![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1) Which of the following compounds will not undergo reaction with an enolate?
A) 1-pentene B) bromine C) propanal D) 1-bromobutane E) benzoyl chloride |
A) 1-pentene
|
|
|
2) The relationship between ketones and their corresponding enols is one of:
A) allotropes. B) tautomers. C) enantiomers D) diastereomers. E) cis-trans isomers. |
B) tautomers.
|
|
|
3) Which of the following reagents will quantitatively convert an enolizable ketone to its enolate salt?
A) lithium hydroxide B) lithium diisopropylamide C) methyllithium D) diethylamine E) pyridine |
B) lithium diisopropylamide
|
|
|
4) The reaction of LDA with acetophenone produces:
A) an enol. B) an enolate. C) an ylide. D) alkylation. E) halogenation. |
B) an enolate.
|
|
|
5) When a ketone and its enol are in equilibrium, under most conditions the concentration of the enol is __________ the concentration of the ketone.
A) slightly higher than B) equal to C) much higher than D) much lower than |
D) much lower than
|
|
|
E) exactly half of
6) Disregarding stereoisomers, how many different enols can phenylacetone form? A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) 4 |
C) 2
|
|
|
7) Disregarding stereoisomers, how many different enols can the β-diketone CH3COCH2COCH2CH3 form?
A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) 4 |
E) 4
|
|
|
8) What type of product results when 3-pentanone is treated with LDA (lithium diisopropylamide) at low temperature?
A) enolate B) enol C) amide D) imine E) enamine |
A) enolate
|
|
|
9) When 2-methylcyclohexanone is treated with catalytic base in excess D2O, how many deuterium atoms become incorporated in the organic compound?
A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) 5 |
D) 3
|
|
|
10) (S)-2-Methylbutanal __________ upon sitting in an acidic or a basic aqueous solution.
A) racemizes B) esterifies C) inverts completely to the R configuration D) hydrolyzes E) irreversibly forms the hydrate |
A) racemizes
|
|
|
11) Which of the following will alkylate a lithium enolate most rapidly?
A) methyl bromide B) isopropyl bromide C) neopentyl bromide D) bromobenzene E) 2-methylbromobenzene |
A) methyl bromide
|
|
|
12) Methylamine reacts with acetophenone to yield the:
A) iminium salt. B) imine. C) acetal. D) amide E) enamine. |
B) imine.
|
|
|
13) Which of the following will react most slowly with an enamine?
A) isopropyl chloride B) methyl bromide C) acetyl chloride D) benzyl chloride E) allyl bromide |
A) isopropyl chloride
|
|
|
14) What type of product results when 3-pentanone reacts with dimethylamine?
A) enolate B) enol C) amide D) imine E) enamine |
E) enamine
|
|
|
15) Which of the following ketones will give a positive iodoform test?
A) 4-heptanone B) 3-hexanone C) 2-hexanone D) cyclohexanone E) 2-methyl-3-pentanone |
C) 2-hexanone
|
|
|
16) The α-halogenation of cyclohexanone:
A) is catalyzed by base. B) is slowed by the presence of acid. C) requires one equivalent of base. D) requires one equivalent of acid. E) is catalyzed by the sodium halide salt. |
C) requires one equivalent of base.
|
|
|
17) What is the carbon nucleophile which attacks molecular bromine in the acid-catalyzed α-bromination of a ketone?
A) an enolate B) a Grignard reagent C) an acetylide D) a carbocation E) an enol |
E) an enol
|
|
|
18) When aldehydes are subjected to the same conditions that α-halogenate ketones (i.e., X2 and aqueous acid or base), they are:
A) α-halogenated as well. B) reduced to alcohols. C) converted to the acid halide. D) oxidized to the acid or carboxylate. E) esterified. |
D) oxidized to the acid or carboxylate.
|
|
|
19) In the iodoform reaction, a methyl ketone is converted to the __________ upon treatment with excess iodine and hydroxide.
