![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Sputum sample.
Name the bug, the gram stain type, and the morphology. |

|
|
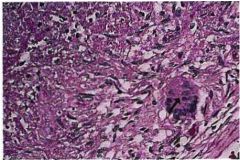
Name the bug
Associated with what inflammation type. What cell is pointed by the arrow. Describe the cell |

|
|

Name the bug.
Bug is ID'd by their RED color with what staining? This redness is also nicknamed what? |

|
|

What is the Dx?
What is the bug? What is the severity? How is it spread? |

|
|

Sputum sample.
What is the bug? What is the gram stain type & morphology? |

|
|

Urethral Discharge Smear.
What is the bug & what are they inside of? What is the gram stain type & morphology? |

Neisseria are Nside pmN's
|
|
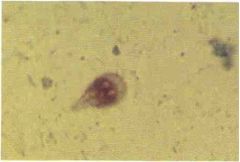
What is the bug?
Bug is in what life cycle phase? Describe bug morphology. What part of the body is the bug in? |

|
|
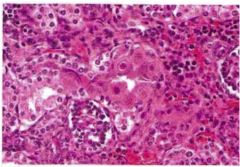
Figure: Renal Tubular Cells in a Neonate.
What is the bug? Infected cells have what prominent feature? This feature is sometimes called what? |

|
|
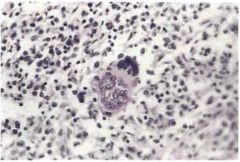
Lung Parenchyma.
What is the bug & endemic to where? Describe the observed pathology. Dissemination occurs when? Dissemination occurs to where? |

|
|

CSF Sample from AIDS pt w/ meningoencephalitis.
What is the bug? What type of staining is used here? |

|
|

What is the bug?
What type of staining is used here? What are 2 prominent feature of the bug seen here? |

|
|

What is the bug?
What stage of the life cycle is this bug in? What structure is notably seen with this bug? |

Trick when you get Tail
|
|
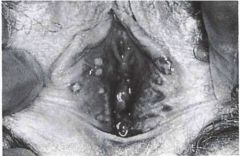
What is the Dx?
What is the bug? Describe the lesion. |

|
|

What is the Dx?
What is the name of the lesion? What is unique about this lesion? Lesion occurs with what Dz subtype? |
|
|

What is the Dx?
Degeneration is seen where on the spinal cord? |

|
|

What is the Dx?
What does the arrow point to? |

|
|

What is the Dx?
What is the Dz subtype? What is important to note about the distribution? |

|
|
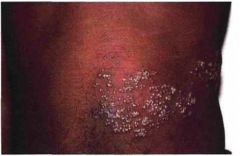
What is the Dx?
This condition is considered benign unless what? x2 |

|
|

Hands of a 3 year old.
What is the Dx? Dz is also called what? Describe the lesions. |

|
|

What is the arrow pointing to?
These are pathognomonic for? Describe the lesions. These lesions will precede the general rash by _____. |

|
|

What is the Dx?
These discrete erythematous lesions become _____ as the rash ________. |

|
|

What is the Dx?
Rash often begins where? |
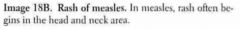
|
|

Lung Epithelium.
What is the bug? Describe the bug morphology. What is the staining technique used? |

PCP = tons of tablet pills for some silver
|
|
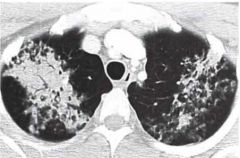
CT of the Chest.
What is the Dx? What is seen bilaterally in the lungs with central distribution? |

|
|

Name the Cell.
Due to what change in ratio? Give 2 examples of Dz & how it affects the ratio. |
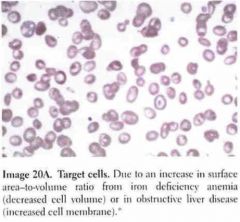
Iron Def. anemia
(incr. cell volume) Obstructive Liver Dz (incr. cell surface membrane) |
|
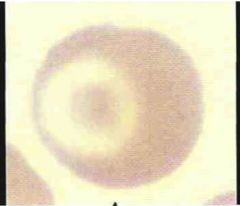
Solitary example of what?
|

|
|

Name the Dx.
Etiology? Note the presence of what cells? |

|
|

Name the Dx.
Give 2 characteristics of the RBCs. |
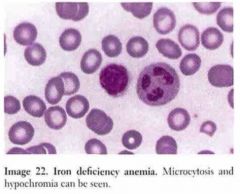
|
|
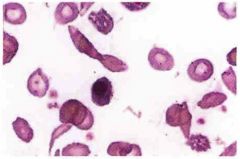
Name the Dx.
List the 4 types of cells seen here. |

|
|
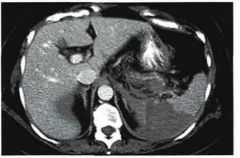
Name the Disease.
CT shows what organ pathology? Why this organ get affected? Wedge shape represents what type of necrosis? Pts w/ this Dz undergo what by adolescence? |

|
|

Specify Dx.
MC population group? |
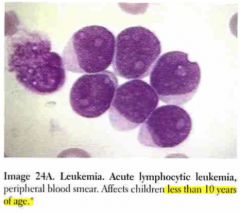
|
|

Specify Dx.
MC population group? What are the arrows pointing to? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
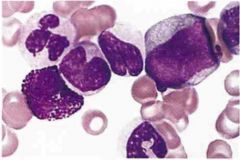
Specify Dx.
MC population group? What cells are seen here and what are they adjacent to? |

|
|
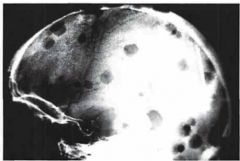
What is the Dx?
Describe the lesions seen. |

|
|
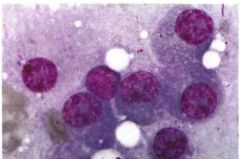
What is the Dx?
Smears from this Dz shows an abundance of what cells? Where are the RBCs? |

|

