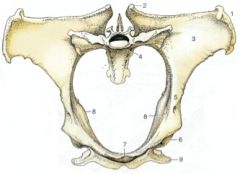
1. Tuber coxae
2. Tuber sacrale 3. Wing of ilium 4. Sacral promontory 5. Shaft of ilium 6. Acetabulum 7. Brim of pubis 8. Ischial spines 9. Tuber ischiadicum |
|
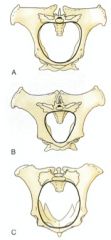
ID the species/sex of these.
|
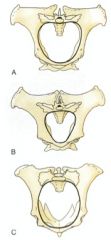
Mare
Stallion Cow |
|
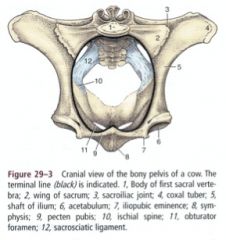
ID 1,2,5,8,12
What do these structures make up? |
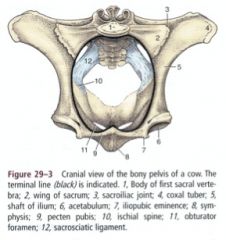
Pelvic roof
Sacrum (1,2) and first few caudal vertebrae Lateral pelvic wall Shaft of the ilium (5) Sacrosciatic ligament (12) Pelvic floor Ischium and pubis Pelvic symphysis (8) These are the boundaries for the pelvic cavity |
|
|
What are the structures coursing through the greater ischiatic foramen in the horse? What are it's borders?
|
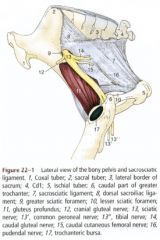
Located cranial to the ischiatic spine
Bordered by the greater ischiatic notch and the sacrosciatic ligament Passageway for the sciatic nerve and cranial gluteal artery, vein, and nerve and caudal gluteal nerve |
|
|
What courses through the lesser ischiatic foramen in the horse? What are its boundaries?
|
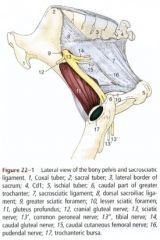
Located caudal to the ischiatic spine
Bordered by the lesser ischiatic notch and the sacrosciatic ligament Tendon of the internal obturator is the only structure to course through the lesser ischiatic foramen in the horse |
|
|
Where does the sacrosciatic ligament course? Where are it's borders attached? What does it form?
|
Fibrous sheet extending from the lateral part of the sacrum to the ilium and ischium
Forms much of the lateral pelvic wall Dorsal border is attached to the sacrum and the transverse processes of Ca1 and Ca2 vertebrae Ventral border is attached to the ischiatic spine and tuber ischiadicum Caudal border is fused with the vertebral head of semimembranosus m. |
|
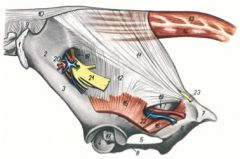
ID 11, 12, 18, 19, 20 , 21, 22
|
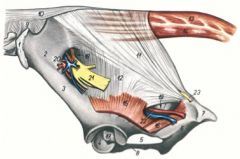
Sacrosciatic ligament (11, 12)
Greater ischiatic foramen (18) Passageway for the sciatic nerve (21) and cranial gluteal artery, vein, and nerve (20) Lesser ischiatic foramen (19) Passageway for the caudal gluteal artery and vein (22) |
|
|
What anatomical differences in the ruminant affect the boundaries of the sacrosciatic ligament?
|
Because of the absence of vertebral heads of the caudal thigh muscles, the caudal part of the sacrosciatic ligament is the dorsolateral boundary of the ischiorectal fossa between the root of the tail and the tuber ischiadicum
|
|
|
What ligament is a parturition marker in a cow?
|
The sacrosciatic ligament softens near parturition
|
|
|
What is correlated to dystocia or birthing difficulty in bovine parturition?
|
The pelvic inlet width
|
|
|
What are the boundaries of the pelvic inlet?
|
Sacral promontory
Iliopectineal line of the ilium -Craniomedial border of the ilium Pecten pubis (pecten ossis pubis) -Cranial margin of the pubis -Located between the pubic tubercle and iliopubic eminences |
|
|
What are the boundaries of the pelvic outlet?
|
Tuber ischiadicum and ischial arch
Free edges of sacrosciatic ligaments 3rd caudal vertebra |
|
|
What are the dimensions for measurement in pelvimetry of the bovine?
