![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
1491 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 2 toxic fumes produced by ultraviolet light. |
–ozone |
|
|
What is the primary function the shielding gas? |
prevents atmospheric contamination
pg 13 |
|
|
what is one of the three variable shielding gas can effect?
|
–mode of metal transfer |
|
|
The powder in a MCAW Wire consists mostly of: |
b)metal |
|
|
Name 3 parts of the the wire feed welder
|
power source |
|
|
Amperage controls what?
|
–Burn off |
|
|
voltage controls what?
|
–Arc stability |
|
|
what does the Regulator do?
|
the regulator brings the gas to a working level |
|
|
what does the flow meter do?
|
the flow meter controls how much gas glows to the Gun.
pg 13 |
|
|
what governing body sets power source specifications.
|
National Electrical Manufactures Association |
|
|
what are the power sources rated based on?
|
–Amperage
–Voltage & –duty cycle pg 15 |
|
|
what is the electrode extension range for self–sheilded FCAW?
|
3/4" – 3 3/4"
pg 9 |
|
|
Define & Desribe the GMAW process.
|
GMAW – Gas Metal Arc Welding
–Electric arc heats metal from a electrode (continuously fed) to join metals –Shielding gas prevents contamination from outside air pg 6 |
|
|
List 3 advantages of GMAW.
|
Advantages |
|
|
list 3 disadvantages of GMAW |
Disadvantages |
|
|
one of the main advantages of metal core wire is: |
d) high deposition rate |
|
|
what are the principles of FCAW?
|
–Uses a flux core arc to join metals
–electrode consumable (continuously fed) –settings maintained by the operator –shielding gas can be obtained from an external source or/and from within the electrode |
|
|
A welding machine that produces an almost horizontal slope is a:
a) Constant Current b) Constant Voltage c) Rising Arc Voltage d) High Amperage Potential |
b) Constant Voltage
pg 17 |
|
|
what type of amp curve does a constant current machine produce?
a) Flat b) Variable c) Rising d) Drooping |
d) Drooping
pg 16 |
|
|
what is a common power source on GMAW welding machines?
|
Constant Voltage |
|
|
constant voltage machines produce a:
a) drooping volt curve b) rising volt curve c) relatively flat volt–amp curve d) constantly changing volt–amp curve |
c) relatively flat volt–amp curve |
|
|
power source best suited for the short – circuit mode of metal transfer is a:
a) rising arc voltage power source b) constant voltage power source c) constant current power source d) constant amperage power source |
b) constant voltage power source
pg 16 |
|
|
How can air quality be affected when welding with shielding gases.
|
–can cause displacement of oxygen
–oxygen deficiency |
|
|
GMAW is also known as?
|
MIG Welding
|
|
|
self shielded FCAW use shielding generated from:
a) a base metal b) an external source c) the flux d) a past flux applied to the base metal before welding |
c) the flux
pg 9 |
|
|
GMAW is recomended for use on which of the following metals?
a) stainless steel b) aluminum c) copper alloys d)carbon and low alloys steels e) all of the above |
e) all of the above
|
|
|
the MCAW process uses the same equipment as? |
c) FCAW
pg 10 |
|
|
How are wire feed guns rated?
|
by current carrying capacity
pg 13 |
|
|
welding power designed for wire feed can be used for SMAW?
a) True b) False |
b) False
pg 16 |
|
|
GMAW may be used in semi–automatic or automatic operation modes?
a) True b) False |
a) True
pg15 |
|
|
Major factor in choosing air cooled gun / water cooled gun is
a) shielding gas b) current/voltage c) joint design d) base metal alloy |
b) current/voltage
pg 14 |
|
|
a potential source of chemical fumes when welding is:
a) Inert Shielding gases b) Chlorinated degreasing solvents c) Carbon dioxide extinguishers d) Anti–spatter nozzle sprays |
b) chlorinated degreasing solvents
pg 3 |
|
|
The use of shielding gases increases the need for?
a) Lighting b) Ventilation c) Heat shielding d) Eye protection |
b) Ventilation
pg 3 |
|
|
what color should you welding clothing be and why?
|
dark colored
to reduce reflected light pg 3 |
|
|
Name 3 advantages of FCAW.
|
–the deposition rate is greater than SMAW
–there is a high operator factor, easily mechanized – the visible arc is easy to use –the weld deposits are high quality pg 20 |
|
|
Name 3 disadvantages of FCAW.
|
–Equipment is more expensive to purchase
–more smoke and fumes are generated –wire feeder must be in close proximity –equipment is more complex/ requires more maintenance pg 20 |
|
|
how does a push–pull system work
|
feeders in the gun pull the wire while simultaneously pushing the wire from the feeder
pg31 |
|
|
What does a push pull system allow for?
|
allows for greater machine to work distances
Pg 31 |
|
|
where are the drive rolls located in a pull system?
|
in the gun
pg 31 |
|
|
what type of wires is the pull system preferred for? |
small diameter or soft electrode wires
pg 31 |
|
|
what power can a pull system use?
a) constant current b) constant voltage c) both |
c) both (constant current or constant voltage)
pg 31 |
|
|
How are filler wires made?
|
Drawn into continuous lengths
(from the same batch to keep a uniform chemical composition) pg 3 |
|
|
what range of diameters can wires come in?
|
0.5mm–3.2mm (0.020" –1/8")
pg 3 |
|
|
what does not influence the selection of a filler wire?
a)base metal chemistry b)the shielding gas c)type of metal transfer d)type of welding machine e)service requirements f)condition of the base metal g)welding position |
d) type of welding machine
pg 5 |
|
|
In ER70S–G what does the G stand for?
|
general classification
pg 11 |
|
|
Name two functions of the Flux?
|
–provides deoxidizers and scavengers to remove impurities
–form a slag cover–prevent contamination –act as an arc stabilizer –add alloying elements –provide a shielding gas pg 15 |
|
|
what units does CSA measure tensile strength in?
|
mPa–(metric) mega pascals
pg 17 |
|
|
what units does AWS measure tensile strength in?
|
psi – (imperial) pressure per square inch
pg17 |
|
|
What numbers do CSA use to classify welding position and which one is which?
|
1–all positions
2–flat and horizontal pg 17 |
|
|
What numbers do AWS use to classify welding position and which one is which?
|
0–flat and horizontal
1–all positions pg17 |
|
|
where in the wire does metal core wire carry current?
|
the metal sheath (the outside)
|
|
|
what type of penetration profile do MCAW wires create?
|
wide penetration profile
|
|
|
what shape of Arc do MCAW wires create?
|
a cone shaped arc
|
|
|
12–22 arc volts is what mode of metal transfer? |
short circuit transfer
pg 25 |
|
|
describe the process of short circuit metal transfer? |
–wire comes into contact with the workpiece
–magnetic buildup causes pinching effect separating the the wire from the puddle –start the process over pg 25 |
|
|
what is short circuit metal transfer ideal for?
|
joining light gauge metals and poor fit ups
pg 25 |
|
|
what is the voltage range of Globular Transfer?
|
22–26 Arc Volts
pg 26 |
|
|
What size are globules from globular transfer in relation to the wire diameter?
|
larger than the wire diameter
pg 26 |
|
|
why is globular transfer generally avoided in GMAW?
|
spatter problems and poor weld appearance
pg 26 |
|
|
What is electrode extension?
|
Distance from the end of the contact tip to the end of the electrode.
pg 45 |
|
|
what happens to the arc voltage when electrode extension increases?
|
when extension increases – Arc voltage lowers
pg 46 |
|
|
what happens to the weld bead if your electrode extension increases?
|
lower arc voltage increases weld bead convexity
pg 45 |
|
|
what process is the pulse arc generally used for?
|
MCAW – positions other than Flat and horizontal.
pg 27 |
|
|
what are inverter type power sources capable of that makes them good for pulse arc transfer?
|
Capable of very fast response times and accurate current control
pg 27 |
|
|
what is the recommended distance for a push system?
|
15 feet
pg 30 |
|
|
where are the drive rolls located in a push system?
|
In the Wire feed unit
pg 30 |
|
|
what does each part Stand for (FCAW–CSA)
F 49 1 T – 6 CH a–b––c–d–––e––f |
a)F – Electrode
b)49 – Minimum tensile strength (MPa) c)1 – Position d)T–metal core wire or tubular/Flux core wire e)6–slag system, current, polarity, shielding gas f)optional controlled hydrogen designator pg 18 |
|
|
what does each part stand for (FCAW–AWS)
E – X X T – X M J HZ a––b c d–––e––f–g––h |
a)E– electrode
b)X–Maximum Tensile strength (psi) c)X–Position d)T–Tubular Flux core wires e)X–usability and performance characteristics f)M–designates whether argon/CO2 or CO2/self shielded g)J–optional Improved toughness value designator h)H–optional controlled hydrogen designator pg 18 |
|
|
what Does DCEN stand for?
|
Direct Current Electrode negative
pg 44 |
|
|
what polarity is DCEN?
|
Straight polarity
pg 44 |
|
|
where is 2/3 of the arc energy in a DCEN system?
|
in the electrode
pg 45 |
|
|
what does DCEP stand for? |
Direct Current Electrode Positive
pg 44 |
|
|
what polarity is DCEP?
|
reverse polarity
pg 44 |
|
|
where is 2/3 of the energy in a DCEP system?
|
in the work piece
pg 45 |
|
|
AC is not used a lot with wire feed welding due to its problems with Arc Stability.
a) True b) False |
a) True
pg 45 |
|
|
which system has better penetration with GMAW: |
b)DCEP |
|
|
How does a Voltage Sensing Wire Feeder work?
|
arc voltage change caused by the change in electrode extension is sensed by the motor drive and it adjusts the wire speed to maintain the arc length.
pg 38 |
|
|
How does a constant speed wire feeder work?
|
the system maintains the arc length by automatically adjusting the amperage output as the electrode extension changes.
pg 37 |
|
|
What does each letter stand for (GMAW–CSA)
B – G 49A 3 C G6 a–––b–c–-d e––f |
a)B–Electrode impact test Average
b)G–welding process c)49A–Tensile strength (MPa) d)3–average temperature of impact test e)C–Shielding gas to be used f)G6–chemical analysis of the electrode pg 8 |
|
|
what does each letter stand for (GMAW–AWS)
ER 70 S – XNHZ –a–b–c E70C– X Y N HZ –-––––d–e–f-–g |
a)ER–filler rod or electrode
b)70–minimum tensile strength (psi) c)S–Solid or composite filler metal d)X–Chemical composition e)Y–types of shielding gas used for classification f)N– N when unclear application g)HZ– optional supplemental diffusable hydrogen designator pg 9 |
|
|
define Cryogenic liquid?
|
a liquid with a normal boiling point below –151.11°C (–240°F)
120103c pg 2 |
|
|
what is specific gravity?
|
the ratio of gas mass in comparison to atmospheric air.
