![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1) Which of the following correctly describes the bond angle and hybridizations present in formaldehyde?
A) C, sp2; O, sp3; HCO, ~120° B) C, sp2; O, sp2; HCO, ~120° C) C, sp2; O, sp2; HCO, ~109.5° D) C, sp3; O, sp2; HCO, ~109.5° E) C, sp3; O, sp3; HCO, ~109.5° |
B) C, sp2; O, sp2; HCO, ~120°
|
|
|
2) The double bond between carbon and oxygen is similar to an alkene C=C, except that C=O is:
A) shorter and weaker. B) shorter and stronger. C) longer and weaker. D) longer and stronger. E) longer. |
B) shorter and stronger.
|
|
|
3) The positively polarized carbon atom of a carbonyl group acts as:
A) an electrophile and a Lewis base. B) a nucleophile and a Lewis base. C) an electrophile and a Lewis acid. D) a nucleophile and a Lewis acid. E) both a Lewis acid and a Lewis base. |
C) an electrophile and a Lewis acid.
|
|
|
4) Another name for β-methoxybutyraldehyde is:
A) 2-methoxypropanal. B) 3-methoxypropanal. C) 2-methoxybutanal. D) 3-methoxybutanal. E) 2-methoxypentanal. |
D) 3-methoxybutanal.
|
|
|
5) Which of the following represents the correct ranking in terms of increasing boiling point?
A) n-butane < 1-butanol < diethyl ether < 2-butanone B) n-butane < 2-butanone < diethyl ether < 1-butanol C) 2-butanone < n-butane < diethyl ether < 1-butanol D) n-butane < diethyl ether < 1-butanol < 2-butanone E) n-butane < diethyl ether < 2-butanone < 1-butanol |
E) n-butane < diethyl ether < 2-butanone < 1-butanol
|
|
|
6) Which of the following compounds is most soluble in water?
A) acetone B) cyclohexanone C) 2-butanone D) 3-butanone E) benzophenone |
A) acetone
|
|
|
7) In carbon NMR, the carbon atom of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones has a chemical shift of about:
A) 20 ppm. B) 40 ppm. C) 60 ppm. D) 120 ppm. E) 200 ppm. |
E) 200 ppm.
|
|
|
8) Which compound will show an intense peak in the mass spectrum at m/z 58?
A) CH3COCH2CH2CH3 B) (CH3)2CHCOCH3 C) CH3CH2COCH2CH3 D) (CH3)3CCHO E) (CH3)3CCOCH3 |
A) CH3COCH2CH2CH3
|
|
|
9) In the mass spectrum of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone, the base peak will occur at m/z:
A) 43 B) 58 C) 84 D) 85 E) 100 |
A) 43
|
|
|
10) When a carbonyl is part of a conjugated π-network, the C=O stretch:
A) has a higher frequency than in a nonconjugated system. B) has a lower frequency than in a nonconjugated system. C) always occurs at 1710 cm-1. D) occurs around 2700 cm-1. E) cannot be distinguished from the C=O stretch in a nonconjugated system. |
B) has a lower frequency than in a nonconjugated system.
|
|
|
11) In the proton NMR spectra of aldehydes and ketones, the protons bonded to carbons adjacent to the carbonyl group typically fall into which of the chemical shift ranges below?
A) 1.0-2.0 ppm B) 2.0-3.0 ppm C) 4.0-4.5 ppm D) 7.0-8.0 ppm E) 9.0-10.0 ppm |
B) 2.0-3.0 ppm
|
|
|
12) The proton NMR spectrum of an unknown compound contains a triplet at 9.8 ppm. Which of the following could be this unknown?
A) (CH3)3CCHO B) CH3CH2CH2CO2H C) CH3CH2CH2CHO D) CH3CO CH2Ph E) PhCHO |
C) CH3CH2CH2CHO
|
|
|
13) Which of the following compounds would show only one triplet in its off resonance decoupled 13C NMR spectrum?
A) acetone B) butanal C) pentanal D) 2-pentanone E) 3-pentanone |
E) 3-pentanone
|
|
|
14) Which of the following transitions is usually observed in the UV spectra of ketones?
A) n to π* B) n to π C) σ to n D) σ to σ* E) n to σ* |
A) n to π*
|
|
|
15) The strongest absorptions in the UV spectra of aldehydes and ketones are ones which result from __________ electronic transitions.
