![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
This is responsible for establishing the cranial-caudal organization of limb development. |
Hox genes |
|
|
Limbs begin development during what time period? |
4-8 Weeks |
|
|
These are an outpocketing on the ventrolateral body: |
limb buds |
|
|
The limb buds are composed of: |
mesenchymal cells with an ectodermal covering |
|
|
Limbs develop in which direction? |
proximodistal |
|
|
The Apical Ectodermal Ridge does what? |
influences mesenchyme core to stay undifferentiated |
|
|
At what time frame do the terminal portions of limb buds flatten out to form hand & foot plates |
6 weeks |
|
|
These separate the limb into 3 segments: |
circular constrictions |
|
|
This process separates the digits in the hands/feet: |
areas of cell death (apoptosis) |
|
|
The core of the limb bud is made up of this cell type: |
Mesenchyme |
|
|
The limb bud core mesenchyme differentiate into: |
chondrocytes |
|
|
Define diaphysis |
shaft |
|
|
Define epiphyses |
ends |
|
|
Define epiphyseal plate |
The growth plate / metaphysis that remains to allow for growth |
|
|
This develops into the secondary ossification center |
epiphyses |
|
|
Describe the stages of endochondral ossification:
|
Stage #1: development of the primary center Stage #2: development of the secondary centers of ossification Step 1: chondrocyte differentiation Step 2: Formation of hyaline cartilage models Step 3: Blood vessels invade, bringing with them osteoblasts Step 4: Secondary ossification centers at ends of bone (epiphysis) develop post-birth. Cartilage (growth) plate remains, allowing for continued bone growth |
|
|
The interzone is: |
the area between developing bones |
|
|
The mesenchyme in the interzones develop into: |
dense fibrous tissue |
|
|
The dense fibrous tissue in the interzone develops into: |
articular cartilage menisci ligaments etc |
|
|
Irregular bones usually has several: |
primary & secondary ossification centers |
|
|
The upper extremities contain what dermatomes? |
C4-T2 |
|
|
The lower extremities contain what dermatomes? |
L2-S2 |
|
|
What rami supplies the limbs? |
Anterior primary rami |
|
|
This division innervates the embryonic ventral mass muscles: |
Anterior |
|
|
This division of the rami innervates the embryonic dorsal mass muscles: |
Posterior |
|
|
What is the embryonic origin of the limb buds? |
lateral plate mesoderm |
|
|
What are the two divisions of the axial line? |
Preaxial - cranial - towards head
Postaxial - caudal - towards tail/hind parts |
|
|
The upper limbs rotate which direction during development? |
90 degrees lateral so that the thumb is lateral |
|
|
The lower limbs rotate which direction during development? |
90 degrees medial so that the big toe is medial |
|
|
BUE: ventral mass muscles are where and do what? |
Flexors, aDDuctors, pronators
on the anterior side |
|
|
BUE: dorsal mass muscles are where and do what? |
extensors, ABductors, supinators
on the posterior side |
|
|
BLE: ventral mass muscles are where and do what? |
Flexors, aDDuctors, pronators
on the posterior side |
|
|
BUE: dorsal mass muscles are where and do what? |
extensors, ABductors, supinators
on the anterior side |
|
|
Describe the sequencing of Dermatomes on the upper limbs |
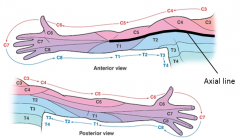
|
|
|
What are the compartments of the shoulder girdle? |
Posterior Axioappendicular Anterior Axioappendicular Scapulohumeral Axillary region |
|
|
Describe the muscles and nerves in the posterior axioappendicular region: |
Muscles: Trapezius, Latissimus dorsi, levator scapulae, rhomboids
Innervations: anterior rami (brachial plexus) |
|
|
Describe the muscles & nerves in the anterior axioappendicular region: |
Muscles: Pectoralis major/minor, subclavius, serratus anterior
Innervations: branches off the brachial plexus |
|
|
Describe the muscles & nerves in the scapulohumeral region: |
Muscles: Deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres major, teres minor, subscapularis
Innervations: posterior cord of brachial plexus
exception: *spinatus muscles are innervated by a branch off the superior trunk |
|
|
Describe the Axillary region borders: |
pyramidal shape with an apex, base, & 4 walls: Anterior: pectoral muscles Posterior: subscapularis Lateral: intertubercular sulcus Medial: serratus anterior Apex: cervico-axillary canal
** ignore: Base: axillary fossa (fascia/skin) |
|
|
Describe the contents of the axillary region: |
axillary sheath surrounds:
axillary artery & vein and the brachial plexus |
|
|
Describe the components of the Arm: |
Humerus! |
|
|
Describe the Arm's posterior compartment: |
Muscles include Extensors such as triceps brachii and the brachioradialis.