120103c pg 3 |
|
|
true spray arc transfer cannot be obtained with mixes that contain more than what percentage of CO2?
|
15% CO2
120103c pg 9 |
|
|
When added to inert gases like argon, oxygen increases what welding puddle property?
|
Puddle Fluidity
120103c pg 9 |
|
|
C25 is what ratio of argon to CO2? |
75% argon to 25% CO2
120103c pg 11 |
|
|
what is CO2 sold by?
|
Weight
120103c pg 11 |
|
|
what is argon, helium, hydrogen, & nitrogen sold by?
|
Volume (meters cubed or or feet cubed)
120103c pg 21 |
|
|
why must CO2 be used in the vertical position?
|
to prevent drawing drawing of liquid CO2
120103c pg 21 |
|
|
atmospheric air contains what percentage of oxygen and Nitrogen?
|
–21% oxygen
–78% nitrogen 120103c pg 2 |
|
|
Name 2 things shielding gas can effect?
|
–arc characteristics
–depth of fusion –weld bead profile –weld speed –cleaning action –mode of metal transfer 120103c pg 3 |
|
|
Name 2 Basic properties of a shielding gas.
|
–specific gravity
–ionized potential –thermal conductivity –dissociation and recombination characteristics –reactivity/oxidation potential 120103c pg 3 |
|
|
What is an inert gas?
|
a gas that does not react or oxidize with other elements across the arc
120103c pg 5 |
|
|
What is a reactive gas?
|
gases the react with the filler and base metal
120103c pg 5 |
|
|
What is the specific gravity of argon?
|
1.38
120103c pg 4 |
|
|
What is thermal conductivity of a gas?
|
it’s ability to conduct heat
120103c pg 4 |
|
|
If a gas has a higher ionization potential it requires more arc voltage to keep it ionized this means more _______ input into the base metal.
|
Heat
120103c pg 4 |
|
|
Pure Argon can cause what when welding?
|
undercut along the bead edges and an erratic arc
120103c pg 6 |
|
|
What is Argon in its pure form mainly used for with GMAW?
|
welding non–ferrous metals(aluminum, magnesium, atc.)
120103c pg 6 |
|
|
The density of Helium is 0.14 times that of air so it requires gas flow rates of how many times more than argon when welding in the flat position?
|
2–3 more times
120103c pg 7 |
|
|
In the heat of the arc CO2 has the ability to dissociate into what?
|
Carbon Monoxide
120103c pg 8 |
|
|
What may be a major concern when using only CO2 for short circuit metal transfer?
|
spatter amount is high and post weld cleanup costs may be a major concern
120103c pg 8 |
|
|
What is CO2 use primarily for welding?
|
mild and low alloy steels
120103c pg 9 |
|
|
When added to inert gases what does hydrogen increase in welds?
|
Heat input into the base material
120103c pg 9 |
|
|
What is argon–helium primarily used for welding?
|
aluminum, copper, magnesium and their alloys
120103c pg 12 |
|
|
What are the three primary factors that affect gas flow rates?
|
–type of shielding gas
–type and thickness of material –position of welding 120103c pg 13 |
|
|
Name three other factors that affect gas flow rates?
|
Joint design
–wire diameter –size of weld pool –air currents –design of welding fixtures –shielding gas pressure –nozzle to work distance –amount of welding current –welding speed –inclination of the welding gun –leaking gas 120103c pg 13 |
|
|
What is the gas flow rate range for GMAW?
|
7–23L/min(15–50cfh)
120103c pg 13 |
|
|
What is the gas flow rate range for FCAW?
|
14–23L/min(30–50cfh)
120103c pg 18 |
|
|
Some cylinders have a permanently attached tulip safety cap what is this type of pressure is this cylinder usually able to carry compared to other cylinders?
|
higher pressures
120103c pg 20 |
|
|
How are compressed cylinders made?
|
they are hot drawn from a single piece of metal
120103c pg 20 |
|
|
What is CO2 sold by?
|
weight
120103c pg 21 |
|
|
What is argon, helium, hydrogen, and nitrogen sold by? |
by volume(m3 or ft3)
120103c pg 21 |
|
|
What is the pressure of a C02 cylinder at 21°C?
|
830psi
120103c pg 21 |
|
|
For some applications, why should cylinders be changed when the pressure drops to 1.38MPa(200psi)?
|
The lower portion of the liquid in the cylinder has higher concentrations of moisture
120103c pg 22 |
|
|
Why are cylinder and regulator connections different sizes and types?
|
to eliminate the possibility of interchanging regulators on cylinders
120103c pg 24 |
|
|
What are Dewars or mini–bulk containers designed to hold?
|
cryogenic gases in liquid form
120103c pg 25 |
|
|
What is the purpose of a regulator?
|
–reduce source pressure to working pressure
–maintain a constant delivery pressure –deliver gas at any desired pressure within the regulator’s rated capacity (Controls pressure not flow rates) 120103c pg 27 |
|
|
What does a flow meter indicate?
|
the rate of flow of a shielding gas in L/min or in cubic feet per hour(cfh)
120103c pg 28 |
|
|
Flow of a gas is measured more accurately by __________ than by pressure.
|
volume
120103c pg 28 |
|
|
Why are hoses generally constructed of plastic materials?
|
Rubber hoses allow helium pressurized above 138 kpa (20psi) to penetrate through the hose causing gas loss
120103c pg 31 |
|
|
What are Gas solenoid valves?
|
electronically operated valves that control the flow of shielding gas to the weld zone
120103c pg 31 |
|
|
Who is required to wire up a welding power source
|
Qualified electrical personnel
120103d pg 2 |
|
|
Where do you find the procedure to wire up a welding power source?
|
Equipment manufacture's operating manual
120103d pg 2 |
|
|
How must a flow meter be mounted to get an accurate reading? Why?
|
–The vertical position
–The flow meter will give an incorrect reading if not mounted correctly 120103d pg 4 |
|
|
What should the drive rolls match?
|
Wire size & type
120103d pg 5 |
|
|
Define Electrode Inclination
|
(work angle)
The position of the electrode in relation to the direction of travel. 120103d pg17 |
|
|
When your electrode is at 0°, where is your electrode in relation to the direction traveling?
|
The electrode is perpendicular(90°) to the direction of travel.
120103d pg17 |
|
|
Why does flux core only use the Backhand method?
|
To prevent slag inclusion in the weld.
120103d pg 17 |
|
|
when loading the wire why must you always hold onto the loose end?
|
Prevents the spool from unwinding and tangling.
prevents the partial or complete loss of the spool. 120103d pg 7 |
|
|
Why use the Jog switch if your machine has one?
|
Activates the wire feeder without energizing the wire or activating the shielding gas.
120103d pg 7 |
|
|
How tight should your your drive rolls be?
|
At a point where you achieve a continuous feed without deforming or scarring the surface of the wire.
120103d pg 9 |
|
|
where should a wire cleaner be placed?
|
Just before the wire feeder.
120103d pg 10 |
|
|
what should you adjust the spool brake to do?
|
To allow the spool to rotate freely but with enough tension to prevent backlash.
120103d pg 10 |
|
|
Contact tubes are not considered a consumable Item?
a)True b)False |
b)False
120103d pg 14 |
|
|
What can happen if you use to much anti–spatter compound?
|
It can contaminate the weld and shorten the life of the nozzle.
120103d pg 15 |
|
|
Define electrode angle?
|
The position of the gun in relation to the included joint angle.
120103d pg 16 |
|
|
If undercut occurs where should you point you electrode to eliminate it?
|
Point it towards the undercut. (forces the undercut area to become hotter so the metal will flow to that point)
120103d pg 16 |
|
|
Backhand or forehand, which one gives you better penetration?
|
Backhand Inclination (15°–20°)
120103d pg 17 |
|
|
What type of bead does Forehand inclination produce?
|
Flatter with less penetration.
120103d pg 17 |
|
|
What type of metal transfer are recessed contact tubes suitable for?
|
Spray arc transfer
120103d pg 19 |
|
|
Contact tips must be centered to ensure what?
|
Equal gas penetration to the weld puddle
120103d pg 19 |
|
|
contact tip must be centered to ensure what?
|
equal gas distribution to the weld puddle
120103d pg 19 |
|
|
what mode of metal transfer are recessed contact tips ment for?
|
Spray arc transfer
120103d pg 19 |
|
|
What can happen if to much spatter builds up between the nozzle & Contact tip?
|
Can cause disruption to the gas flow and can cause an arc between the nozzle and tne contact tip.
120103d pg 21 |
|
|
What can happen if your work lead connection is poor?
|
It can cause an unstable arc.
120103d pg 21 |
|
|
What is stubbing generally caused by?
|
–excessive wire speed
–low arc voltage –heavily scaled base metal 120103d pg 21 |
|
|
Wire size is selected to match the_________ and ________ properties of the metal.
|
Chemical & Mechanical
120103e |
|
|
Name 2 characteristics you look for in a GMAW 1F weld.
|
–Weld size
–Weld uniformity –weld contour –Absence of weld defects –Good penetration and Tie ins 120103e pg 12 |
|
|
what should your weld surface be free of before Fit up?
|
Clean no rust, oil, grease, & scale
120103e pg 11 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 1F?
|
–Stringer root
–3–6 passes or weave beads 120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 1F GMAW weld?
|
15°–30°
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 1F GMAW Weld?
|
0°–20°
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 1F GMAW weld?
|
18
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 1F GMAW weld?
|
120
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 1F GMAW Weld?
|
180
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 2F?
|
–Stringer root
–3–6 passes for the fill & cap 120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 2F GMAW weld?
|
15°–30°
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 2F GMAW Weld?
|
0°–20°
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 2F GMAW weld?
|
18
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 2F GMAW weld?
|
120
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 2F GMAW Weld?
|
180
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 3F?
|
–Stringer & weave beads
–root down hill –Fill & Cap uphill 120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 3F GMAW weld?
|
15°–30°
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 3F GMAW Weld?
|
0°–10°
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3F GMAW weld: a)Root
b)Fill & Cap |
a)18
b)17 120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 3F GMAW weld: a)Root
b)Fill & Cap |
a)120
b)110 120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 3F GMAW Weld:
a)Root b)Fill & Cap |
a)180
b)170 120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is you electrode extension on a GMAW fillet weld?
|
6.4mm–10mm( ¼”–¾”)
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your electrode angle on a GMAW fillet weld?
|
½ the included Joint angle
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
Where should your wire be sitting in the puddle on a GMAW fillet weld?
|
Maintain the leading edge of the puddle
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What Mode of metal transfer are you using for a GMAW fillet weld?