A) carboxylate B) acyl iodide C) primary alkyl iodide D) aldehyde E) primary amide |
A) carboxylate
|
|
|
21) The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction involves:
A) the α-bromination of carboxylic acids. B) the α-bromination of ketones. C) the bromination of alcohols. D) the oxidation of aldehydes to acids. E) none of the above. |
A) the α-bromination of carboxylic acids.
|
|
|
22) An enolate attacks an aldehyde and the resulting product is subsequently protonated. What type of reaction is this?
A) a Fischer esterification B) an acid-catalyzed aldol condensation C) a base-mediated aldol condensation D) a Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction E) a Selman-Jones reaction |
C) a base-mediated aldol condensation
|
|
|
23) The aldol condensation is:
A) an irreversible reaction. B) an equilibrium reaction. C) a tautomerization. D) an isomerization. E) a type of esterification. |
B) an equilibrium reaction.
|
|
|
24) Which of the following is another name for the product of an aldol condensation
A) β-hydroxyaldehyde B) α-hydroxyaldehyde C) acetal D) β-ketoester E) 1,3-dialdehyde |
A) β-hydroxyaldehyde
|
|
|
25) Which of the following could result from the dehydration of a self-aldol condensation product?
A) 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one B) 4-methyl-4-penten-2-one C) 4-methyl-5-hexen-2-one D) 4-methyl-4-hexen-2-one E) 3-methyl-4-penten-2-one |
A) 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one
|
|
|
26) What product results when an aldol is dehydrated?
A) conjugated alkyne B) β-diketone C) β-ketoester D) α,β-unsaturated aldehyde E) β,γ-unsaturated aldehyde |
D) α,β-unsaturated aldehyde
|
|
|
27) In theory a poorly planned crossed aldol reaction can produce how many different aldol regioisomers?
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 |
D) 4
|
|
|
28) Which of the following is least likely to undergo a smooth crossed Claisen condensation with methyl pentanoate?
A) (CH3)3CCO2CH3 B) PhCH2CO2CH3 C) PhCO2CH3 D) HCO2CH3 E) (CH3O)2CO |
B) PhCH2CO2CH3
|
|
|
29) Which of the following is most acidic?
A) acetone B) ethyl acetate C) malonic ester D) acetoacetic ester E) acetaldehyde |
D) acetoacetic ester
|
|
|
30) What is the approximate pKa of acetone?
A) 45 B) 20 C) 13 D) 10 E) 4 |
B) 20
|
|
|
31) What is the approximate pKa of diethyl malonate?
A) 45 B) 20 C) 13 D) 10 E) 4 |
C) 13
|
|
|
32) Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing acidity:
acetone, ethyl acetoacetate, ethyl acetate, and ethanol. A) acetone < ethyl acetate < ethanol < ethyl acetoacetate B) acetone < ethanol < ethyl acetate < ethyl acetoacetate C) ethyl acetate < ethanol < acetone < ethyl acetoacetate D) ethyl acetate < acetone < ethanol < ethyl acetoacetate |
D) ethyl acetate < acetone < ethanol < ethyl acetoacetate
|
|
|
34) In the Michael reaction, addition to the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl occurs in a:
A) 1,2-fashion. B) 1,3-fashion. C) 1,4-fashion. D) 1,5-fashion. E) Diels-Alder reaction. |
C) 1,4-fashion.
|
|
|
35) Which of the following is a nucleophile that does conjugate additions?
A) CH2=CHCHO B) CH2=CHCN C) CH2=CHCO2CH3 D) CH3CH2MgBr E) (CH3)2CuLi |
E) (CH3)2CuLi
|
|

20) Which set of reagents would best accomplish the following transformation?
A) Br2 / HBr B) Br2 / PBr3 C) Br2 / NaOH D) PBr3 |
A) Br2 / HBr
|
|
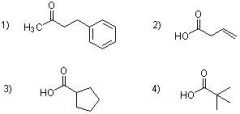
33) Which of the following structures could be constructed by way of a malonate ester alkylation?
A) 1 only B) 3 only C) 3 & 4 D) 1 & 3 |
C) 3 & 4
|
|
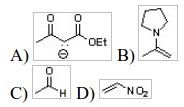
36) Which of the following is the best Michael acceptor?
|

D)
|

