![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Number one world power in 1900 |
Europe |
|
|
European colonialism was based on: |
- economic supremacy - industrialisation - science and technology - military power - medicine |
|
|
19th Century Europe |
- relatively peaceful since end of Napoleonic Wars (1815) - Wars (Crimean, Franco-Prussian [france vs germany]) contained - rising tensions and rivalries - German Unification (1871) |
|
|
19th C Progress |
- material, social, cultural and moral - 1st in Britain; USA; Japan |
|
|
Scramble for Africa |
- 1875-1910 - almost complete European takeover - period of rapid capitalism - caused intra-European rivalries - reasons: economic, political, nationalist, strategic |
|
|
Labour Movements |
1905 Revolution in Russia (unsuccessful) Extremist (German) Moderate (British) |
|
|
Socialism |
Public (state) ownership of economic resources |
|
|
Favoured European emigration destination? |
USA
-fostered tension but promoted wealth and power |
|
|
Suffragettes |
British campaigners for women's votes |
|
|
Women's Suffrage |
Campaign in the late 19th C for women's rights |
|
|
Anti-colonial movements |
- lead by indigenous elites - late 19th C - Indian National Congress (f. 1885) - African National Congress (f. 1912) - Chinese Revolution (1911) - end of imperial rule |
|
|
Nationalism |
Group sentiment, belonging, patriotism
- achieved through media, institutions (school, military), rituals (holidays) |
|
|
Multinational Empires |
Hasburg (Austro-Hungarian)
Ottoman |
|
|
International Rivalries (late 19C early 20C) |
- resulted in rising tensions - major Euro powers sign series of alliances - once conflict began, all drawn into war |
|
|
Major Causes of WWI |
- Nationalism - Increasing rivalries in W¢ral Europe - Nationalist movements demanding end to Habsburg and Ottoman empires - Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Slavic nationalist (June 1914) |
|
|
Total War |
- entire national pops, economics and industries mobilized for war - gov't more active - women employed in industry (fill in for men) - mobilisation of colonised people - propoganda |
|
|
Individual Nation Reasons for WWI |
France - revenge against Germany Britain- protect imperialist interests Russia- eithnic loyalties, warm water port, anti-AusHung, revenge against Japan Germany- recognition as world power Balkans- desire for freedom from Turkish rule Austria- to remain a state Serbia- freedom
|
|
|
Women and WWI |
- increased employment in industry - intended as temporary during war - disruption in gender roles can't be undone |
|
|
Entrance and Exits into WWI |
1917 USA enters Russia leaves (revolution at home) |
|
|
Post War Treaties |
Drafted by victorious powers w/ no input from defeated
-Versailles (1919) Germany -St Germain (1919) Austria - Trianon (1920) Hungary - Neuilly (1920) Bulgaria - Sevres (1920) Turkey
|
|
|
Big 3 |
USA, Britain, France
(Russia excluded, Italy and Japan ignored) |
|
|
Paris Peace Conference |
1919-1920 - Dominated by big 3 - US Pres Woodrow Wilson "14 Points for a Just Peace" - France and UK want revenge against Germany - Germany forced to admit "war guilt" and pay heavy fines to prevent them from ever returning to power |
|
|
Treaty of Versailles |
(1919) - Post WWI Treaty - designed to crush Germany and prevent them from ever returning to power - Germany and Russia excluded from talks |
|
|
League of Nations |
- formed after WWI to prevent WW from occuring ever again - US refuses to join - Russia and Germany not present - little success |
|
|
Redrawing the Map |
-Habsburg and Ottoman empires disbanded - New Nations: Yugoslavia, Czechslovakia, Poland, Finland, Austria, Hungary, Romania, Estonia -ethnic/natinal groups not neatly divided into separate states |
|
|
Mustafa Kemal |
- New leader of independent Turkey after WWI - tried to modernise and westernise Turkey |
|
|
Colonial Issues after WWI |
- colonial troops desire recognition and recomense - stranger anti-colonial movements - unease at injustice |
|
|
February Russian Revolution |
1917 -Czar abdocated - establishment of Provisional Gov't dominated by liberal and moderate socialists |
|
|
October Russian Revolution |
1917 - Bolsheviks topple provisional gov't - lead by Vladmir Ilyich - Lenin Bolshevik and followers (Bolsheviks) gain power |
|
|
Marxism |
- Karl Marx (German philosopher) - economic factors always more important than others in social functioning and change - forces of production (raw materials+techniques of manufacture) in hands of minority - dictatorship of proletariat (transition stage to communist society) - communist society = utopia (no exploitation) - 1st Countries to develop it- capitalist (UK, Germany, USA) |
|
|
bourgeoisie |
- capitalists - own forces of production - exploit proletariats |
|
|
proletariat |
- working class - exploited by bourgeoisie |
|
|
1st Successful Marxist Revolution |
Russia 1917 |
|
|
Russian Civil War |
(1918-1921) - Reds (Bolsheviks) vs Whites (Anti-Bolsheviks; radical socialists to monarchists) - Reds disciplined - Foreign capitalist support to Whites ensures Bolshevik distrust of capitalists - Bolsheviks win |
|
|
Single Party State |
- Soviet Union - Bolsheviks monopolise power - Cheka (secret police) stifle opposition - Marxism/Leninism: leadership was essential to represent the true interests of the proletariat - "vanguard of the proletariat" - Bolsheviks = vanguard |
|
|
Lenin's New Economic Policy |
(1921-1929) - elements of free market in socialist system - women given equality - initial artistic experimentation that quickly was repressed |
|
|
Josef Stalin |
Soviet leader 1924-1953 - 5 year plans to rapidly stimulate economy - abolished Lenin's New Economic Policy - repressed kulaks (well-off peasants) - Great Purges - removed all opposition |
|
|
5 Year Plans |
- supposed to rapidly stimulateeconomy - heavy industry, armaments, hydroelectricity - collective farms established -huge famines resulted |
|
|
Influenza Pandemic description |
1918-1919 - consequence of globalisation (brought by US) - everyone exhausted after WWI and susceptable to disease - "Spanish Flu" - 1st wave - mild virulence - 2nd wave - high virulence, high mortality |
|
|
Influenza |
- viral disease 3 types: A -causes pandemics, from birds, mutates to affect humans B- causes disease but not pandemics C- rarely causes human disease |
|
|
3 Major Influenza Pandemics |
1.) Hong Kong Flu (1968) - high spread, low mortality 2.) Asian Flu (1957) 3.) Spanish Flu (1918-19) |
|
|
3 aspects that set 1918-19 Flu apart from other pandemics |
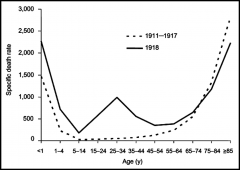
1.) large magnitude 2.) high mortality rate 3.) W - shaped age profile of deaths (infants, young adults, and elderly likely to die)
|

