![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
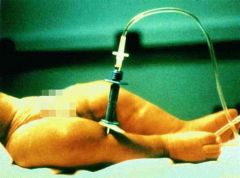
How many (mL) of intravascular blood volume are present per kilogram of body wt in a healthy 5-yo child? 1- 40-50 mL; 2-75-80 mL; 3-90-95 mL; 4-110-120 mL; 5-140-150 mL
|
Although blood volume estimations based on body weight lack precision compared to other invasive methods of measuring, a rough estimate of blood volume for pediatric patients of this age group is 75 - 80 mL/kg.Ans2
|
|
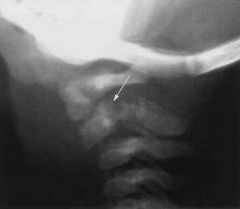
Hx:4yoG w/ an L3 myelomeningocele presents for routine f/u. Pelvic xray reveal a complete dislocation of the L hip w/well formed acetabulum, & a nl R hip. Her gait is symmetric w/use of a walker and brace. Which of the tx options should be offered to the pt @ this time? 1-R sided fem shortening osteotomy; 2-Continued observ & routine f/u; 3-L > trochanteric advanc 4-L sided pelvic osteotomy; 5-OR L hip
|
Surgical reduction of hips in patients with spina bifida is associated with a high failure rate and therefore treatment indications are controversial. In general, reduction for patients with L4 level is most controversial and may be considered if unilateral. Dislocated hips in patients with L3 level and above are typically left alone, in patients with a symmetric gait, reduction of the hip is unnecessary. Ans2
|
|
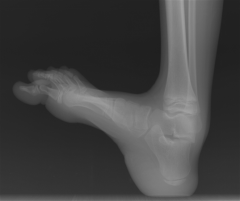
Hx:6yoB w/spina bifida presents to your clinic w/a progressive foot deformity. He can walk independently and ankle DF and toe ext demonstrate full strength. He has a bulky, hypertrophied heel pad, but no open ulceration. Foot Xrays Fig A. What myelomeningocele level does this pt have and what surgical procedure is indicated for the ft? 1-L1 level requiring triple arthrodesis; 2-L3 level requiring triple arthrodesis
3-L3 level requiring pos transfer of the ant tibial tendon 4-L5 level requiring triple arthrodesis 5-L5 level requiring posterior transfer of the anterior tibial tendon |
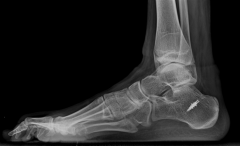
This patient has a L5 level myelomeningocele as he is an ambulator with talipes calcaneus demonstrated on the radiograph. L1 level myelomeningocele patients have externally rotated and flexed hips, equinovarus feet, require a HKAFO, and cannot functionally ambulate. L3 level myelomeningocele patients have adducted and flexed hips, recurvatum knee, equinovarus feet, require a KAFO, and are household ambulators, posterior transfer of the anterior tibial tendon to balance the dynamic forces and obtain a plantigrade foot. The correction increased peak plantar flexion, decreased peak dorsiflexion, and increased peak pressures under the forefoot and midfoot.Ans5
|
|
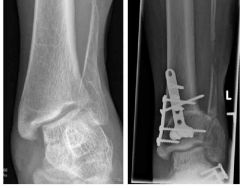
Hx:18 yo ambulatory F w/ spina bifida presents with a painful planovalgus L foot, failed tx w/ orthoses & heel-cord stretching. Ankle xray demonstrate that the distal tibia is tilted 15° into valgus relative to the long axis. Which of the following tx options would best correct the deformity? 1-Triple arthrodesis of the ankle
2-Supramalleolar osteotomy; 3-Medial tibial epiphysiodesis; 4-Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy & tendo-Achilles lengthening; 5-Midfoot osteotomy (+) plantar release |
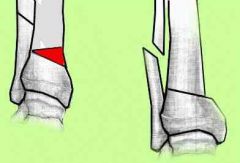
the deformity is occuring through the distal tibia, and therefore is best treated with a supramalleolar osteotomy as the patient is skeletally mature, Valgus occuring through the hindfoot can be treated with a calcaneal lengthening procedure to lengthen the lateral column of the foot and reduce the talonavicular joint. It is usually combined with a tendo-achilles lengthening, and offers further benefit in that it usually corrects the accompanying midfoot abduction deformity. Arthrodesis has been suggested for severe foot deformity & non ambulitory pt, however is usually avoided because it increases the risk of skin sores and Charcot changes in the foot.Ans2
|