|
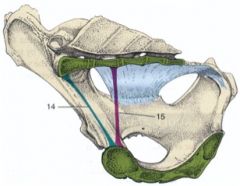
Transverse diameter
Distance between right and left psoas minor tubercles Measuring the widest part Vertical diameter (15) Distance between pecten pubis and roof of the pelvic cavity Measuring the narrowest part Conjugata (14) Distance between sacral promontory |
|
|
In which species is the sacrosciatic ligament more extensive? Which has more soft tissues in the pelvic canal?
|
The mare has both a more extensive sacrosciatic ligament and more soft tissues in the pelvic canal.
|
|
|
Who typically has more problems with parturition mares or cows?
|
Mares
You can pull out a calf with chains. Horse birth is more forceful. Check this with Rita |
|
|
Define that region of body wall that closes the pelvic cavity caudally
|
Perineum
|
|
|
Define the perineal region
|
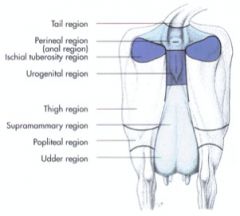
Dorsal boundary – base of tail
Ventral boundary – udder or scrotum Lateral boundary – sacrotuberous ligament, tuber ischiadicum Urogenital and anal regions |
|

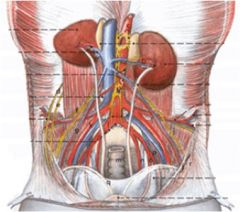
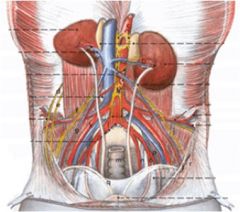
ID these female structures in the abdominal cavity.
What would 1 be in the pelvic cavity? What would 2 be in a male? |
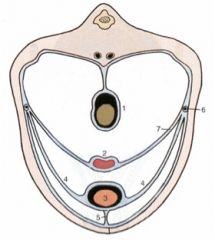
1 Colon (rectum in the pelvic cavity)
2 Uterus (ductus deferens in the male) 3 Bladder 4 Lateral ligament of the bladder 5 Median ligament of the bladder 6 Ureter 7 Broad ligament of the uterus (mesometrium) |
|
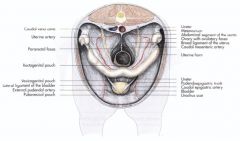
What can you ID here in this mare pelvic peritoneal reflections?
|
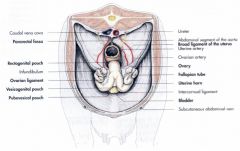
What can you ID here in this bovid pelvic peritoneal reflections?
|
|
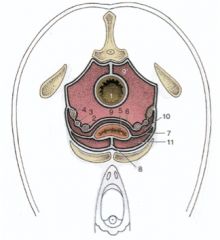
ID these Peritoneal reflections of the pelvis – Stallion
|
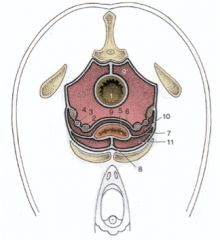
1. Rectum
2. Ductus deferens 3. Ureter 4. Vesicular gland 5. Bladder 6. Genital fold 7. Lateral ligament of the bladder 8. Median ligament of the bladder 9. Rectogenital pouch 9’. Pararectal fossa 10. Vesicogenital pouch 11. Pubovesical pouch |
|
|
What are the layers of the rectus sheath? Where does it insert?
|
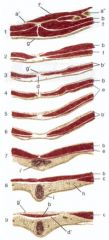
Internal lamina
-Aponeurosis of transversus abdominis m. -Transversalis fascia External lamina -Fused aponeuroses of internal (c) and external abdominal oblique mm. Rectus sheath (b’) surrounds rectus abdominis m. (b) Insertion: prepubic tendon (d’) on pecten pubis |
|
|
What structures course through the inguinal canal in the male and female?
|
In the male:
External pudendal a. and v., genitofemoral n., lymphatics Spermatic cord In the female: External pudendal a. and v., genitofemoral n., lymphatics |
|
|
What are the boundaries of the deep inguinal ring?
|
Cranial boundary is caudal edge of internal abdominal oblique m.
