![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
148 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Matter Consists of
|
Mass and Volume
|
|
|
Mass
|
is Weight
|
|
|
Volume
|
Takes up Space
|
|
|
Properties of Matter
|
Solid, Liquid, Gas. They Consist of Atoms
|
|
|
Smallest unit of an element that can exist alone
|
Atom
|
|
|
Subatomic Particles of an Atom
|
Protons (p)
Neutrons (n) Electrons (e) |
|
|
Non Subatomic Particle
|
Nucleus
|
|
|
Positive Charge
in the Nucleus |
Protons
|
|
|
Neutral Charge (0)
In the nucleus |
Neutrons
|
|
|
Negative Charge
Not in Nucleus Moves at Speed of Light Spec of Sand Compared to Protons and Neutrons |
Electrons
|
|
|
Diagram of an Atom
|
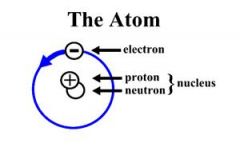
|
|
|
Substances that consists of atoms with unique properties
|
Element
|
|
|
Calculating Protons Neutrons and Electrons
|
Protons = Atomic Number
Electrons = Atomic Number Neutrons = Atomic Mass - Atomic Number |
|
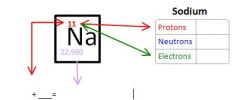
Calculating Protons Neutrons and Electrons of Sodium
|
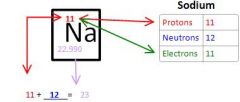
|
|
|
How Many Electrons in First Electron Shell
|
2
|
|
|
How Many Electrons in Second Electron Shell
|
8
|
|
|
How Many Electrons in Third and Beyond Electron Shell
|
18
|
|
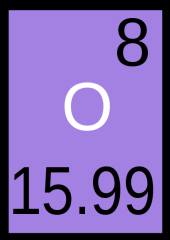
How Many
Protons Electrons Neutrons |
Protons = 8
Neutrons = 8 Electrons = 8 |
|
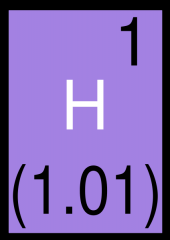
How Many
Protons Neutrons Electrons |
Protons = 1
Neutrons = 0 Electrons = 0 |
|

What is Electron Configuration of Argon
|
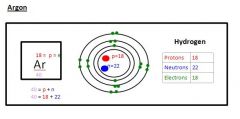
|
|
|
Atoms of the same element of with different Atomic Masses
|
Isotopes
|
|
|
What causes an Isotope
|
Different Number of Neutrons in Nucleus
|
|
|
Sharing of a pair of Electrons between 2 Atoms
|
Covalent Bond
|
|
|
Types of Covalent Bonds
|
Polar Covalent Bond
Non Polar Covalent Bond |
|
|
Polar Covalent Bond
|
The Electron Between 2 Atoms are Shared UNEqually
|
|
|
Non Polar Covalent Bond
|
Electrons are shared equally between atoms
|
|
|
Substance made up of atoms with 2 or more elements (in a fixed ratio)
|
Compounds
|
|
|
Only Consists of Covalent Bonds (smallest unit is a Molecule)
|
Molecular Bond
|
|
|
Structural Formula of Water
|
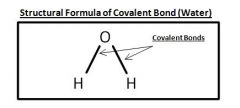
|
|
|
Most Common Elements
(CHNOPS) + Ca |
Carbon
Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur Calcium |
|
|
Most abundant Element in the universe
|
Hydrogen
|
|
|
Electrons that are Shared unequally and generates partial electron charges on the surface of the molecule
|
Polar Covalent Bond
|
|
|
Most Electronegative Element
|
Oxygen
|
|
|
Least Electronegative Element
|
Hydrogen
|
|
|
Diatomic Molecules (Not Compounds)
|
Elements of Same Type Bonded Together:
O2 N2 H2 |
|
|
Ionic Bonds made up of oppositely charged ions