|
Short circuit metal transfer
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 3F (10 gauge) ?
|
–Stringer or slight weave
–1 pass downhill 120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 3F (10 gauge) GMAW weld?
|
15°–30°
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3F (10 gauge) GMAW weld?
|
18.5
120103e pg 10 |
|
|
What is 1F position? How are your coupons position when welding?
|
Flat 45° to the floor 120103e
|
|
|
when you tack–up what should you make sure you don't have between your coupons?
|
Space 120103e
|
|
|
where should you tack welds be placed on a fillet weld?
|
ends of the coupon or in the joint. 120103e
|
|
|
What is the 4F position?
|
overhead 120103e
|
|
|
What is the 3F position?
|
vertical 120103e
|
|
|
What is the 2F position?
|
Horizontal 120103e
|
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 1G?
|
–Stringer root
3–4 passes or weave beads 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 1G GMAW weld?
|
0°–10°backhand
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 1G GMAW Weld?
|
0°–20°
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 1G GMAW weld a)roots b)fill&Cap?
|
a)16.5
b)18 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 1G GMAW weld a)root b)fill&Cap?
|
a)110
b)120 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 1G GMAW Weld a)170 b)180?
|
a)170
b)180 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 2G?
|
–Stringer root
weave beads 5,6,or7 passes 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 2G GMAW weld?
|
15°–30°backhandfor root
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 2G GMAW Weld?
|
0°–20° backhand or forehand for fill and cap
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 2G GMAW weld a)roots b)fill&Cap?
|
a)16.5
b)18 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 2G GMAW weld a)root b)fill&Cap?
|
a)110
b)120 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 2G GMAW Weld a)170 b)180?
|
a)170
b)180 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 3G?
|
–Stringer and weave beads
5,6,or7 passes 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 3G GMAW weld?
|
15°–30°backhand for root
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 3G GMAW Weld?
|
0°–20° backhand or forehand for fill and cap
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3G GMAW weld?
|
17.5
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 3G GMAW weld?
|
117
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 3G GMAW Weld?
|
175
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW 4G?
|
–Stringer and weave beads
3–4 passes 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 4G GMAW weld?
|
0°–10°backhand
120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 4G GMAW weld a)roots b)fill&Cap?
|
a)16.5
b)18 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 4G GMAW weld a)root b)fill&Cap?
|
a)110
b)120 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 4G GMAW Weld a)170 b)180?
|
a)170
b)180 120103e pg 18 |
|
|
When tacking up pipe why do you weld away from your spacer?
|
so when your tacks shrink your spacer doesn’t become stuck
120103e pg 30 |
|
|
When grinding permanent tacks what must you be careful not to do?
|
make the root face thinner or the gap wider
120103e pg 32 |
|
|
How much strength should be left after feathering a permanent tack?
|
enough strength to hold the joint securely
120103a pg 32 |
|
|
What must be done to all stop and starts of a pipe root weld?
|
must be feathered
120103e pg 32 |
|
|
What is the maximum length of a pipe tack?
|
19mm(¾”)
120103e pg 32 |
|
|
Why do you feather permanent tacks?
|
to ensure full fusion
120103e pg 32 |
|
|
How are bridge tacks different from permanent tacks?
|
bridge tacks do not contact the land of a weld.
120103a pg 33 |
|
|
Bridge tacks are blended into the pipe weld.
a)True b)False |
b)False(bridge tacks must be removed)
120103e pg 33 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a 1G pipe with GMAW?
|
downhill progression between 1 o’ clock to 2 o’ clock position pipe is rotated
120103e pg 34 |
|
|
What is the minimum number of tacks that can be used when welding pipe?
|
Three
120103e pg 36 |
|
|
What is the distance between the plates on a 1GF, 3GF, & 4GF?
|
13mm(½“)
120103e pg 38 |
|
|
What is the distance between the plates on a 2G CWB plate? |
8 mm(5/16”) |
|
|
What is the included angle on all FCAW fillet welds?
|
½ the included angle(45°)
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What is the electrical stick–out for all FCAW Fillet welds?
|
12.7mm–19mm (½”–¾”)
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 1F?
|
Stringer and weave beads
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 1F FCAW weld?
|
15°–30°backhand
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 1F FCAW Weld?
|
0°–20°backhand
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 1F FCAW weld?
|
22
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 1F FCAW weld?
|
170
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 1F FCAW Weld?
|
220
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 2F?
|
–Stringers
120103f pg 13 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 2F FCAW weld?
|
15°–30° backhand
120103f pg 13 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 2F FCAW Weld?
|
0°–20°backhand (possible slight weave on cap to eliminate undercut)
120103f pg 13 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 2F FCAW weld?
|
22
120103f pg 13 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 2F FCAW weld?
|
160
120103f pg 13 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 2F FCAW Weld?
|
200
120103f pg 13 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 3F?
|
Christmas tree weave beads
120103f pg 16 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the root of a 3F FCAW weld?
|
0°–10°forehand with vertical uphill progression
120103f pg 16 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for the fill & Cap pass for a 3F FCAW Weld?
|
0°–10° forehand with a vertical uphill progression
120103f pg 16 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3F FCAW weld
|
22.5
120103f pg 16 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 3F FCAW
|
170
120103f pg 16 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 3F FCAW Weld
|
220
120103f pg 16 |
|
|
What is you electrode extension on a MCAW fillet weld?
|
12.7mm–19.0mm( ½”–¾”)
120103f pg 20 |
|
|
What is your electrode angle on a MCAW fillet weld?
|
½ the included Joint angle
120103f pg 20 |
|
|
Where should your wire be sitting in the puddle on a FCAW and MCAW fillet welds?
|
Maintain the leading edge of the puddle
120103f pg 20&10 |
|
|
What Mode of metal transfer are you using for a FCAW fillet weld?
|
Globular metal transfer
120103 pg 10 |
|
|
What Mode of metal transfer are you using for a MCAW 1F fillet weld?
|
Spray metal transfer
120103f pg 10 |
|
|
What Mode of metal transfer are you using for a MCAW 2F and 3F fillet weld?
|
Pulsed arc metal transfer
120103f pg 20&23 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a MCAW 1F?
|
stringers & weave beads
120103e pg 20 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 1F MCAW weld?
|
0°–20°(possible slight weave on cap to eliminate undercut)
120103f pg 20 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 1F MCAW weld?
|
25
120103f pg 20 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 1F MCAW
|
188
120103f pg 20 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 1F MCAW Weld
|
225
120103f pg 20 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a MCAW 2F?
|
Stringer beads
120103e pg 23 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 2F MCAW weld?
|
0°–20°(possible slight weave on cap to eliminate undercut)
120103f pg 23 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 2F MCAW weld?
|
25
120103f pg 23 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 2F MCAW?
|
188
120103f pg 23 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 2F MCAW Weld?
|
225
120103f pg 23 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a MCAW 3F?
|
Christmas tree pattern
120103e pg 26 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 3F MCAW weld?
|
0°–20°(possible slight weave on cap to eliminate undercut)
120103f pg 26 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3F MCAW weld?
|
19
120103f pg 26 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 3F MCAW?
|
115
120103f pg 26 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 3F MCAW Weld?
|
175
120103f pg 26 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 2G?
|
stringers for all passes
120103f pg 37 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 2G FCAW weld?
|
0°–20° backhand for all passes
120103f pg 37 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 2G FCAW weld?
|
22
120103f pg 37 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 2G FCAW weld?
|
170
120103f pg 37 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 2G FCAW Weld?
|
220
120103f pg 37 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 1GF?
|
Stringers beads
120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 1GF FCAW weld?
|
0°–20° backhand for all passes
120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 1GF FCAW weld?
|
22.5
120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 1GF FCAW weld?
|
170
120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 1GF FCAW Weld?
|
220
120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 3GF root pass?
|
Stringers beads
120103f pg 40 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 3GF fill & Cap pass?
|
Weave beads
120103f pg 40 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 3 GF FCAW weld?
|
0°–10° Forehand for all passes
120103f pg 40 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3GF FCAW weld?
|
22.5
120103f pg 40 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 3GF FCAW weld?
|
170
120103f pg 40 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 3GF FCAW Weld?
|
220
120103f pg 40 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a FCAW 4GF?
|
Stringers beads, weave beads may be needed to prevent undercutting on the cap
120103f pg 42 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 4GF FCAW weld?
|
0°–20° backhand for all passes
120103f pg 42 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 4GF FCAW weld a)Root b)fill&Cap?
|
a)16.5
b)18 120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 4GF FCAW weld a)root b)fill and cap?
|
a)110
b)120 120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 4GF FCAW Weld a)root b)fill and cap?
|
a)140
b)180 120103f pg 34 |
|
|
What does WPS stand for?
|
welding procedure Specifications.
120103f pg 29 |
|
|
Name 3 of the welding variables found on a WPS.
|
–base metal
–filler metals –positions –preheat –postheat –joint configuration –techniques any other detail pertaining to the weld 120103f pg 29 |
|
|
What is a WPS backed or supported by?
|
Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)
120103f pg 29 |
|
|
What does CWB use in conjunction with a WPS?
|
A welding procedure data sheet (WPDS)
120103f pg 29 |
|
|
What is the space between the Flat and Grooved plate on a CWB test?
|
16mm(5/8”)
120103f pg 28 |
|
|
What are two things a WPDS details?
|
–Supporting WPS
–referencing documents –base metal types thickness or diameter ranges –filler metal type, diameter and amperage range –shielding gas type, gas flow rate –joint design(edge preparation, root gap, root face, tacking type, backing) –weld techniques –extra notes and direction for low temperature service 120103f pg 31 |
|
|
What is the common practice when using two methods of welding?
|
Put the root in with one process and fill the joint in with another process that is capable of increasing weld metal Deposition
120103g pg 2 |
|
|
Ensure uniform root edge preparation and alignment with equal spacing along the entire length of the joint on fit up of a groove weld.
