![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Protons |
Positive charge, inside nucleus |
|
|
Neutron |
Neutral charge, inside nucleus |
|
|
Electron |
Negative charge, on electron cloud |
|
|
Majority of the mass |
Located inside the nucleus |
|
|
What subatomic particle determines the identity of a element |
Protons and electrons |
|
|
How do u determine an elements reactivity |
Number of valence electrons |
|
|
Groups determine |
The number of valence electrons |
|
|
Periods determine |
Number of energy levels |
|
|
Evidence of Chemical Reactions |
1. Gas produced 2.color produced 3.0dor 4.temperature 5.precipitate 6.light |
|
|
Law of conservation of mass |
Energy isn't created nor destroyed but merely transformed |
|
|
Unbalanced forces |
Speed up, slow down, change direction |
|
|
Balanced forces |
Constant speed, no change in motion or speed |
|
|
Speed |
Is distance an object makes over a period of time |
|
|
Velocity |
How fast a object travels in a particular direction |
|
|
Acceleration |
Increasing or decreasing its speed or changing direction |
|
|
Newtons First law |
An object will remain at rest or stay in motion until an unbalanced force acts upon it |
|
|
Newtons 2nd Law |
F=MA |
|
|
Newtons 3rd Law |
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction |
|
|
Describe the role the sun plays on the earth |
Forms currents, convection in the atmosphere, evaporation |
|
|
Convection |
The movement caused within a liquid by the tendency of heat, and therefore less dense causing it to rise and cold to sink |
|
|
Conduction |
Process by which heat or electricity is transmitted through a substance |
|
|
Radiation |
The transfer of energy via electromagnetic waves |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of high pressure |
Cold, dry, clockwise |
|
|
Low pressure |
Moist, wet, warm, precipitation, counter clockwise |
|
|
How are fronts formed |
When 2 air masses met, but don't mix because of different humidity and temperatures |
|
|
How is wind formed |
High to low pressure |
|
|
What does a hurricane need to form |
Warm water, water vapor, high and low pressure, wind |
|
|
Subscript |
It tells you how many atoms |
|
|
Coefficient |
Tells you how many molecules of the certain equation |
|
|
Precipitation |
Snow, hail, sleet, rain |
|
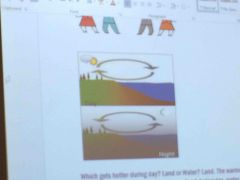
Front (Term) |
Sea breeze Land breeze |
|

Front (Term) |
The more lines, the more wind |