|
Ionic Compounds
Example Na+ Cl- |
|
|
Attractive force between oppositely charged ions
|
Ionic Bond
|
|
|
Atom or group of atoms tat have lost or gained an Electron
|
Ion
|
|
|
Positively Charged Ion
|
Cat Ion
|
|
|
Negatively Charged Ion
|
Anion
|
|
|
Single Atom Ion
|
Monoatomic Ion
Na+ Cl- |
|
|
Example of Ion
|
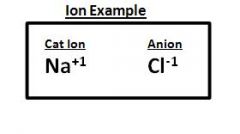
|
|
|
4 Polyatomic Ions
|
Phosphate
Hydroxyl Bicarbonate Ammonium |
|
|
Polyatomic Ion
Phosphate Ion |
PO4 -3
|
|
|
Polyatomic Ion
Hydroxyl Ion |
OH -
|
|
|
Polyatomic Ion
Bicarbonate |
NCO -3
|
|
|
Polyatomic Ion
Ammonium |
NH4
|
|
|
Sodium Atom to Sodium Ion
|
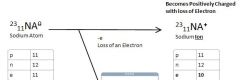
Loses An electron to Become an Sodium Ion
|
|
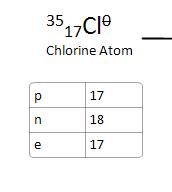
Chlorine atom to Chloride Ion
|
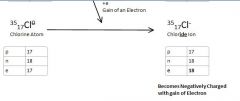
Chlorine Atom gains an electron to become an Chlorine Ion
|
|
|
Absence of Water
|
Dehydration
|
|
|
Describe how Salts breakup in H2O
|
H2O breaks the ionic bond and surrounds the ions with hydration spores which prevents the ions from rebinding
|
|
|
Weak Attraction Bonds between Polar Covalent Bonds
|
Hydrogen Bonds (H-Bond)
|
|
|
Up to how many bonds per water molecule
|
4
|
|
|
How does water become slippery and wet
|
H-Bonds rapidly break and rebind
|
|
|
How do you make h-bonds harder to break
|
drop the temperature
|
|
|
Sticking together of like molecules (H2O)
|
Cohesion
|
|
|
Sticking together of different molecules (water on wall)
|
Adhesion
|
|
|
Substance that increases the Hydrogen Ion Concentration [H+] of a water base solution
|
Acids
|
|
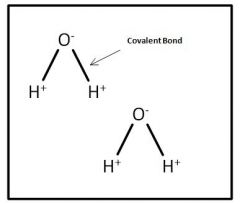
How Do water Molecules Link together
|
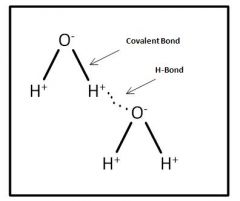
Through an H-bond
|
|
|
How do you make Hydrogen Concentration
|
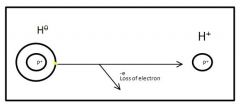
Remove the electron from the Hydrogen Atom to make it a Hydrogen Ion
|
|
|
Substance that releases Hydrogen Ions into a Solution and increases [H+] of an aqueous
|
Acid
|
|
|
Decreases the pH of a solution and makes it more Acidic
|
Proton Donors
|
|
|
How does adding HCl make a beaker of Water more Acidic
|
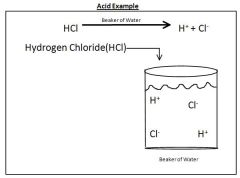
H+ unbinds from the HCl making the solution more acidic
|
|
|
Substance when added to water will decrease [H+] of that solution
|
Base (alkaline)
|
|
|
Value along the pH scale that measures the [H+] of a solution
|
pH (Power of Hydrogen)
|
|
|
Calculating pH
pH = log10([H+] mole/L) pH = log10(1x10-3 mole/L) |
3
|
|
|
How to Make a Base by adding NaOH
|
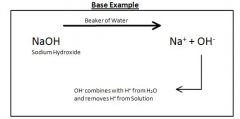
OH- combines with H+ from H20 and removes H+ from Solution
|
|
|
Chemical Added to solution so that the solution will resist changes in pH
|
Buffer
|
|
|
Buffer in an Acid
|
Binds to H+
Acids have High H+ |
|
|
Buffer in a Base
|
Releases H+