A)True B)False |
A)True
120103g pg5 |
|
|
What is the included angle on all double process GMAW/FCAW welds?
|
½ the included angle
120103g pg 6 |
|
|
What is the electrical stick–out for all GMAW/FCAW welds?
|
–GMAW–6.4mm to 10mm( ¼” to 3/8”)
–FCAW–12.7mm–19mm (½”–¾”) 120103g pg 6 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW/FCAW 1G?
|
Weave beads, GMAW root, FCAW fill and cap
120103g pg 6 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 1G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
0°–10°backhand for all passes
120103g pg 6 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 1G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
16.5–GMAW
22–FCAW 120103g pg 6 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 1G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
110–GMAW
170–FCAW 120103g pg 6 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 1G GMAW/FCAW Weld?
|
140–GMAW
220–FCAW 120103g pg 6 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 2G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
15°–30°backhand
120103g pg 9 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 2G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
16.5–GMAW
22.5–FCAW 120103g pg 9 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 2G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
110–GMAW
170–FCAW 120103g pg 9 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 2G GMAW/FCAW Weld?
|
140–GMAW
220–FCAW 120103g pg 9 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW/FCAW 3G?
|
Weave beads all passes
120103g pg 13 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 3G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
15°–30°backhand for root
0°–10°backhand or forehand for fill & Cap passes 120103g pg 13 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
17.5–GMAW
22.5–FCAW 120103g pg 13 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 3G GMAW/FCAW weld?
|
120–GMAW
170–FCAW 120103g pg 13 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 3G GMAW/FCAW Weld?
|
175–GMAW
220–FCAW 120103g pg 13 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW/MCAW 1G?
|
Weave beads, GMAW root, MCAW fill and cap
120103g pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 1G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
0°–10° backhand for GMAW
0°–10° forehand for MCAW 120103g pg 18 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 1G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
16.5–GMAW
25–MCAW 120103g pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 1G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
110–GMAW
188–MCAW 120103g pg 18 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 1G GMAW/MCAW Weld?
|
140–GMAW
225–FCAW 120103g pg 18 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 2G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
15°–30° backhand for GMAW
0°–10° forehand for MCAW 120103g pg 21 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 2G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
16.5–GMAW
19–MCAW 120103g pg 21 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 2G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
110–GMAW
115–MCAW 120103g pg 21 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 2G GMAW/MCAW Weld?
|
140–GMAW
175–MCAW 120103g pg 18 |
|
|
What technique do you use to weld a GMAW/MCAW 3G?
|
Triangular or Christmas tree for fill /cap
120103g pg 25 |
|
|
What inclination do you use for a 3G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
15°–30° backhand for downhill root pass
0°–10° forehand for uphill fill/cap pass 120103g pg 25 |
|
|
What is your arc voltage for a 3G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
17.5–GMAW
19–MCAW 120103g pg 25 |
|
|
What is your Amperage for a 3G GMAW/MCAW weld?
|
120–GMAW
115–MCAW 120103g pg 25 |
|
|
What is your Wire feed speed for a 3G GMAW/MCAW Weld?
|
175–GMAW
175–FCAW 120103g pg 25 |
|
|
1)what does each letter stand for in the wrought Aluminum numbering system?
1 8 30 A B C 2) what do the last two digits (C) represents if the first number (A) is 2 through 8? |
1) A) Aluminum Group
B)Modification to the Alloy Group C)Aluminum Purity 2)Various Alloy Additions 120103h pg 16&17 |
|
|
1)What does each letter stand for in the Cast Aluminum Numbering system?
A 3 60 .0 a b_c__d 2) What does the C digits stand for when The B digit is 1? |
1)a)Modification to the alloy
b)Major alloy group c)specific alloy additions d)Indicates the product form 2)The Minimum Aluminum Content. (99.00% or greater) 120103h pg 13 |
|
|
all wrought aluminum alloys Experience increased strength when they are
a)Heated b)Cold worked c)under pressure d)b and c |
b) cold worked
120103h pg 14 |
|
|
Name 2 factors when choosing a filler metal for aluminum GMAW.
|
–required tensile strength
–Ductility –operating temperature –corrosion resistance –ease of welding –color match 120103h pg34 |
|
|
storing aluminum filler wires in a dry heated area prevents what?
|
–prevents moisture pickup
–prevents harmful oxides from forming on the surface 120103h pg 34 |
|
|
what does anodizing do?
|
Makes the Oxide layer thicker
(electro chemical process) 120103h pg7 |
|
|
what is one of the properties anodizing changes?
|
–Hardness
–Wear resistance –Electrical insulation –Increased corrosion resistance 120103h pg7 |
|
|
Name 2 ways aluminum is formed.
|
–extruded
–rolled –stamped –drawn –forged –cast 120103h pg10 |
|
|
Name one way Aluminum can be Cast?
|
–Die Cast
–Permanent mould –Sand Casting –cenrifugal Casting 120103h pg10 |
|
|
Name one hydrogen source that could affect your GMAW weld on aluminum.
|
–Lubricants
–hydrated surface oxides –filler rods –torch leaks 120103h pg9 |
|
|
Fill in the Blanks
Due to it's _______ ________ _________, Aluminum requires a heat input four times more rapid than mild steel to raise it's temperature to the melting point. |
high thermal conductivity
120103h pg4 |
|
|
what is the melting point of pure aluminum?
|
660°C (1220°F)
120103h pg5 |
|
|
What is the range of melting points for aluminum alloys?
|
477°C – 657°C (890°F – 1215°F)
120103h pg 5 |
|
|
What is not a physical property of Aluminum?
a)Density f)Melting point b)Electrical conductivity g)Non–megnetic c)Thermal conductivity h)Non–sparkling d)Ductility I)Reflective e)Coefficient of linear expansion J)None of the above |
d)Ductility (mechanical property)
120103h pg4 |
|
|
How much visible light can polished aluminum Reflect?
a)80% b)75% c)60% d)90% |
80%
120103h pg5 |
|
|
list two mechanical properties of aluminum?
|
–tensile strength
–yield strength –modulus of elasticity –Ductility 120103h pg 5 |
|
|
why is aluminum well suited for cryogenic applications?
|
aluminum's strength increases at sub zero temperatures
120103h pg 6 |
|
|
How do you offset the distortion that can occur when welding aluminum?
|
Use more tacks
120103h pg9 |
|
|
What must be removed before any welding can occur on aluminum?
|
the Oxide Layer
120103h pg6 |
|
|
a) Aluminum is corrosion resistant but what type of corrosion can take place?
b) Through what process? |
a) Galvanic Corrosion
b) Electrolysis process 120103h pg 6 |
|
|
What is aluminum obtained from?
|
Bauxite ore
120103h pg 2 |
|
|
Why is aluminum generally added to steel?
|
to deoxidize and control grain growth
120103h pg 2 |
|
|
Why should oxygen never be used for cleaning conduit liners?
|
Oil may be present which presents an explosion hazard.
120103h pg 27 |
|
|
Name one factor to consider when choosing a wire feed system?
|
–type of wire your welding
–the location of welding –size and shape of the structure being welded 120103h pg27 |
|
|
what is the desired mode of metal transfer when welding aluminum with GMAW?
|
spray metal transfer
120103h pg 24 |
|
|
What does a constant voltage power source offer GMAW when welding aluminum?
|
stable arc characteristics
120103h pg 24 |
|
|
What is the most common aluminum alloy for casting?
|
aluminum silicon alloy
120103h pg 13 |
|
|
What are wrought alloys made from?
|
Cast ingots
120103h pg 13 |
|
|
Name 2 forms wrought aluminum can be formed into.
|
–foil
–wires –sheet –tubes –plate –extruded shapes & forgings –bars 120103h pg 13 |
|
|
What welding current is used for welding aluminum?
|
DCEP
120103i pg 8 |
|
|
What can determine your arc length when welding aluminum?
|
Alloy group
120103i pg 8 |
|
|
What happens to water when welding aluminum?
|
water breaks down, the hydrogen enters the aluminum and causes porosity.
120103i pg 10 |
|
|
Is electrode extension as critical on aluminum as it is on steel? Why?
|
No. Due to high electrical conductivity of the aluminum
120103i pg 10 |
|
|
Due to higher travel speeds what may need to be longer when welding aluminum?
|
a larger gas nozzle
120103i pg 10 |
|
|
Aluminum oxide is a natural insulator. A) True B) False
|
A) True
120103i pg 5 |
|
|
What are the most common gasses you will use on aluminum with GMAW?
|
(inert gases) argon and helium
120103i pg 5 |
|
|
What does aluminum need to be cleaned with?
|
stainless steel wire brush
–power brush/stainless steel wire wool 120103i pg 5 |
|
|
What is 2 advantages of using GMAW on aluminum?
|
–higher deposition rates
–no flux or slag –reduced cleanup –can weld in all positions –works on materials as thin as 1/8” thick –spot welding works well on light gauge aluminum 120103i pg 2 |
|
|
How soon after the cleaning process should you weld an aluminum joint? Why?
|
As soon as possible. The aluminum oxide layer will rapidly return
120103i pg 7 |
|
|
Why must you apply light pressure only when cleaning aluminum?
|
To avoid embedding abrasive particles in the metals surface as this can result in weld contamination.
120103i pg 7 |
|
|
Why would you lightly preheat the aluminum before welding?
|
To remove traces of moisture
120103i pg 7 |
|
|
What are the two most common filler metals for aluminum?
|
4043 & 5356
120103i pg 2 |
|
|
What is one of the four filler alloys not recommended for sustained high temperature service?
|
5356
–5654 –5183 –5556 120103i pg 3 |
|
|
What are the three important dimensions on pipe?
|
–Outside Diameter (OD)
–Inside Diameter (ID) –Schedule (Wall Thickness) 120103j pg 2 |
|
|
At what size is a pipe identified by the outside diameter?
|
14” or larger
120103j pg 2 |
|
|
What is Tubing measured by?
|
The Outer Diameter
120103j pg3 |
|
|
What does the Wall thickness effect?
|
The heavier the wall thickness the smaller the ID
120103j pg 3 |
|
|
What is the included angle when fitting up pipe?
|
60°–75°
120103j pg 3 |
|
|
What should you ensure the land be on a pipe edge?
|
Uniform and accurate
120103j pg 4 |
|
|
What shape jig do you use to tack up pipe?
|
L shaped
120103j pg 5 |
|
|
What can be a problem with an L shape jig when tacking up pipe?
|
May not give good alignment of interior of the pipe.