Caudal boundary is inguinal ligament (caudal edge of aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique m.) |
|
|
Where does the superficial inguinal ring sit?
|
Slit in the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique m. – between pelvic and abdominal tendons
|
|
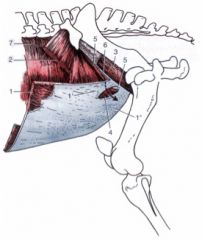
What are the boundaries of the superficial and deep inguinal rings?
|
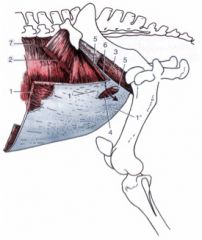
Superficial inguinal ring (4)
Slit in the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique m. – between pelvic (1’) and abdominal (1”) tendons Deep inguinal ring Cranial boundary is caudal edge of internal abdominal oblique m. (5) Caudal boundary is inguinal ligament (6) (caudal edge of aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique m.) |
|
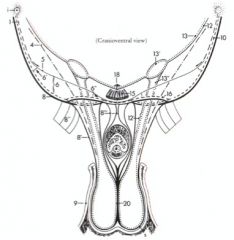
ID these inguinal canal structures
|
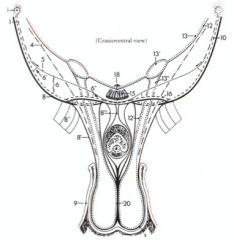
4. Cremaster m.
5. Internal abdominal oblique m. 6. Deep inguinal ring 6’ Lateral angle 6’’ Medial angle 8. Abdominal tunic 8’ External spermatic fascia 8’’ Femoral lamina 8’’’ Suspensory ligament of penis 9. Skin 10. External abdominal oblique m. 12. Transversalis fascia 12’ Internal spermatic fascia 13. Peritoneum 13’ Vaginal ring 13’’ Vaginal process 15. Rectus abdominis m. 16. Superficial inguinal ring |
|
ID g, j, q, and r
|
g. Testicular a. and v.
j. Genitofemoral n. q. Ductus deferens r. Deep inguinal ring |
|
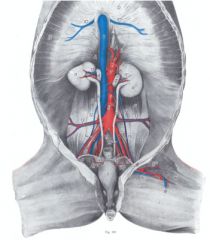
ID 1, 12, 8, 14, 13, 15, 19 in this horse
|
Aorta (1)
Testicular a. (12) / Ovarian a. Caudal mesenteric a. (8) External iliac a. (14) Deep circumflex iliac a. (13) Cremaster a. (15) / Uterine a. Internal iliac a. (19) |
|
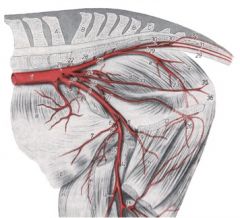
ID 2-10 in this horse (branches off of external iliac a)
|
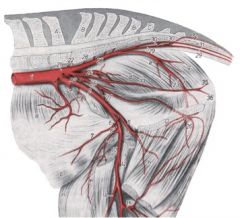
External iliac a. (2)
-Deep circumflex iliac a. (3) -Uterine a. (4) (important and big) / Cremaster a. -Deep femoral a. (5) --Pudendoepigastric trunk (6) ---Caudal epigastric a. (7) ---External pudendal a. (8) -Femoral a. (10) |
|
|
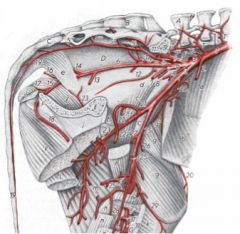
Follow the pudendoepigastric trunk in the horse
|
Pudendoepigastric trunk (53)
-Caudal epigastric a. (54) -External pudendal a. (55) --Caudal superficial epigastric a. / cranial mammary a. (56) --Ventral scrotal (57) / caudal mammary a. --Cranial artery of the penis (58) |
|
|
where do the cranial and caudal mammary arteries come from?
|
external pudendal a
|
|
|
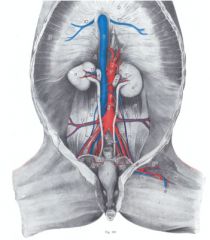
What are the branches from the caudal abdominal aorta of the ruminant?