Bases has low H+ |
|
|
Acidic Solution on pH scale
|
0-6
|
|
|
Base (alkaline) on a pH scale
|
7.01-14
|
|
|
Water on a pH scale
|
7
|
|
|
pH is inversely proportional to [H+]
|
pH goes up, [H+] goes down
pH goes down, [H+] goes up |
|
|
Calculating Scientific Notation
10 -6 10 +5 |
10 -6 = .000001
10 +5 = 100000 |
|
|
Compound that DOESNOT contain Carbon
|
Inorganic Compound
|
|
|
Carbon Containing Compound
|
Organic Compound
|
|
|
Exception in Inorganic Compound
|
CO2
|
|
|
Inorganic Compounds
|
NaCl
H2O O2 MgSO4 |
|
|
3 Solutions of Water
|
Cytoplasm
Interstitial Fluid Blood Plasma |
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
Water in Cells
|
|
|
Interstitial Fluid
|
Water Between Cells
|
|
|
Blood Plasma
|
Water that circulates in blood vessels
|
|
|
Solvent
|
Always Water
|
|
|
Solute
|
Mix into a solvent
|
|
|
Ease at which it can be mixed into water
|
Solubility
|
|
|
Easy to dissolve
(Salt, glucose) |
Hydrophilic
|
|
|
Difficult to Dissolve
(Fat, oil, wax) |
Hydrophobic
|
|
|
Organic Compounds
4 |
Carbohydrates
Lipids (fats, oils) Proteins Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA) |
|
|
3 Carbon Skeletons
|
Straight Chain
Branched Chain Ring Chain (Contains O or N) |
|
|
Straight Chain Carbon
|
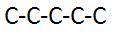
|
|
|
Branched Chain Carbon Skeleton
|
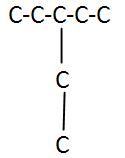
|
|
|
Ring Chain Carbon Skeleton
|
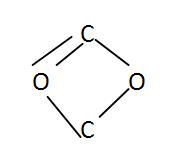
|
|
|
Groups of atoms that attached to carbon chain. They have chemical properties of organic compounds
|
Functional Groups
|
|
|
List 6 Functional Groups
|
Hydroxyl -OH
Carboxyl -COOH Amine -NH2 Carbonyl -C=O Phosphate -PO4 Methyl - CH3 |
|
|
Hydroxyl Group Functional Group
|
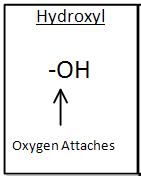
|
|
|
Carbynol
|
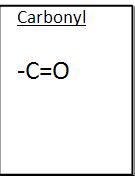
|
|
|
Carboxyl Group
|
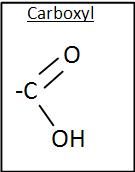
|
|
|
Amine Group
|
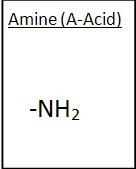
|
|
|
Phosphate Group
|
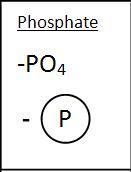
|
|
|
Methyl Group
|
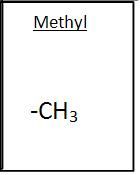
|
|
|
Includes sugars and large complex molecules like starch and glycogen
|
Carbohydrates
|
|
|
List 4 Types of Carbohydrates
|
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides Oligosaccharides Polysaccharides |
|
|
Building block unites that are used to make other carbohydrates
Contains 3-7 Carbons |
Monosaccharides
|
|
|
Monosaccharides
5 in carbon Skeleton |
Pentose
Ribose, Deoxyribose |
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
Hexose
*Glucose*, Fructose |
|
|
Drawing of Glucose
|
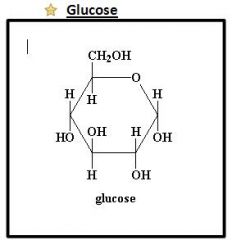
|
|
|
Glucose
|
To make ATP (dextrose)
|
|
|
2 Monosaccharides bonded together
|
Disaccharides
|
|
|
Bond between 2 Disaccharides (Glucose and Fructose)
|
Covalent Bond called
Glycosidic Bond |
|
|