Vessels include deep brachial artery that travels with the radial nerve.
Innervations include only the radial nerve. |
|
|
Describe the Arm's anterior compartment: |
Muscles include Flexors such as biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis, brachial artery.
Vessels include deep brachial artery.
Innervations include only the musculo-cutaneous nerve |
|
|
Describe the Cubital fossa |
A triangular depression anterior to the elbow b/w the forearm flexor and extensor muscles. The boundaries include protator teres (medially), brachioradialis (laterally) and a line drawn between medial & lateral epicondyles. Contents: biceps brachii tendon, brachial artery, median nerve, and the median cubital vein that communicates b/w cephalic & basilic veins. |
|
|
Describe the components of the Forearm: [bones] |
radius & ulna!! |
|
|
Describe the Forearm's posterior compartment: |
Muscles: extensors, supinator. Vessels: Posterior interosseus artery. Innervated: radial nerve [& branches]. |
|
|
Describe the Forearm's anterior compartment: |
Muscles: flexors & pronators. Vessels: Radial & Ulnar artery. Innervated by median & ulnar nerves. |
|
|
Describe the boundaries of the carpal tunnel: |
Floor & walls include the carpal bones.
Roof includes the flexor retinaculum. |
|
|
Describe the contents of the carpal tunnel: |
Tendons: Flexor digitorum profundus & superficialis, Flexor pollicis longus
Nerves: Median nerve |
|
|
List the compartments of the hand: |
Thenar, hypothenar, central, interosseous, adductor |
|
|
Describe the Thenar compartment of the hands: |
Muscles include the abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, and opponens pollicis.
It is innervated by the median nerve (C6) |
|
|
Describe the Hypothenar compartment of the hands: |
Muscles include the abductor digit minimi, flexor digit minimi, and opponens digit minimi.
It is innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve. |
|
|
Describe the Central compartment of the hands: |
Muscles include the lumbricals (acts on medial phalange). Tendons include the the FDS & FDP. They are innervated by the ulnar nerve except for 1/2 LOAF. |
|
|
Describe 1/2 LOAF mnemonic |
1 & 2 Lumbrical.
Opponens pollicis.
ABductor pollicis brevis.
Flexor pollicis brevis. |
|
|
Describe the Interosseous compartment of the hands: |
Muscles include the palmar interossei (3) and dorsal interossei (4).
It is innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve. |
|
|
Describe the Adductor compartment of the hands: |
Muscles include the adductor pollicis and it is innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve. |
|
|
Describe the snuff box: |
Boundaries include the tendon of extensor pollicis longus for the medial border and the tendon of extensor pollicis brevis & abductor pollicis longus. The contents include the radial artery and is a location for s/sx of a fractured scaphoid bone. |
|
|
Describe how the sheaths and spaces in the hand can be involved in infection. |
The potential spaces in the hand include the thenar and midpalmar which are spaces usually filled with connective tissue that provide access into the tendon sheaths. This provides access points for infection to travel directly to the forearm. - Midpalmar space > carpal tunnel > forearm - 5th digit synovial sheath > common flexor sheath > carpal tunnel > forearm - flexor pollicis longus sheath > carpal tunnel > forearm |

