![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Indian Music influence |
America has been influenced by Indian Music since the 1960's they have a great history of music tradition |
|
|
Similarities between Western and Indian Music |
-Popular danceand film music
-Music forreligion and rituals -Classical andtraditional music -Work songs -Festive musicfor occasions |
|
|
Indian Classical Music |
-Art Music ( Highly developed music that has been researched, recorded, and reported) ~bases on ancient traditions and associated with great artists ~"classical" music based off a musical theoretical system created by Indian Scholars |
|
|
Indian classical Music and Harmony |
~harmony (chord progressions) not valued as part of music however simultaneous sounds played by plucked instruments and vocal line together will create harmony
|
|
|
2 Kinds of Indian Music |
1. North-Hindustani Music 2. South-Karnatic Music |
|
|
Rasa |
the power of music to convey thoughts, feelings, moods, and images |
|
|
Valued in Indian Music |
-Music to nature relationships -religious relationship -Stages of time (seasons, life events, time of day) |
|
|
Hindustani |
-Main instrument-Sitar
-Other instrument-Sarod -Rhythmic Stability-Tabla -Drone Instrument (Constant repetition, trancelike sound)-Tambura |
|
|
Karnatic |
-Main Instrument-Vina -Other Instrument-Sarangi (Bowed instrument) -Rhythmic Stability-Mridangam -No Drone Instrument-Possible solosinger will provide the drone |
|

|
Sitar |
|

|
SarodTable |
|

|
Tabla |
|

|
Vina |
|

the one on the right |
Sarangi |
|

|
Mridangam |
|
|
Similarities between Hindustani and Karnatic |
-Precomposed songs learned from memory-Notation exists but is not commonly used -Raga-Melodic pattern of organization -Tala- Rhythmic pattern of organization ~True artistry-Being able to expand and explore all aspects of the Raga and Tala within a given song ~Practice this by studying with a Guru (Master) |
|
|
Raga |
-Melodic Aspect of a piece is determined by the raga
-Western Music-Scales -Sequence of ascending and descending pitches to scale, but conveys more than a scale. ~Melodic Shape rather than Abstract pitch structure -Convey many different patterns ~Pitch register-High, middle, low ~Ornamentations -Communicated the mood and feeling of the piece |
|
|
Tala |
-Organizing rhythm or durational aspect
-Dictates the complete pattern or cycle of counts, as well as subdivisions in the cycle -Example: 16 beats= 4+4+4+4: 14 beats=5+2+3=4 -Two or more Tala patterns make a Phrase -Drummer learns improv using drum strokes, and rhythmic patterns that subdivide the ongoing pulse of the Tala -The Drummer will learn patterns that pull AWAY from the Tala ~Creates Tension - Will then return to the regular pattern to created |
|
|
Listening to Indian "Art" Music |
-Raga performance can be 30 minutes or longer What you will hear
1. Lead instrumentalist-slow rhythmically free, improvised statement of the raga to establish musical theme 2. Second section-Provides repetitive rhythmic intensity in anticipation of the next section 3. Final Section-Establish the Tala and devoted to extend the improvisation and interaction between the lead and percussion |
|
|
Indian Popular Music |
-The Cassette Tape-Main way to spread popular music from film and radio
-India’s Music Industry known as the Cassette Culture -Has many Western Genres of music Jazz, Rock and Roll |
|
|
Bollywood |
-Music in Indian films mostly produced in Mumbai
-Success-Male star, Director and Music -Almost all of the films are musicals -Instrumental Music in Bollywood Films ~100-Piece Orchestras or small synthesizers ~Combine Indian Music with Western Music ~Playback-Singers that record music for the star of the movie in advanced ~Lata Mangeshkar |
|
|
African Music Influences |
-Africa is a country with over 200 languages and even more different cultures -North Africa-Mediterranean countries ~ Algeria, Morocco, Libya, Tunisia and Egypt ~Influence-Islamic and Arab traditions -South Africa: Sub-Saharan ~INFLUENCED American Music ~Spirituals, Blues, Jazz, Ragtime, and Gospel |
|
|
Music in Context |
-music is was created for a specific purpose and only performed for that purpose Some music isn't just ~ex. religious, work, dancing, and entertainment -includes props, costumes, dancing, sculpture, and drama ~increases the level of participation from several people |
|
|
African Music is... |
-outlet for social integreation and shared attitudes -Enhancessocial activities and is performed of amusements, communicates importantmessages and feelings -Traditionalmusic is more popular amongst older people ~ Younger peopleabandon tradition for Western influences |
|
|
Performers for African Music |
- performing groups may be organized or spontaneous -range from 2-3 musicians -Large drum orchestras numbering at the hundreds |
|
|
Instruments of African Music |
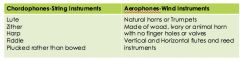
|
|
|
Instruments of African Music Cont. |