A) σ to σ* B) σ to π* C) n to π* D) π to π* E) π to σ* |
D) π to π*
|
|
|
16) What name is given to the linear polymer which contains many formaldehyde units?
A) trioxane B) formalin C) paraformaldehyde D) polyacetaldehyde E) polyalal |
C) paraformaldehyde
|
|
|
17) What reagent can be used to convert 2-methylbutan-1-ol into 2-methylbutanal?
A) LiAlH4 B) Na2Cr2O7 C) O3 D) KMnO4 E) PCC |
A) LiAlH4
|
|
|
18) What reagents can be used to convert 1-hexyne into 2-hexanone?
A) 1. Sia2BH; 2. H2O2, NaOH B) Hg2+, H2SO4, H2O C) 1. O3; 2. (CH3)2S D) 1. CH3MgBr; 2. CO2 E) 1. H2, Ni; 2. Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4 |
B) Hg2+, H2SO4, H2O
|
|
|
19) Oxidation of a 1° alcohol with chromic acid results in the production of __________.
A) an ester B) a ketone C) an aldehyde D) an ether E) none of the above |
E) none of the above
|
|
|
20) Oxidation of a 2° alcohol with chromic acid results in the production of __________.
A) an ester B) a ketone C) an aldehyde D) an ether E) none of the above |
B) a ketone
|
|
|
21) Oxidation of a 3° alcohol with chromic acid results in the production of __________.
A) an ester B) a ketone C) an aldehyde D) an ether E) none of the above |
E) none of the above
|
|
|
22) Oxidation of a 1° alcohol with pyridinium chlorochromate results in the production of __________.
A) an ester B) a ketone C) an aldehyde D) an ether E) none of the above |
C) an aldehyde
|
|
|
24) Which of the following carbonyl compounds may be made from 1,3-dithiane?
1) methyl vinyl ketone 2) 2-pentanone 3) 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone 4) 2-phenylethanal A) 1 & 4 B) 2 only C) 2 & 3 D) 2 & 4 |
D) 2 & 4
|
|
|
25) Treatment of a nitrile with a Grignard reagent followed by hydrolysis results in __________.
A) an ester B) a ketone C) an aldehyde D) an ether E) an alcohol |
B) a ketone
|
|
|
26) Which of the following describes a synthesis of an aldehyde?
A) hydrogenation of an acid chloride using Pd/BaSO4/S as a poisoned catalyst B) reaction of a primary alcohol with Na2Cr2O7 C) reaction of a ketone with ozone D) treatment of an alkene with Sia2BH E) none of the above |
A) hydrogenation of an acid chloride using Pd/BaSO4/S as a poisoned catalyst
|
|
|
27) Which series of reactions described below, if any, will result in the formation of 2-methylpentan-3-one starting with 1-propanol?
A) 1. (CH3)2CHMgBr/ diethyl ether 2. dilute H3O+ 3. PCC B) 1. Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4 and heat 2. SOCl2 3. 2 (CH3)2CHMgBr/ diethly ether 4. H3O+ C) 1. Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4 and heat 2. (CH3)2CHMgBr/ diethyl ether 3. dilute H3O+ 4. LiAlH4 D) 1. PCC 2. (CH3)2CHLi/ diethyl ether 3. dilute H3O+ 4. Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4 and heat E) none of the above |
D) 1. PCC
2. (CH3)2CHLi/ diethyl ether 3. dilute H3O+ 4. Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4 and heat |
|
|
28) When the carbonyl group of a neutral ketone is protonated,:
A) the resulting species becomes more electrophilic. B) the resulting species is activated toward nucleophilic attack. C) subsequent nucleophilic attack on the resulting species is said to occur under acid-catalyzed conditions. D) the resulting species has a positive charge. E) all of the above. |
E) all of the above.
|
|
|
29) Consider the equilbrium of each of the carbonyl compounds with HCN to produce cyanohydrins. Which is the correct ranking of compounds in order of increasing Keq for this equilbrium?