120103j pg 5 |
|
|
What should you do if you find that the gap between two pipes is slightly unequal when tacking up?
|
rotate the pipe and tack the wider gap using the weld metal shrinkage to equalize the gap
120103j pg 6 |
|
|
What wedges useful for controlling when tacking up pipe?
|
gap spacing
120103j pg 6 |
|
|
When feathering the tacks on pipe what must you be careful about not doing? |
not making the root face thinner or the gap wider
120103j pg 7 |
|
|
Why must you feather permanent tacks?
|
Ensure full fusion when welding the root bead |
|
|
When welding a 2G weld why do you always start with the bottom weld and layer upwards?
|
It prevents weld metal from rolling down and causing overlap or lack of fusion. |
|
|
ASME certified companies must perform all welds how?
|
Using specific weld procedures
120103j pg 21 |
|
|
What does a Welding Procedure Specifications sheet provide welders with?
|
Directions for the welder to make repeatable quality welds of proven reliability while fulfilling all code requirements
120103j pg 21 |
|
|
What are three variables on a Welding Procedure Specification sheet?
|
–base metals
–filler metals –positions –preheat –postheat –joint configurations –techniques –any other details pertaining to the weld 120103j pg 22 |
|
|
What are three ranges documented on a Welding Procedure Specification sheet?
|
–Thickness |
|
|
What does is a WPS backed or supported by?
|
Procedure Qualification Record(PQR)
120103j pg 22 |
|
|
Name two processes of heat treating aluminum.
|
–Annealing
–Tempering –Solution heat treating –Homogenizing –Precipitation hardening –Refrigerating –Stabilizing –Stress relieving 120103h pg 20 |
|
|
What does a PQR State?
|
weld test specimen has been tested with WPS variables and consistently yields good welds
120103j pg 22 |
|
|
What are three SPECIFIC details on a WPS?
|
–Supporting PQR(s) |
|
|
Why is the Fill and Cap on a 5G weld completed up hill?
|
–Generally easier to get fusion
–fill and cap requires fewer passes reducing overall weld time 120103j pg 27 |
|
|
Why should the root weld on a 5G weld be done with a slight weave?
|
to control the puddle and obtain full fusion |
|
|
What is the correct placement of tacks for a 5G weld and what order do you put the tacks in at?
|
3,6,9,12(‘o’ clock)
180° from each other(12 then 6,3 then 9) 120103j pg 32 |
|
|
What is your inclination when welding a GMAW 2G pipe weld root pass?
|
15°–30° backhand with the electrode square to the root
120103j pg 9 |
|
|
What is the inclination on a fill and Cap GMAW 2G pipe weld?
|
0°–30° backhand or 0°–10° forehand
120103j pg 9 |
|
|
What inclination do you use on a 1G GMAW/FCAW/MCAW pipe root bead?
|
15°–30° backhand, square to the root with a slight weave
120103j pg 13 |
|
|
What inclination do you use on a 1G GMAW/FCAW pipe fill and cap?
|
15°–30° backhand with a slight weave
120103j pg 13 |
|
|
What inclination do you use on a 1G GMAW/MCAW pipe fill and cap?
|
0°–20° forehand, with a slight weave
120103j pg 13 |
|
|
What is the inclination of the root pass on a 2G GMAW/FCAW pipe weld?
|
15°–30° backhand, square to the root with a slight weave
120103j pg 19 |
|
|
What is the inclination of the fill & cap pass of a GMAW/FCAW pipe weld?
|
0°–30° backhand
120103j pg 19 |
|
|
When doing a 5G GMAW pipe weld what inclination do you use for the root pass?
|
5°–20° backhand
120103j pg 28 |
|
|
When doing a 5G GMAW pipe weld what inclination do you use for the fill & cap pass?
|
0°–20° backhand or 0°–10° forehand
120103j pg 28 |
|
|
What does SAW stand for?
|
Submerged Arc Welding
120103k pg 2 |
|
|
Why is a screw type work lead connection recommended for SAW?
|
provides a strong positive contact to the work and minimize heat build up
120103k pg 7 |
|
|
Name three components of a SAW welding head assembly?
|
–control unit
–variable speed electric motor and gear box –wire straightener –drive roll assembly –wire feed set–ups –torch assembly –flux feed and recovery system 120103k pg 9 |
|
|
How tight should you set your drive roll pressure?
|
wire feeds smoothly, yet will slip should a problem occur in the gun and cable assembly
120103k pg 11 |
|
|
What does Amperage control in SAW?
|
Penetration & burn off rate
120103k pg 16 |
|
|
What is voltage?
|
The force that overcomes resistance to allow amperage to flow
120103k pg 16 |
|
|
What does voltage have a major effect on?
|
The weld bead fluidity and stick–out
120103k pg 16 |
|
|
What does travel speed effect?
|
Penetration and weld bead profile
120103k pg 16 |
|
|
Decreasing travel speed increases what?
|
–increases heat input
–possibility of burn through 120103k pg 16 |
|
|
Increasing travel speed causes what?
|
–weld bead narrow
–greater penetration –possible undercut on at the toes of the weld 120103k pg |
|
|
What does the flux layer influence?
|
–Arc action
–bead appearance –weld metal soundness 120103k pg 17 |
|
|
What happens if the flux layer is too deep?
|
The arc will be too restricted(results in rough looking and ropy beads)
120103k pg 17 |
|
|
What happens if the flux layer is to shallow?
|
flashing, sputtering, and my lead to porosity
120103k pg 17 |
|
|
What is a general rule when setting the flux depth of SAW?
|
the appropriate depth is reached once the arc is fully submerged with no flashing
120103k pg 17 |
|
|
Where is the two thirds of the arc energy in DCEP?
|
In the base metal
120103k pg 18 |
|
|
Where is two thirds of the arc energy in DCEN?
|
in the electrode
120103k pg 18 |
|
|
What does using DCEP allow for?
|
–Deeper penetration
–slower welding speeds –narrower metal flow 120103k pg |
|
|
What does using DCEN allow for?
|
faster welding speeds
–shallower penetration –wider metal flow 120103k pg 18 |
|
|
What are three characteristics in the wire specifications?
|
–Chemistry and wire sizing
–testing requirements –identification and packaging –Cast and Helix –wire finish 120103k pg 20 |
|
|
What are two testing requirements for a SAW filler metal?
|
–chemical analysis
–radiographic acceptability –tensile strength –yield strength –ductility –impact values 120103k pg 20 |
|
|
What are solid electrodes classified based on?
|
as–manufactured chemical composition
120103k pg 23 |
|
|
What are composite electrodes based on?
|
Deposited chemistry in conjunction with a particular flux
120103k pg 23 |
|
|
What are fluxes classified on?
|
Weld metal properties obtained when used with specific electrodes
120103k pg 23 |
|
|
What is the main difference between the classification system of GMAW/FCAW/MCAW and SAW filler metals?
|
The SAW flux and electrode are identified together
120103k pg 23 |
|
|
In the AWS/CSA SAW filler metal classification system what does the ‘F’ stand for in F7A3–EL12K?
|
F indicates a submerged arc welding unit
120103k pg 24 |
|
|
In the AWS/CSA SAW filler metal classification system what does the ‘L’ stand for in F7A3–EL12K?
|
L indicates the manganese content
120103k pg 24 |
|
|
What should you consider when choosing SAW consumables?
|
–balanced chemical composition for use with the electrode
– required mechanical properties –the Flux/electrode combination must be usable –multi pass vs single pass flux selection –Flux meets wanted alloy additions 120103k pg 23 |
|
|
What fluxes can be reused in SAW?
|
fused Fluxes
120103k pg 28 |
|
|
What are bonded fluxes a mixture of?
|
finely divided oxides of two or more metal metals
120103k pg 28 |
|
|
Why are bonded fluxes not able to be reused in the SAW process?
|
The properties change drastically during welding
120103k pg 28 |
|
|
Do neutral fluxes significantly change a SAW weld chemical analysis?
|
No
120103k pg 29 |
|
|
In SAW the weld metal composition changes when what is varied?
|
Voltage
120103k pg 29 |
|
|
What do Alloy Fluxes contain?
|
Enough alloy metal in their composition to produce an alloy weld using a carbon steel electrode.
120103k pg 29 |
|
|
If manufactures specifications are followed how long can you store consumables in their packaging?
|
up to 6 months
120103k pg 29 |
|
|
Welding characteristics of the Flux may suffer in SAW if what occurs?
|
overheating
120103k pg 29 |
|
|
What are the specific problem areas often related with SAW equipment?
|
–correct setting of key variables
–contact tube condition –work lead condition –flux condition –flux feed and recovery 120103k pg 33 |
|
|
What is a possible cause of porosity with SAW?
|
–damp or dirty wire
–wet flux –contaminated flux 120103k pg 31 |
|
|
what is a possible cause of pock marks on the surface of a SAW weld?
|
–dirty wire
–insufficient deoxidizers in the wire or flux 120103k pg 31 |
|
|
Erratic arc when welding SAW can be cause by?
|
–dirty wire
–wet or oily flux –clogged conduit liner 120103k pg 31 |
|
|
OHS Stands for what?
|
Occupational Health and Safety
650101a pg 3 |
|
|
OHS provides workers with a what?
|
Minimum legal standard for workers health and safety
650101a pg 3 |
|
|
What are the three type of hazard controls?
|
engineering controls, administrative controls, Personal Protective Equipment
650101a pg 4 |
|
|
Define Engineering controls.
|
equipment engineered and implemented to reduce or eliminate exposure to chemical or physical hazards at the source.
|
|
|
Define administrative controls?
|
safe work practices, scheduling work to limit worker exposure to hazardous conditions or substances and safety policies and rules
650101a pg 4 |
|
|
Define personal protective equipment (PPE)
|
clothing and equipment designed to reduce your exposure to a known hazard.
650101a pg 4 |
|
|
What does Bill C–45 state?
|
The bill states that representatives must do everything reasonable to protect all workers from injury or death.
650101a pg 6 |
|
|
Who can face fine or imprisonment under Bill C–45?
|
Employers and/or their representatives
650101a pg 6 |
|
|
Your employer must set up safe work practices at the worksite and ensure that employees adhere to these practices. a)True b)False
|
a)True
|
|
|
Name two key responsibilities of the employee.
|
report any hazardous situations to the supervisor
–report all injuries immediately –wear all required PPE ensure in good condition –inspect all equipment, tools, and machinery before use –participate in regularly scheduled work site safety planning meetings –ensure you know and follow emergency procedures –do not perform any work you feel unsafe 650101a pg 9 |
|
|
What is the law that requires you to refuse unsafe work but prevents you from receiving disciplinary action by your employer.
|
The Occupational Health and Safety Act. 650101a pg 8
|
|
|
What can generic worker training include in regards to whimia?
|
a general introduction to WHMIS
Training on WHMIS labels and MSDSs training in information to workers health and safety on the job. 650101a pg 11 |
|
|
Your employer is responsible to provide training to all employees in what?
|
WHMIS training
650101a pg 12 |
|
|
What are the three elements of fire?
|
fuel
air ignition 650101a pg 12 |
|
|
Employees are responsible for what in regards to WHIMIS?
|
–participating in training
–using information obtained to protect yourself and others –applying workplace labels where and when required –demonstrating and applying safe work procedures 650101a pg 12 |
|
|
What do engineering controls include?
|
–elimination–––(Eli)
–substitution––(Says) –redesign–––––––(Run) –isolation–––––––(It) –automation––(Again) 650101a pg 19 |
|
|
What do administrative controls include
|
–safe work practices, job procedures, policies, rules
–work/rest schedules to reduce exposure –limiting hours of work –scheduling hazardous work to limit exposure to other workers –wet methods 650101a pg 19 |
|
|
Name two tools for assessing and controlling workplace hazards?
|
–hazard assessment reports
–checklists –health and safety plans –emergency response plans –first aid records and incident reports 650101a pg20 |
|
|
How long must an employer keep a first aid report?
|
three years
650101a pg 25 |
|
|
OHS requires an emergency response plan to be what?
|
in writing and available to workers.
