![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plasma cells officially come from ___-cells.
|
B cells!
|
|
|
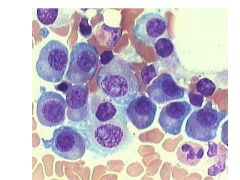
What is a plasma cell dyscrasia?
|
Proliferation of a clone of plasma cells that will either synthesize a homogenous Ig or Ig fragment
monoclonal Ig production |
|
|
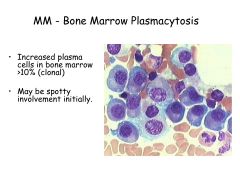
Multiple Myeloma:
What is it? Diagnostic triad |
Masses of plasma cells scattered trough skeletal system
1) M-protein in serum and/or urine 2) Clonal plasmal cells in BM 3) Evidence of damage from clone (organ tissue impairment): CRAB: HyperCa2+ Renal Insuff Anemia Bone Lzns |
|
|
What's on chromosome 14?
|
Immunoglobulin heavy chain
|
|
|
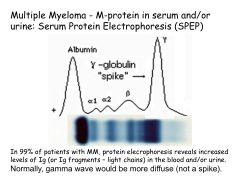
Serum Protein Electrophoresis:
Diagnostic utility What would you look for? |
Note: Gamma-globulin is where Ig's migrate
Normal Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP): gamma should be diffuse Would see a gamma spike in Multiple Myeloma (M-protein!) |
|
|
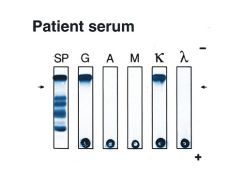
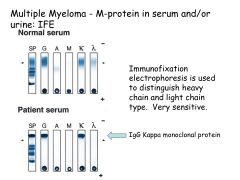
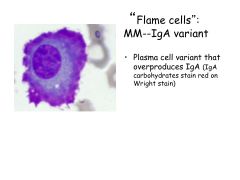
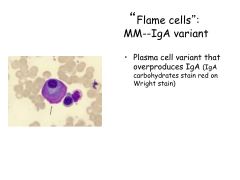
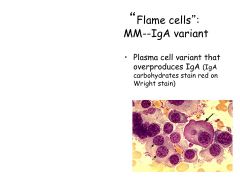
What is the most common Ig monoclonal protein made in multiple myeloma?
Other Ig's? |
IgG kappa is most common
Also see IgA Or JUST light chains (kappa or lambda)--Bence Jones Proteins |
|
|
Multiple Myeloma:
Diagnostics |
-SPEP
-If SPEP negative-->24 hour urine for light chains and/or serum free light chains |
|
|
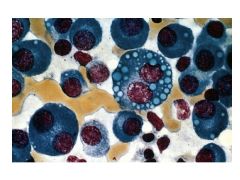
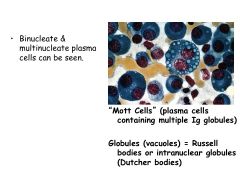
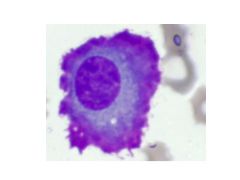
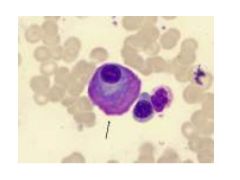
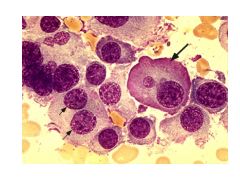
Mott Cells:
What are they? Indicative of? |
Mott Cells are plasma cells containing multiple Ig globules (vacuoles)
Indicates multiple myeloma |
|
|
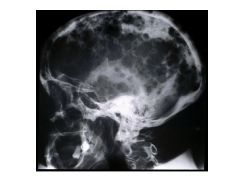
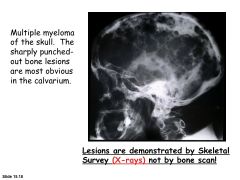
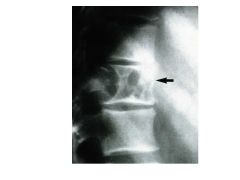
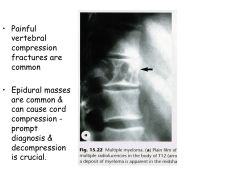
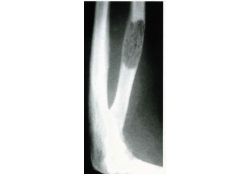
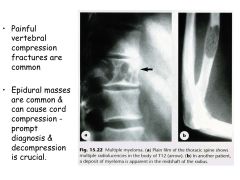
Bone symptoms of MM.
|
Bone pain, pathologic fractures (lytic lesions) in axial skeleton.
|
|
|
How does bone destruction occur in MM?
