![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mutualism |
Ecological relationship where in both partners benefit from the interaction |
|
|
Commensalism |
Ecological relationship where in one partner benefits but there is no effect on the other |
|
|
Parasitism |
Ecological relationship where in one partner benefits at the expense of the other |
|
|
Autotrophic |
This types of organisms can synthesize their own organic constituents from inorganic substances |
|
|
Heterotrophic |
These types of organisms must obtain organic molecules synthesized by other organisms in order to survive |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
"Cell eating" Infolding or invagination of the plasma membrane to surround a visible food particle |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
"Cell drinking" |
|
|
Holozoic feeders |
A.k.a. phagotrophs Heterotrophs that feed on visible particles |
|
|
Saprozoic feeders |
A k a osmotrops Organisms that ingest soluble food |
|
|
Phototrophs |
Autotrophic organisms that use light energy to synthesize their organic molecules, but often practice phagotrophy and osmo trophy as well |
|
|
Flagella |
A single whip-like structure in unicellular organisms used for locomotion |
|
|
Cilia |
Short whip-like structures that covers the whole organism that is used for locomotion |
|
|
Pseudopods |
Used for locomotion in amoebas |
|
|
Lobopodia Filipodia Rhizopodia Reticulopodia Axopodia |
5 types of pseudopod shapes in Amebas |
|
|
Lobopodia |
-Blunt tipped ameba pseudopods -Containing both endoplasm and ectoplasm |
|
|
Filopodia |
-Thin sharply pointed pseudopods in amebas - containing only ectoplasm |
|
|
Reticulopodia |
-Pseudopods that are branched filaments that merge to form a net like structure |
|
|
Rhizopodia |
Pseudopods that are branched filaments |
|
|
Axopodia |
Pseudopods that are thin, pointed and contains an axoneme |
|
|
Axoneme |
Central longitudinal (axial) filament of microtubules in Axopodia (ciliates and flagellates) |
|
|
Testate |
Amebas that make shells |
|
|
Naked amebas |
Amebas without shells are called ____ ___ |
|
|
False |
True or false: Unicellular eukaryotes have germ layers |
|
|
True |
True or false: Some unicellular eukaryotes are provided with simple endoskeleton or exoskeleton, but most are naked |
|
|
False Syngamy and conjugation are actually examples for sexual reproduction |
True or false: Conjugation and syngamy are examples of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms |
|
|
Kinetosome |
AKA basal body -9 triplets of microtubules in ciliates and flagellates - identical in structure to centrioles |
|
|
Sliding-microtubule hypothesis |
The current explanation used for ciliary and flagellar movement |
|
|
Radial spokes |
multi-unit protein structure found in the axonemes of eukaryotic cilia and flagella |
|
|
Dynein arm |
molecular complex that drives the beating motion of cilia/flagella |
|
|
A= Radial Spoke B= Dynien Arm |
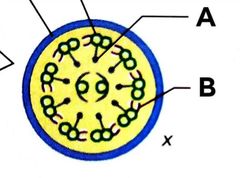
What is A in the diagram? What is B? |
|
|
Pseudopodia |
Extensions of the cell cytoplasm used in locomotion and feeding |
|
|
Ectoplasm |
Appears more transparent (hyaline) by light microscopy, and it bears the bases of the cilia and the flagella -Rigid, peripheral area of cytoplasm |
|
|
Endoplasm |
Appears more granular and contains the nucleus and the cytoplasmic organelles -Fluid (sol state), central area of cytoplasm |
|
|
Hyaline cap |
An extension of the ectoplasm when lopodium begins to form |
|
|
Nucleus |
-Membrane-bound structure whose interior communicates with the cytoplasm by small pores - DNA is found here |
|
|
Nucleoli |
a small dense spherical structure in the nucleus of a cell present during interphase, especially in the active transcription of ribosomal RNA |
|
|
Macronucleus Micronucleus |
Two kinds of nuclei that ciliates have |
|
|
Micronucleus |
Germ line nucleus in ciliates |
|
|
Macronucleus |
Somatic nucleus in ciliates |
|
|
Mitochondria |
An organelle used in recovering energy from carbon bonds of fuel molecules where oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor |
|
|
Hydrogenosomes |
In cells without mitochondria, _____ may be present |
|
|
Hydrogenosomes |
Organelles that perform a respiratory function in absence of oxygen and are assumed to have evolved from mitochondria |
|
|
Kinetoplasts |
______ also assumed to be mitochondrial derivatives |
|
|
Golgi complex |
Part of the endomembrane system that participates in cellular secretory processes and intracellular digestion of ingested food vacuoles |