650101a pg 26 |
|
|
What is the type of first aid equipment based on?
|
–how hazardous the work is
–time to the nearest health facility –number of workers each shift 650101a pg 27 |
|
|
What are 2 points to help keep your work place safe, clean and organized
|
collect and dispose of garbage
–store tools and machinery properly – Store supplies and materials properly –store hazardous materials securely –Sweep & Clean –wear PPE –wipe up all spills immediately –650101a pg 29 |
|
|
Your employer must ensure all workers wear and use the required PPE a)True b)False
|
b)True
650101a pg 32 |
|
|
Is your employer required to provide you with respiratory protective equipment
|
yes
650101a pg 40 |
|
|
What must your inspection of your harness ensure?
|
Free from substances that could cause it to fail. 650101b pg 6
|
|
|
Who is in charge of making sure you inspect your harness? |
Your employer
650101b pg 6 |
|
|
Any fall arrest that has stopped a fall can continue being used. a)True b)False |
b)false |
|
|
Where must you never work from on a ladder unless permitted by manufacture’s specifications?
|
the top two rungs |
|
|
What does the double stepladder have?
|
It has steps on both sides. 650101b pg 7
|
|
|
What are twin stepladders sometimes used in conjunction with?
|
planks or aluminum stages.
650101b pg 7 |
|
|
How do you determine the proper angle of a ladder?
|
1 horizontal length for every 4 vertical height
650101b pg 8 |
|
|
What is the minimum overlap of an extension ladder?
|
1 meter
650101b pg 8 |
|
|
Your employer under what regulation is required to train you in the safe operation of equipment?
|
OHS Regulation
650101b pg 11 |
|
|
Does Alberta have a law regulating the maximum weight a worker can lift?
|
No
650101b pg 14 |
|
|
What does rigging a load involve?
|
–the weight
–the centre of gravity –start location of the load –end location of the load 650101b pg 21 |
|
|
What is the safety ratio for general rigging and hoisting |
5:1
650101b pg 24 |
|
|
What is the safety ratio for lifting and transporting workers
|
10:1
650101b pg 24 |
|
|
What is the safety factor used for public elevators?
|
20:1
650101b pg 24 |
|
|
What causes shock loading?
|
any sudden movement of the load by the hoisting equipment.
650101b pg 24 |
|
|
What do load softeners do?
|
limits the possibility of kinking or cutting a sling.
650101b pg |
|
|
What will slings not do to polished or delicate surfaces?
|
Mar,deface or scratch
650101b pg 25 |
|
|
Slings are highly elastic which makes them better for absorbing what?
|
shock loads
650101b pg 25 |
|
|
What is a chains safety factor?
|
the comparison between minimum working load and working load limit.
650101b pg 28 |
|
|
What should the legs of a sling bridal never exceed?
|
45°
650101b pg 32 |
|
|
The steeper the angle on a bridal sling the higher the what?
|
higher the tension.
650101b pg 33 |
|
|
What must wire slings be inspected for?
|
–wear
–fatigued wire –crushed or broken wires –kinks –ballooning –bird caging –any sign of heat damage 650101b pg 29 |
|
|
Should damaged rigging equipment continue to be used?
|
No
650101b pg 29 |
|
|
If a sling shows signs of stretching what is to be done with it?
|
it should be discarded
650101b pg 30 |
|
|
What must chain hooks have stamped on them?
|
load ratings in tons.
650101b pg 30 |
|
|
What are some things to check for on links of a chain sling?
|
–kinked & gouged links
–bent links –twisted links –stretched link –lifted fins(fingernailing) 650101b pg 30 |
|
|
What are some things you should check for on a chain hook?
|
–cracks and twisting
–wear and deformation – signs of opening up –wear 650101b pg 30 |
|
|
What is centre of gravity?
|
point at which all an objects weight is considered to be concentrated.
650101b pg 33 |
|
|
What does centre of gravity influence when lifting?
|
influences the balance of the object.
650101b pg 33 |
|
|
What is the minimum lifting angle for sling legs?
|
60°
650101b pg 33 |
|
|
What four steps do you use to measure if your sling angle is acceptable?
|
1.measure the length of the sling legs an fittings
2.find the centre of gravity of the load 3.measure an equal distance on either side of the centre of gravity 4.position the sling legs to these two points before making the lift 650101b pg 33 |
|
|
What degree should an eyebolt be lifted at? why?
|
90°
the safe working load of an eyebolt is reduced when lifted at any other angle. 650101b pg 34 |
|
|
What is the most common type of shackle used?
|
anchor type with a screw pin
650101b pg 35 |
|
|
What are the 4 parts of a hook?
|
–eye
–neck –saddle –throat 650101b pg 36 |
|
|
What happens to the safe working load as the load is moved towards the hook tip?
|
it is reduced
650101b pg 37 |
|
|
If a chain hook is not fitted with a safety latch what must it have?
|
Mousing
650101b pg 37 |
|
|
What chain hooks are exempt from having a safety latches?
|
grab chains and sorting hooks
650101b pg 37 |
|
|
What are spreader bar used for?
|
–used to reduce severe sling angles
–provide safety for difficult lifts 650101b pg 38 |
|
|
Where are rope blocks typically used?
|
overhead hoists and cranes
650101b pg 39 |
|
|
What doe sheaves do on a wire rope block?
|
transfer the load from the rope to the centre pin and straps.
650101b pg 39 |
|
|
What situation is a snatch block used in?
|
Where the situation requires a change in direction of pull on a wire rope, but does not provide mechanical advantage
650101b pg 40 |
|
|
What is the sheave?
|
the part of the block that carries the rope
650101b pg 41 |
|
|
The OHS code provides requirements for operating equipment able to lift how much?
|
2000 kg or more (mobile cranes, boom trucks, and tower cranes)
650101b pg 43 |
|
|
Tag line enables what?
|
control to maneuver a load while keeping a safe distance
650101b pg 44 |
|
|
Where are taglines generally connected to a load?
|
to a corner of the load
650101b pg 44 |
|
|
A vertical hitch allows for what?
|
the load can equal the safe working load of the sling
650101b pg 44 |
|
|
What does a bridal hitch give you when the load is distributed equally among all sling legs?
|
excellent load stability
650101b pg 45 |
|
|
Where must the hook be over even if a load is not balanced?
|
over the centre of gravity
650101b pg 45 |
|
|
What is a double wrap basket hitch
|
where the sling is wrapped completely around the load
650101b pg 48 |
|
|
What is good about a double wrap basket hitch?
|
–makes 360° of contact
–pulls loads together 650101b pg 48 |
|
|
A double wrap basket hitch is good to move?
|
smooth material
–loose material –cylindrical objects (hydraulic cylinders or pipe) 650101b pg 48 |
|
|
Why is a single choker hitch not recommended for lifting loose bundles?
|
they do not make 360° contact with the load.
650101b pg 48 |
|
|
Which way should hooks be facing on a double choker hitch?
|
outward
650101b pg 49 |
|
|
Double wrap choker hitch tends to draw loads tightly together.
A)True B)false |
A) True
650101b pg 49 |
|
|
When is the signalman required to signal the operator?
|
–the operator cannot see the load or landing area
–its difficult for the operator to judge distance –boom within reach of electrical lines –operator does not have clear view of travel path 650101b pg 50 |
|
|
A signalman should what?
|
–have a clear view of the operator
–have a clear view of the object and it’s path –be out of the objects travel path 650101b pg 50 |
|
|
What does WHMIS stand for?
|
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System
650101c pg 2 |
|
|
What is WHMIS designed to ensure?
|
Designed to ensure workers have the information to safely work with hazardous materials at the workplace.
650101c pg 2 |
|
|
What is a controlled product?
|
any product, material, or substance that is identified in the Federal Government’s Controlled Products Regulations.
650101c pg 2 |
|
|
Suppliers, employers, and employees all have specific responsibilities under WHMIS to what?
|
Ensure those working with hazardous products are not only informed of the danger, but also informed of the precautions that need to be taken when working around these products.
650101c pg 2 |
|
|
The supplier is responsible, as a condition of sale to what?
|
–classify controlled products
–label controlled products –provide MSDS sheets 650101c pg 3 |
|
|
Name two things a suppliers label has on it?
|
–product identifier
–supplier identifier –hazardous symbols –statement that an MSDS is available –risk phrase –precautionary statement –first aid measures 650101c pg 3 |
|
|
What must employers ensure in regards to WHMIS responsibility?
|
–every container has a supplier or workplace label
–MSDS are readily available –workers are trained to understand the hazards and apply safe handling information provided 650101c pg 4 |
|
|
WHMIS training for employees must include how to?
|
–interpret supplier labels, workplace labels and MSDS
–safely handle, use and store controlled products used in the workplace –safely dispose of used controlled products –respond to a spill or leak of a controlled product –interpret visible identification systems 650101c pg 4 |
|
|
In terms of WHMIS an employee is responsible to what?
|
–participate in WHMIS training
–use information obtained to protect yourself and others –prepare and apply workplace labels where and when required –report where labels have become detached, damaged or unreadable. 650101c pg 4 |
|
|
When dangerous goods are being transported what regulations apply?
|
Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations
650101c pg 5 |
|
|
What is a class A hazard?
|
Compressed gas
650101c pg 6 |
|
|
What is the best protection to keep toxic chemicals out of the body?
|
by handling them properly.
650101c pg 15 |
|
|
What are the three key elements of WHMIS?
|
–Worker education,
–product labeling –Material Safety data sheets(MSDS) |
|
|
Is your employer responsible to test your WHMIS knowledge?
|
yes
650101c pg 17 |
|
|
What are the four characteristics of a supplier label?(shape,color,etc.)
|
–Identifiable cross–hatched boarder
–label must be a different color from the container –size should be appropriate – text must be in English & French 650101c pg 18 |
|
|
When is a workplace label not required on a container(transferred from supplier container)?
|
–when the containers substance is being used by one employee
– will be used up by the one employee within the one work shift 650101c pg 19 |
|
|
Whose responsibility is it to ensure the correct information is put on a workplace label?
|
the employee
650101c pg 19 |
|
|
Who must provide an MSDS sheet?
|
the supplier
650101c pg 22 |
|
|
How old can an MSDS Sheet be?
|
No more than three years old
650101c pg 22 |
|
|
When gas cylinders are not in a transport cart or being used where should be?
|
Secured to a wall or storage compartment.(must have valve cover installed)
650101c pg 28 |
|
|
A gas storage container must be what?
|
–secured to prevent dislodging
–adequate ventilation 650101c pg 28 |
|
|
Where should flammable liquids or compressed gas not be transported ever?
|
The cab or trunk of any vehicle.