|
|
|
African Musical Characteristics |
-Voice: Limitedrange, disjunct melodic contour (rhythmic interruption with calls)
-Melody andHarmony progressions are not important in TRADITIONAL music ~In folk andpopular music it has more of an influence |
|
|
Rhythm of African Music |
-The Heart of African Music ~more integral than Melody and harmony -Rhythmic textures are complicated and very complex. -Produced not only drums but also strings, winds, and voices |
|
|
African Popular Music |
-The urbanization of the cultures were influenced by Western Music ~jazz, rock, soul, African-Latin music (reggae) and Brazilian Samba -Africans are also creating their own gneres of music ~nationalism, Regionalism |
|
|
African Genres |
-highlife -juju-Nigerian popular music -Afro beat -Griot MUsic |
|
|
African Artists |
-Miriam Makeba-Popular singer. Spoke and sang out against Apartheid (Racial Segregation of South Africa) Grammy winner in 1966 with Harry Belefonte (Folk Song) -Fela Kuti-Nigerian Singer. Used songs as political expression for human rights and equality. Afro-Beat -King Sunny Adé- Popularmusician from Nigeria. Singer, composer, guitarist. “King of Juju” |
|
|
Ethnomusicology |
Study of Music from other cultures and what music is and why it exists in that cultural setting |
|
|
Training forEthnomusiclolgy |
-Music
-Culturalanthropology - FolklorePerformancestudies - Dance - Gender studies - Racial Studies |
|
|
The Beliefs of Ethnomusicologists |
-Taking a global approach to music regardless of area, style, origin, or genre -understand music as a social practice ~viewing music as a human activity that is shaped through cultural context -Engaging on ethnographic fieldwork ~participating and observing music being studied and relating it to the cultural context |
|
|
Important People to Ethnomusicology |
-MantleHood-Indian Ethnomusicologist. Created the first ethnomusicology program in acollegiate setting.
-BelaBartok-Hungarian Ethnomusicologist. Recorded Folk songs, and had a huge role inpreserving those works. -Frances Densmore-NativeAmerican Ethnomusicologist-Collected Thousands of recordings of Native AmericanSongs -Jaap Kunst-Created the Term Ethnomusicology in 1955. Prize namedafter him for excellence in the field |
|
|
Gamelan |
-Set of instruments as well as a genre of music
-Gongs-Forged metal -Drums -Metal Mallet Instruments (Xylophone) -Can have Winds, Strings, or Singers |
|
|
Gamelan Orchestras |
-Used forrecreation and entertainment
- Provide musicfor ceremonies, weddings, funerals, street music - 4-30 musicians - Formalconcerts are rare - Connection topoetry, drama, or dance |
|
|
Balinese Gamelans |
-Most highlydeveloped and known in the United States
-PerformTraditional as well as new Music -Not performedfrom notation - Veryrepetitive |
|
|
Balinese Gamelans Tuning |
-Orchestras useTwo tunings or scales
1. 5-note-Slendro 2. 7-note-Pelog - Tuning willsound “out of tune” to Western Ears |
|
|
Indonesian Popular Music |
-Diverse,commercial, hit-based, star oriented
-Uses Westerninstruments and other elements of music - Kroncong-The “old” style. Popular in films through 20th century ~Named forukulele-type instrument that represents patriotism and authentic culture |
|
|
Indonesian Popular Music Contd.
|
-Dangdut-”youthmusic”
- Used fordancing, film religion (Islam), protest -Inspired byWestern pop and rock - Drum Set,Electric Guitar - Rhoma Irama-First Dangdut superstar |
|
|
Music in Eastern Europe |
-Greece-GreekOrthodox Church chants