|
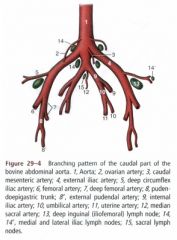
Aorta (1)
-Ovarian a. (2) / Testicular a. -Caudal mesenteric a. (3) -External iliac a. (4) --Deep circumflex iliac a. (5) --Deep femoral a. (7) ---Pudendoepigastric trunk (8) ----Caudal epigastric a. ----External pudendal a. (8’) --Femoral a. (6) -Internal iliac a. (9) -Median sacral a. (12) |
|
|
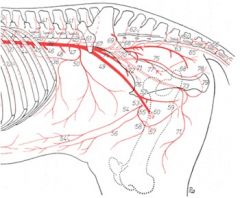
What are the external iliac a in the ruminant?
|
External iliac a. (3)
-Deep circumflex iliac a. (20) -Deep femoral a. (21) --Pudendoepigastric trunk (22) ---Caudal epigastric a. (22’) ---External pudendal a. (22’’) -Femoral a. (25) no uterine artery off of ext. iliac in the ruminant! That come off of internal iliac a. |
|
|
What are the branches of the pudendoepigastric trunk in the ruminant?
|
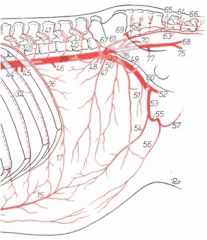
Pudendoepigastric trunk (53)
-Caudal epigastric a. (54) -External pudendal a. (55) --Caudal superficial epigastric a. / cranial mammary a. (56) --Ventral scrotal (57) / caudal mammary a. |
|
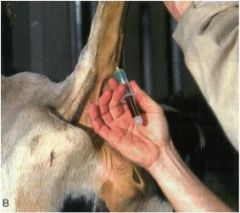
What do you have to watch out for when drawing blood from the median caudal tail vein in the ox?
|
Artery is more superficial distally
Go between the hemal arches |
|
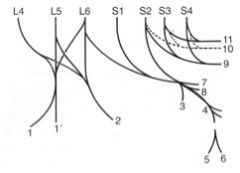
Can you ID these nerves of the pelvis? What do some of them make up?
|
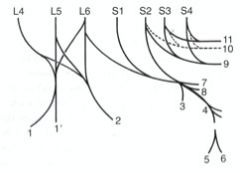
Lumbosacral plexus - femoral n, obturator n, and lumbosacral trunk; L4 to S2
Femoral n. (1) Obturator n. (2) Lumbosacral trunk -Sciatic n. (4) -Cranial gluteal n. (3) -Caudal gluteal n. (7) -Caudal cutaneous femoral n. (8) Pudendal n. (9) Caudal rectal nn. (11) Pelvic n. (10) Hypogastric n. |
|
|
Where is the pudendal n. sensory to and motor to? What does it continue as?
|
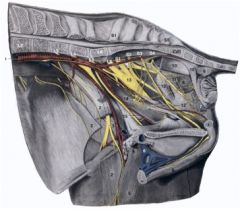
Pudendal n. (12) (superficial and deep perineal brs.)
Sensory to rectum, internal and external reproductive organs, perineal skin Motor to muscles of the perineum Continues as dorsal nerve of penis (or clitoris) |
|
|
What are the caudal rectal nn. motor to and sensory to?
|
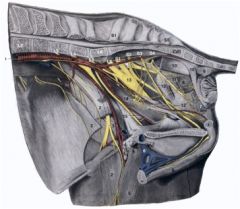
11
Sensory to rectum, anus, perianal skin Motor to dorsal perineal muscles |
|
|
What sort of nerve is the pelvic nerve? What does it innervate?
|
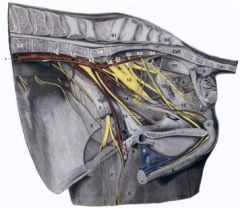
Pelvic n. (19)
Parasympathetic supply to pelvic viscera |
|
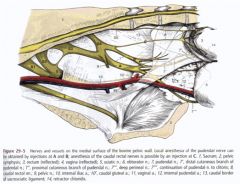
Can you name these nerves of the pelvic structures and perineum?
|
freebie
|
|
|
What are the branches of the genitofemoral n.? What do they supply? What does it course through?
|
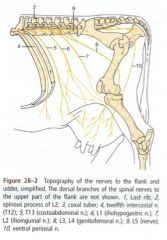
Genitofemoral n. (L3-L4) - courses through the inguinal canal.
Femoral branch Cutaneous to skin over medial aspect of thigh Genital branch Supplies spermatic fascia, scrotum, prepuce, mammary gland, part of skin over middle section of udder |