650101c pg 28 |
|
|
In most welding shops, the ventilation system should change the air how many times per hour?
|
four time
650101c pg 31 |
|
|
What does a flexible ducting system allow?
|
Allows you to position the hood in the most effective position to remove fumes.
650101c pg 32 |
|
|
What happens to the risk of explosion when working in containers, vessels, or confined spaces?
|
Increases dramatically.
650101c pg 34 |
|
|
What do portable gas detectors do?
|
Monitors the air continually.
650101c pg 35 |
|
|
What must a watch person do?
|
must see and communicate with you
–must be able to implement the rescue plan 650101c pg 35 |
|
|
What are Class A fires?
|
Wood and paper
650101c pg 38 |
|
|
What are Class B Fires?
|
Flammable liquids
650101c pg 38 |
|
|
What are Class C fires?
|
Electrical equipment
650101c pg 38 |
|
|
What are class D fires?
|
Combustible metals |
|
|
What are class K fires?
|
Combustible cooking media |
|
|
What class of fire is each method good for?
a)water b)foam d)CO2 c)Regular dry chemical d)Purple k dry chemical e)multi purpose dry chemical f)Dry powder g)Wet chemical |
a)A
b)A,B c)B,C d)B,C e)B,C f)A,B,C g)D h)K 650101c pg 41 |
|
|
What does PASS stand for?
|
–Pull the pin
–Aim –Squeeze –Sweep 650101c pg 44 |
|
|
What is the Alberta Industry training Boards primary responsibility?
|
Establishing the standards and requirements for training and certification in programs.
650401a pg 3 |
|
|
What are two principles of the board
|
–Accessible
–Funded by all –Industry Driven –supported by Government –Collaborative –Integrated 650401a pg 5 |
|
|
What is a post secondary institution roll in the apprenticeship program?
|
To deliver technical training as described in the course outline established by the industry.
650401a pg 8 |
|
|
What does PAC stand for?
|
Provincial Apprenticeship Committee
|
|
|
What do PACs do?
|
Monitor the activities of local apprenticeship committees in their trade
650401a pg 9 |
|
|
What are PACs responsible making recommendations to the board about?
|
Training and certification requirements and standards for their trade.
650401a pg 9 |
|
|
What does LAC stand for?
|
Local Apprenticeship committees
650401a pg 10 |
|
|
Disputes between an apprentice and employer that cannot be handle by an apprenticeship client service consultant are handled by who?
|
Local apprenticeship committee.
650401a pg 10 |
|
|
What do LACs make recommendations to the board about?
|
The appointment of members to their trade’s PAC’s
650401a pg 10 |
|
|
What are the three types of radiant energy?
|
–visible light
–ultraviolet rays –infrared rays 120101e pg 2 |
|
|
What is arc flash?
|
When your eyes are burned by ultraviolet rays.
120101e pg 2 |
|
|
What is another name for arc flash?
|
–welding flash
–arc eye 120101e pg 2 |
|
|
Why should you see a specialist after arc flash occurs?
|
to make sure no foreign objects lodged in your eyes.
120101e pg 3 |
|
|
What can overexposure to ultraviolet radiation lead too?
|
Skin cancer
120101e pg 3 |
|
|
What effect can extended exposure to infrared rays do to your eyes?
|
Can cause Cataracts
120101e pg 3 |
|
|
What is a common cause of deep burns?
|
metal at temperatures lower than red hot
120101e pg 5 |
|
|
What should all metal surfaces be treated as?
|
a possible source of burns(HOT)
120101e pg 5 |
|
|
What is the rule of metal in a shop?
|
–treat everything as
–mark as all hot metal as HOT 120101e pg 5 |
|
|
What do you do if your clothing catches fire?
|
Stop, Drop, & Roll
120101e pg 5 |
|
|
What is noise defined as?
|
Unwanted noise
120101e pg 6 |
|
|
What are major contributors to hearing loss?
|
–work site overall noise level
–frequency distribution of the noise –duration of the noise exposure during the work day –time distribution of the noise exposure –susceptibility of the individual to noise–induced hearing loss 120101e pg 6 |
|
|
What are the two warning signs of high noise levels?
|
–you have to raise your voice to a person a meter or less away
–you develop a ringing or buzzing sound in your ears 120101e pg 7 |
|
|
What is the decibel level of:
a)conversational speech b)riveting a steel tank c)Jet plane |
a)65
b)130 c)140 120101e pg 7 |
|
|
What is the maximum amount of time you can be exposed to:
a)100 dBA b)112 dBA c)115 dBA |
a)15 mins
b)56 sec c)0 seconds |
|
|
What is the maximum permitted sound level for an 8 hour day?
|
85 dBA
120101e pg 8 |
|
|
If after cutting or welding
A)You see light spots your lens is to what? B)You see dark spots your lens is to what? |
A)light
B)Dark 120101e pg 10 |
|
|
What do you want your welding shade to do?
|
eliminate glare but allow you to see your work distinctly
120101e pg 11 |
|
|
What does the gasket help prevent the filter plate from doing? How?
|
Cracking
provides an air space 120101e pg 12 |
|
|
What do the clear plate on the outside and inside of the filter plate do?
|
–protect the filter plate from slag and spatter
–protects you if the plate shatters 120101e pg 12 |
|
|
Excessive heat to concrete floors can cause it to what?
|
Explode
120101e pg 13 |
|
|
What can leathers lead to in warm weather?
|
over heating
120101e pg 14 |
|
|
Why should you not wear synthetic such as polyester and nylon?
|
tends to melt can possible catch fire and melt to your skin
120101e pg 15 |
|
|
What does a face piece?
|
a close seal to the face
120101e pg 16 |
|
|
What respirator is a close seal to the face important for?
|
negative pressure respirators
120101e pg 16 |
|
|
If there is more than one user of a respirator what should you do to it before using it?
|
Disinfect it
120101e pg 16 |
|
|
Where should airline respirators be used?
|
Oxygen deficient atmospheres and where toxic gas is
120101e pg 18 |
|
|
What can cadmium fumes cause?
|
kidney damage and emphysema
120101e pg 21 |
|
|
What is Occupational exposure limit?
|
maximum concentration of a hazardous substance that a healthy person can be exposed to without suffering adverse health effects
120101e pg 23 |
|
|
What is the maximum ppm of H2S per 8 hours of exposure?
|
10 ppm
120101e pg 24 |
|
|
At what level can H2S cause immediate unconsciousness and can result in death?
|
700 ppm(0.07%)
120101e pg 25 |
|
|
What is a ground fault circuit interrupter?
|
a device that senses when current is traveling through a body and breaks that circuit in 1/40 of a second
120101e pg 31 |
|
|
what are the major electrical rescue procedures?
|
–alert the proper autorities
–act quickly –do not touch the victim –use adequate insulation if conductor must be moved –make sure people at heights don't fall –in a confined space the walls or floor may conduct electricity 120101e pg 31 |
|
|
When locking out something what does the tag do?
|
shows the owners name and date the lock was put on
120101e pg 32 |
|
|
Who is the only person allowed to remove a lockout?
|
the person who put it on
120101e pg 33 |
|
|
What must you be aware of no matter where you work?
|
hazards around you(flammables or energized equipment)
|
|
|
How long must a fire watch person stay after work is completed?
|
Sixty minutes
120101e pg 36 |
|
|
When welding in a confined space the hazards what?
|
Increase (heat, noise, suffocation, electric shock, etc.)
120101e pg 38 |
|
|
Where should torches be ignited when working inside a confined space?
|
outside
120101e pg 38 |
|
|
Why should you use extreme caution when working on boxed in pipe or tubing or equipment frames?
|
build up of oil can form an explosive mixture
120101e pg 39 |
|
|
What is the cheapest method of rendering a container safe?
|
steaming
120101e pg 40 |
|
|
What are the three methods of rendering a container safe?
|
–boiling in a caustics solutions
–inert gas purging –steaming 120101e pg 40 |
|
|
When should a container be welded after being steamed?
|
right away
120101e pg 41 |
|
|
If steaming is stopped for any reason what must happen before you can start again?
|
you must wait for the container to completely cool
120101e pg 42 |
|
|
What should you do before you ever start any process on a container?
|
use a sniffer to check for gasses in the container
120101e pg 42 |
|
|
Testing work atmosphere is the responsibility of who?
|
the employer (istruments must be designed for the job)
120101e pg 44 |
|
|
When can a worker be under a suspended load?
|
when the load is supported by a vehicle hoist or stand or blocks designed for that purpose
|
|
|
A portable ladders base must be no further from the base of a wall than?
|
one quarter of the distance between the base of the latter and the point where the ladder contacts the wall
120101e pg 45 |
|
|
A portable ladders side rails must extend at least how far above the work surface?
|
1 meter
120101e pg 45 |
|
|
A cylinder of flammable gas cannot be stored in the same room as what?
|
compressed cylinder of oxygen
120101e pg 46 |
|
|
All oxygen fittings must be kept clean of what?
|
oil and grease
120101e pg 46 |
|
|
An employer must ensure everything done to/with welding or allied equipment is done in accordance to who’s specifications?
|
Manufactures
120101e pg 47 |
|
|
An employer is responsible for checking for what on gas equipments immediately after its hooked up?
|
leaks
120101e pg 47 |
|
|
Gas cylinders should be stored in solid walled storage compartments.
a)True b)False |
a)True
120101e pg 47 |
|
|
What is the allowable distance of top guardrail from the ground?
|
920mm–1070mm
120101e pg 50 |
|
|
A grinder must be equipped with a what?
|
a grinding guard
120101e pg 51 |
|
|
A grinding wheels _______ must be equal to or greater than a grinders ______.
|
Revolutions Per Minute
120101e pg 51 |
|
|
A tool rest on a fixed grinder must be within what distance of the grinding wheel?
|
3mm
120101e pg 51 |
|
|
Where in relation to the centre of the wheel on a fixed grinder should the guard sit?
|
at or above the centre line
120101e pg 51 |
|
|
Before starting any task what should you ensure?
|
–A safe work environment
–appropriate PPE –work area cleanliness – right tool for the job –good working condition of tools 120101f pg 2 |
|
|
When does personal injury and damage to equipment occur?
|
when tools are used improperly
120101f pg 2 |
|
|
what are making sure your hammer is before you use it?
|
–clean
–crack free –tight to the head 120101f pg 2 |
|
|
Should you ever strike a hardened object directly with a hammer?