|
Osteoclast Activating Factor
Myeloma cells secrete RANK Ligand which stimulates diff of osteoclasts (bone resorption) Myeloma cells inhibit osteoprotegerin (OPG) production (which blocks RANK-L) |
|
|
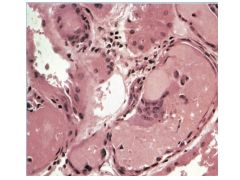
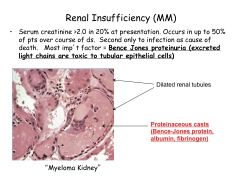
Most important factor in MM renal insufficiency?
|
Bence Jones proteinuria
|
|
|
How does anemia develop in MM?
|
Multifactorial:
Invasion by myeloid cells EPO deficiency due to renal failure Anemia of chronic dz |
|
|
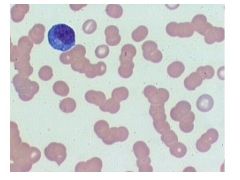
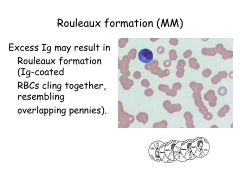
What is an erythrocyte sedimentation rate?
What would it be like in someone with MM? |
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; how far go down tube RBCs in an hour.
Rate of fall is higher if proteins present in plasma (in someone with MM) |
|
|
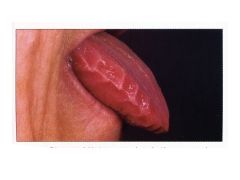
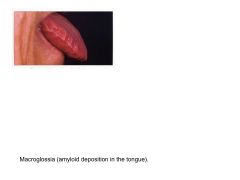
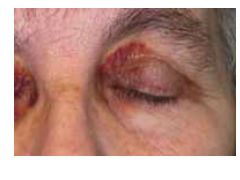
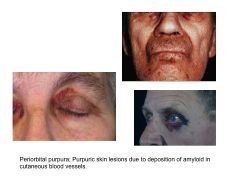
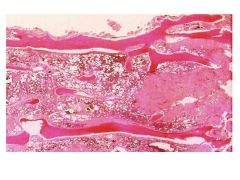
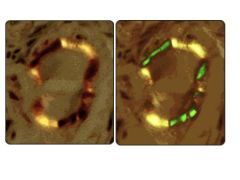
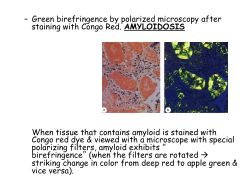
What is amyloidosis?
Where can it occur? |
Result of number of unrelated dz processes that lead to abnormal depositino of amyloid proteins in organs/tissues.
Occurs ANYWHERE IN BODY |
|
|
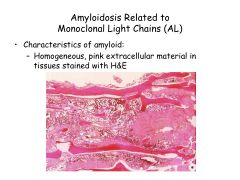
Amyloidosis Related to Monoclonal Light Chains:
How is it a plasma cell dyscrasia? |
AL amyloidosis = plasma cell dyscrasia of unknown cause
Ig light chain produced by plasma cell clones deposits as extracell amyloid fibers. |
|
|
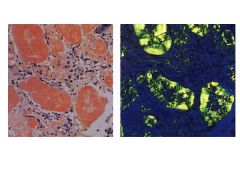
Amyloidosis:
Diagnosis |
Aspiration of abdominal fat and stain with Congo red, if negative, do a rectal biopsy.
|
|
|
Monoclonal Gammopathies of Undetermined Significance (MGUS):
What is it? Clinical significance? |
-<3g/dl of monoclonal protein in serum
-No Bence-Jones proteinuria -BM plasma cells <10% ACCOUNTS for 70% of monoclonal gammopathies. No CRAB! Clin Sig: 1% per year progress to multiple myeloma |
|
|
What is smoldering myeloma?
|
MGUS-->Smoledering Myeloma-->MM
Asymptomatic MM: >3g M-protein OR >10% plasma cells (no CRAB) 10% per year go on to multiple myeloma |
|
|
Solitary Myeloma:
What is it? |
Single area of plasma cell dyscrasia, everything else normal.
No serum protein production. Can progress to MM. Tx w/localized XRT |
|
|
Multiple Myeloma:
Treatment with drug classes |
Thalidomide-dexamethasone (immunomodulatory)
Lenalidomide-dexamethasone (immunomodulatory) Bortezomib (proteasome inhibitor) |
|
|
What occurs in stage III of MM?
|
Advanced lytic bone lesions!
This doesn't occur in stage I or II. |
|
|
Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia:
What is it? How does it differ from other MM's? |
Indolent, Clone of plasma cells making IgM
Do not form tumor masses or lytic lesions! LAD, hepatosplenomegaly. IgM buildup-->hyperviscosity syndrome. |
|
|
What causes hyperviscosity syndrome?
|
Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia: lots of IgM (pentameric) clumps up
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