- Mongolia-Pentatonicmodes -Islamicnations-Various genres of music, Calls to Worship -Whytraditional music barely exists in these cultures ~UrbanInfluences and the shift to industrialization ~Governmentcontrol of traditional music in the most oppressive regimes ~Changes innational and regional boundaries ~Ethnicpopulation shifts and changing loyalties |
|
|
Instrumental Music in Eastern Europe |
-Very common
- Used as dancemusic, or accompaniment to song - Instruments ~Bagpipe,double recorder, cimbalom (hammer dulcimer) ~ Buttonaccordion, Fiddle, several types of flutes |
|
|
Government and Music (Europe) |
-Governments try to control the music that is created
-Government approved music may receive funding, and other support -The opposite for disapproved music -Export music the Government likes; may not represent the population accurately |
|
|
European Artists |
- Gheorge Zamfir-Romania
- BulgarianRadio Woman’s Choir -Ivo Pasasov-Bulgarianjazz clarinetist - Márta Sebestyén- Hungary’s leading folk singer -Tánchéz-Dance house ~ HungarianTraditional music andHungariangypsy music |
|
|
Japanese Music Origin |
-Very set in old tradition -however, modern music is influenced by Western Music -Texture: Band,choir, big band jazz - ChordProgressions and Harmonies - Major andMinor tonalities with emphasis on tonic and dominant - Melodicchanges and use of different timbres |
|
|
Performance Practice of Japanese Music
|
-Performed in concert halls, theaters, courtyards of shrines and temples
- When indoors-used of painted scenery that create an illusion of nature and being outside - Part of theatrical productions -Music meant to be seen and heard -Performances in traditional dress |
|
|
Musical Characteristics of Japanese Music |
- Value small-group performances ~ Public performances 1-3 performers ~Hear each part separately -Manipulates TRADITIONAL material ~Does not explore new material within an already begun song -Restraint and control is used to communicate the emotion of the song rather than the performers emotions - Music learned by memory ~Teacher called Sensai ~Notation is vague and needs interpretation by student and sensai |
|
|
Musical Characteristics of Japanese Music Contd.
|
-Narrow rangeof dynamics
- Pentatonicscale with ornamentation - Nonexistent ofincidental harmony - Regular rhythm -Variedtimbres, unblended, delicate - Melody andtimbre are main values - Little to noimprovisation |
|
|
Gagaku |
-Oldest instrumental music in the WORLD
- Imperial courts in ninth-eleventh century - Total theater experience ~ Dance, Music, Masks, and Visual effects -Musical Characteristics ~Static ~Blocks of sounds ~ Hichiridi-double-reed, oboe like instrument ~Sho-Mouth organ having 17 small pipes |
|
|
Koto |
-Large 13stringed instrument - Uses slide,scrapes, plucked strings -Genteel instrument of Japan - Presence of a Koto in a Japanese home suggests goodbreeding and upbringing |
|
|
Shakuhachi |
-End-Blownflute
-Descendant ofa bamboo flute -Used forornaments |
|
|
Shamisen
|
-3 Stringedinstrument
-Used for folkmusic - Plucked |
|
|
Sankyoku |
Combination of Koto, Shakuhachi, and Shamisen |
|
|
Kabuki |
-Theater andmusic
- Noh traditionoutside of imperial court - Noh-Classicalmusic drama that has been performed since the 14th century - Melodrama ~ Colorfuldancing ~ Onstageensemble called Nagauta |
|
|
Nagauta and other aspects of performance
|
-Provides basicvocal and instrumental accompaniment- Developed ownpopularity outside of Kabuki - 12 Musicians ~ 3 drums, Flute, SeveralShamisen Players, and Singers -Gidayu Songs-Narrative songs performed onstage with shamisenaccompaniment- Geza-Offstage ensemble that performs noises, sound effects
|