When a H and OH are removed form the reactants and end up as a water molecule as a covalent bond forms
|
Dehydration Synthesis
|
|
|
Example of Dehydration Synthesis
|

Glucose + Fructrose Form Sucrose + H20 molecule
|
|
|
7-10 Monosaccharides linked together to make glucose
|
Polysaccharides
|
|
|
Animal Cells are made up of
|
7-10 Glycogen liked by Glycocidic Bonds
|
|
|
Plant cells are made up of
|
Starch
|
|
|
Types of Lipids
|
Fats
Oils Steroids Phospholipds |
|
|
Fatty Acids
|
Saturated Fats
Unsaturated Fats |
|
|
Saturated Fats
|
DOESNOT contain a double bond (C=C) in the hydrocarbon chain between 2 Carbons
|
|
|
Unsaturated Fats
|
Contains at least 1 double bond (C=C) between 2 carbons in the hydrocarbon chain **Fewer Hydrogen**
|
|
|
Saturated Fatty Acid Drawing
|
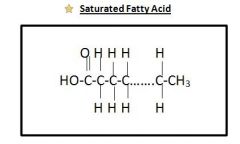
|
|
|
Drawing of Unsaturated Fatty Acids
|
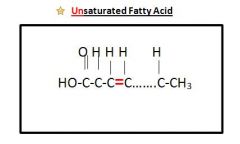
|
|
|
Triglycerides
|
Fats and Oils
3 Carbon glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids Forms and Estrobond when joins a Saturated Fatty Acid |
|
|
Lipids
3 |
Fats
Oils Phospholipids |
|
|
Fats
|
Saturated Fats found in Animals
|
|
|
Oils
|
Unsaturated Fats found in Plants
|
|
|
Phosopholipid
|
Drawn as Clothes Pin
3 Carbon Clycerol +FA + P |
|
|
Phospholipid Drawing
|
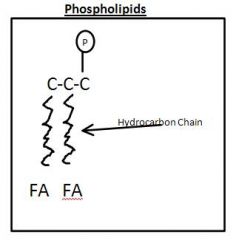
|
|
|
Linked by peptide bonds and has a Biological function
|
Proteins
|
|
|
Speeds of the rate of chemical reaction in Proteins
|
Catalyst
|
|
|
Protein Hormones
|
Insulin
Growth Hormone |
|
|
Alter Structure of Protein by exposing it to hard conditions (becomes not functional)
Boiling Strong Acids |
Denaturation
|
|
|
Nucleic Acids
|
DNA
RNA |
|
|
3 Carbons in Nucleatides
|
Pentosugar (5 Carbons)
N-Base Phosphate Group |
|
|
Bond between DNA
|
Phosdyester Bond
|
|
|
Bonds between Amino Acids
|
Peptide Bonds
|
|
|
Drawing of Amino Acid
|
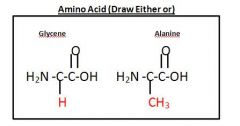
|
|
|
Phospholipid Drawing
|
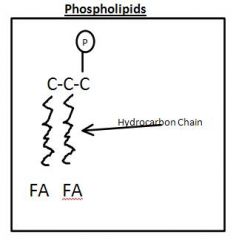
|
|
|
DNA Bond
|
Phosphodiester bond
|
|
|
High energy phosphate bond
|
ATP
|
|
|
When is ATP energy released
|
when the terminal phosphate bond is broken
|
|
|
Process within cell by which fule substrates are broken to CO2 and H20 to make ATP
|
Cellular Respiration
|
|
|
Why Do we breathe O2
|
Cells take in O2 to make ATP
|
|
|
Poison that prevents cells fro making ATP
|
Cyanide
|
|
|
ATP Dependent Processes
|
Muscle Contractions
Urine Formation Thinking Sperm Protein Synthesis Steroid Hormone |
|
|
Sum of total of all reactions occurring within a living system
|
Metabolism
|
|
|
2 Phases of Metabolism
|
Anabolism
Catabolism |
|
|
Reactions that build larger molecules from smaller ones
|
Anabolism
|
|
|
Decomposition of break down reactions where larger molecules are broken down into smaller ones
|
Catabolism
|