A) H2CO < cyclohexanone < CH3CHO < 2-methylcyclohexanone B) CH3CHO < 2-methylcyclohexanone < cyclohexanone < H2CO C) cyclohexanone < 2-methylcyclohexanone < H2CO < CH3CHO D) cyclohexanone < 2-methylcyclohexanone < CH3CHO < H2CO E) 2-methylcyclohexanone < cyclohexanone < CH3CHO < H2CO |
E) 2-methylcyclohexanone < cyclohexanone < CH3CHO < H2CO
|
|
|
30) The following compound has been found effective in treating pain and inflammation (J. Med. Chem. 2007, 4222). Which sequence correctly ranks each carbonyl group in order of increasing reactivity toward nucleophilic addition?
A) 1 < 2 < 3 B) 2 < 3 < 1 C) 3 < 1 < 2 D) 1 < 3 < 2 |
B) 2 < 3 < 1
|
|
|
31) Rank the following compounds in order of their propensity to become a hydrate in water (ie, start with the least easy to hydrate: CH3COCH2CH3, H2CO, Cl3CCHO, and CH3CH2CHO.
A) CH3CH2CHO < CH3COCH2CH3 < H2CO < Cl3CCHO B) CH3CH2CHO < H2CO < CH3COCH2CH3 < Cl3CCHO C) CH3COCH2CH3 < H2CO < CH3CH2CHO < Cl3CCHO D) CH3COCH2CH3 < CH3CH2CHO < H2CO < Cl3CCHO |
D) CH3COCH2CH3 < CH3CH2CHO < H2CO < Cl3CCHO
|
|
|
32) An ylide is a molecule that can be described as a:
A) carbanion bound to a negatively charged heteroatom. B) carbocation bound to a positively charged heteroatom. C) carbocation bound to a carbon radical. D) carbocation bound to a diazonium ion. E) carbanion bound to a positively charged heteroatom. |
E) carbanion bound to a positively charged heteroatom.
|
|
|
33) Which of the following is also known as a Schiff base?
A) an imine B) a cyanohydrin C) a hydrate D) sodium hydroxide E) an aldehyde |
A) an imine
|
|
|
34) Acetals will react with:
A) H3O+ B) NaOCH3 C) PhLi D) CH3CH2MgBr E) NaBH4 |
A) H3O+
|
|
|
36) Why do acetal-forming reactions that use ethylene glycol have more favorable equilbrium constants than those using methanol?
A) Ethylene glycol reacts more rapidly. B) They are more favorable on entropy grounds. C) They are more favorable on enthalpy grounds. D) Ethylene glycol is acidic and catalyzes the reaction. E) The ethylene acetal can serve as a protecting group. |
B) They are more favorable on entropy grounds.
|
|
|
38) What intermediate occurs when a ketone undergoes a Wolff-Kishner reduction?
A) a cyanohydrin B) a hydrated aldehyde C) a carboxylate D) a semicarbazone E) a hydrazone |
E) a hydrazone
|
|
|
39) The reagent which converts a carbonyl group of a ketone into a methylene group is:
A) Na, NH3, CH3CH2OH B) LiAlH4 C) NaBH4, CH3CH2OH D) Zn(Hg), conc. HCl E) LiAlH[OC(CH3)3]3 |
D) Zn(Hg), conc. HCl
|
|

23) Which of the following reactions will not yield a ketone product?
|
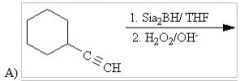
A)
|
|
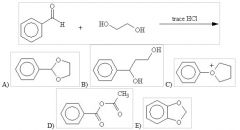
35) What would be the product of the following reaction?
|

A)
|
|
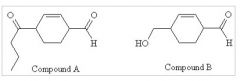
37) RxNs forming A from B?
A) 1. HO-(CH2)2-OH /trace H3O+ 2. DMSO (COCl2)/Et3N, CH2Cl2 3. MgBr-(CH2)2-CH3/diethylether 4. H3O+ B) 1. PCC 2. SOCl2 3. LiCu-((CH2)2-CH3)2 4. H3O+ C) 1. Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4 2. SOCl2 3. 2 MgBr-(CH2)2-CH3/diethylether 4. H3O+ D) both A and B E) both B and C |
A) 1. HO-(CH2)2-OH /trace H3O+
2. DMSO (COCl2)/Et3N, CH2Cl2 3. MgBr-(CH2)2-CH3/diethylether 4. work-up with H3O+ |