|
No use a softener such as wood
120101f pg 2 |
|
|
Screw drivers should not be used as a pry bars or chisels.
a)True b)False |
a)True
120101f pg 2 |
|
|
How should a screwdriver fit into a screw?
|
Snugly
120101f pg 2 |
|
|
What should you do to a chisel with a mushroomed head?
|
Grind away the mushroomed head before the chisel splits
120101f pg 3 |
|
|
Why should you always use a handle on a file?
|
To avoid injury to your hand
120101f pg 3 |
|
|
How much pressure should you apply to a file and why?
|
enough to keep the file cutting to reduce wear on the file
120101f pg 3 |
|
|
Should you use a file as a pry bar?
|
No
120101f pg 3 |
|
|
How many teeth on a hacksaw should be in contact with the material at all times?
|
2 teeth
120101f pg 3 |
|
|
What lengths are straight edges generally?
|
305mm–3m(1’–10’)
120101f pg 7 |
|
|
What length do short length tapes go up to?
|
8 meters(25’)
120101f pg 7 |
|
|
What two lengths do long tapes generally come in?
|
–15m(50’)
–30m(100’) 120101f pg 7 |
|
|
What is the tang on a tape measure? Why is it loose?
|
It is the hook. It is loose so it can measure if being pushed against something or pulled from the outside(it allows for the tangs thickness in the measurement)
120101f pg 8 |
|
|
What is the most common carpenters squares?
|
2 foot carpenters square
120101f pg 8 |
|
|
What does a Try square consist of?
|
–a beam (a thick wood or metal stock) |
|
|
What are the 4 parts of a combination square?
|
–a steel ruler
–a square head –a bevel protractor –centre head 120101f pg 10 |
|
|
Why must a level be truly horizontal or truly vertical?
|
any tilting of the level causes the bubble to move off centre
120101f pg 12 |
|
|
What does the magnetic base on the level allow for?
|
allows the operator the use of both hands for other tasks
120101f pg 12 |
|
|
How many times should a wraparound be able to go around the pipe?
|
twice to ensure the edge is lined up.
120101f pg 13 |
|
|
What are trammel points used for?
|
used to scribe arcs and circles and to transfer measurements that are beyond the range of dividers
120101f pg 17 |
|
|
The point of a center punch is accurately ground in line with the shank to what included angle?
|
90°
120101f pg 18 |
|
|
What angle is the point of a prick punch ground to?
|
30°–60°
120101f pg 18 |
|
|
How does a prick punch differ from a centre punch?
|
–a prick punch is generally smaller, and its point angle is sharper
120101f pg 18 |
|
|
What determines the size of a C–clamp?
|
The maximum distance between the jaws when the Jaws are fully open
120101f pg 22 |
|
|
What is a bar clamp useful for?
|
clamping materials over longer distances.
120101f pg 22 |
|
|
What are soft Jaws?
|
Soft jaws are jaws made of aluminum, copper, or wood to used to avoid serration bite marks
120101f pg 25 |
|
|
What should you always do to a drill press vise before drilling?
|
clamp it down.
120101f pg 26 |
|
|
What is a 14 teeth per inch hack saw blade meant for cutting?
|
machined steel, cold rolled steel or structural steel
120101f pg 28 |
|
|
What is a 18 teeth per inch hack saw blade meant for cutting?
|
aluminum, tool steel, high speed steel and cast iron
120101f pg 28 |
|
|
What is a 24 teeth per inch hack saw blade meant for cutting?
|
tin, brass, copper, channel iron & sheet metal
120101f pg 28 |
|
|
What is a 32 teeth per inch hack saw blade meant for cutting?
|
thin–walled tubing and conduit and sheet metal thinner than 18 gauge
120101f pg 28 |
|
|
What is the set? What does it allow for?
|
The set is the where the teeth are bent slightly outward on a saw blade.
Allows clearance of the saw blade inside the Kerf 120101f pg 29 |
|
|
What are files classified by?
|
Their length, shape and cut
120101f pg 30 |
|
|
When using a hacksaw what are the important steps?
|
–Be sure the work is gripped tightly
–Start cutting on the widest surface of the work –At the end of the stroke relieve pressure and pull straight back –After the first few strokes make each one long as possible –when you are cutting very thin material clamp it between two pieces of wood or soft metal 120101f pg 30 |
|
|
What is the primary danger when using a hacksaw?
|
Injury to the hand when the blade breaks
120101f pg 30 |
|
|
What File produces a smooth finish?
|
single–cut files
120101f pg 31 |
|
|
Why do you use a handle on a file?
|
To prevent the tang from driving into your hand
120101f pg 32 |
|
|
What do you use to clean a file?
|
A course bristle brush
120101f pg 32 |
|
|
Why should you never drag a file backward over a work piece?
|
It breaks the teeth
120101f pg 33 |
|
|
What can happen if you use a file as a pry bar?
|
The chisel can shatter and cause major personal injury
120101f pg 33 |
|
|
What are Serrated Blades snips able to do better than Tinners’ snips?
|
cut smaller and more intricate patterns.
120101f pg 35 |
|
|
what are the three guidelines when using a screwdriver?
|
–Never work with a screwdriver pointed towards you
–never use a screwdriver as a chisel, pry bar or wedge –never hammer on a screwdriver handle 120101f pg 40 |
|
|
Is a adjustable designed to replace open–end or box–end wrenches?
|
No
120101f pg |
|
|
When is the only time you should use an adjustable wrench?
|
When the proper sized wrench is not available.
120101f pg 44 |
|
|
What is an adjustable wrench size determined by?
|
The total length of the wrench
120101f pg 44 |
|
|
What is the advantage of aluminum handled pipe wrenches?
|
They are lighter then conventional drop–forged steel pipe wrenches
120101f pg 46 |
|
|
Grinding wheels should be free of what?
|
cracks and other defects (ring test)
120101g pg 2 |
|
|
Why do you not grind on the side face of a pedestal wheel or zip disk?
|
the wheel can explode
120101g pg 2 |
|
|
What should you always have on when working with a portable grinder?
|
the spark guard and handle
120101g pg 3 |
|
|
What is the most common grinding wheel size range for pedestal grinders?
|
203mm–355mm(8”–14”)
120101g pg 3 |
|
|
Bench grinders are generally use wheels up to what size?
|
175mm(7”) in diameter
120101g pg 4 |
|
|
How mush of the wheel should a wheel guard on a bench grinder cover?
|
At least 2/3 of the wheel (extend 30°–45° past the horizontal plane)
120101g pg 4 |
|
|
How far should the tool rest be sitting away from the face of the grinding wheel?
|
3mm(1/8”)
120101g pg 5 |
|
|
What are grinding wheels classified by?
|
Abrasives type and size
120101g pg 5 |
|
|
What is the most common abrasive when grinding steel?
|
Aluminum oxide
120101g pg 5 |
|
|
What is the most common bonding agent for grinding wheel?
|
clay based(sometimes called vitrified)
120101g pg 5 |
|
|
What are abrasives available in other than oxides?
|
Grits (comes in 4–600)(most shops 24–60)
120101g pg 5 |
|
|
What is a blotter?
|
pieces of heavy paper attached to each side of the grinding wheel
120101g pg 5 |
|
|
What three things does the blotter do?
|
–protects the flanges
–compensate for uneven surfaces on the side of the wheel –display important information about the wheel(RPM,Size,type,etc.) 120101g pg 5 |
|
|
What is Dressing a wheel?
|
cleaning & restoring the sharpness of a wheel
120101g pg 6 |
|
|
What is Truing of a grinding wheel?
|
removal of material from the cutting face of a wheel if it is out of round in some way
120101g pg 7 |
|
|
What are some things you must do when replacing a grinding wheel?
|
–select suitable grinding wheel
–check rpm rating –Inspect the wheel for visible defects –ring test –wheel should fit shaft –place safety washers –steel flange is flat –nut tight enough to hold wheel –replace wheel guard –run at full speed for one minute –true the wheel if required 120101g pg 8 |
|
|
What are the two types of portable grinders?
|
straight and angle
120101g pg 8 |
|
|
What are small straight grinders also known as?
|
Die grinders
120101g pg 8 |
|
|
For flat or surface grinding what angle do you hold the grinder?
|
10°
120101g pg 11 |
|
|
When grinding how much pressure should you use?
|
equal to the weight of the grinder or slightly more
120101g pg 11 |
|
|
When close tolerance grinding is required what technique can you use? What does this technique allow you to see?
|
–cross grinding(changing 90° every pass)
–allows you to see every pass 120101g pg 11 |
|
|
What is a sensitive drill press meant for?
|
Drilling precise holes up to approximately 12.7mm(1/2”) in diameter
|
|
|
How does an upright drilling machine differ from a sensitive drilling machine?
|
larger and has a power feed system
120101g pg 15 |
|
|
What is an upright drilling machine meant for drilling?
|
12.7mm(½”)–101.6mm(4”) holes120101g pg 16
|
|
|
What does an upright drilling machine usually have that allows for slow speed high torque?
|
a Geared head
120101g pg 16 |
|
|
What are hand drills rated by?
|
their chuck size
120101g pg 13 |
|
|
What does a magnetic base drill allow for?
|
operation in any position(use a lanyard in positions other than Flat) on material with magnetic properties
120101g pg 16 |
|
|
What are Radial drilling machines used for?
|
Drilling holes in large work pieces that are to difficult to position under the sensitive or upright drill press
(position spindle anywhere within a certain radius) 120101g pg 17 |
|
|
What are the two methods of manual feed on a radial arm drill press?
|
–hand feed lever(drilling head)
–hand wheel(underside)(mechanical advantage & fine feed control) 120101g pg 17 |
|
|
What are the three types of drill chucks?
|
–keyed drill chucks
–keyless chuck –drill socket and sleeve 120101g pg 18 |
|
|
What size do key type chucks normally come in?
|
6.4mm–19.2mm(¼” to ¾”)
120101g pg 19 |
|
|
Where are keyless chucks normally found?
|
battery powered hand drills
120101g pg 19 |
|
|
Name one advantage of a drill chuck?
|
–hold any number of things within its size range
–used with twist drills that have straight shanks –wide range of accessories 120101g pg 20 |
|
|
What are the three main parts of a twist drills?
|
–the shank
–the body –the point 120101g pg 21 |
|
|
Where are taper shanks found?
|
Found on drills 12.7mm(½”) in diameter
120101g |
|
|
How is a taper shank twist drill from a drill sleeve?
|
a wedge shaped drift tool is driven into a slot just above the tang of the twist drill
120101g pg 21 |
|
|
Where is the diameter of a twist drill measured?
|
measured across the margins
120101g pg 22 |
|
|
What are the four methods used to designate twist drill sizes?
|
–number
–letter –fractional –metric 120101g pg 23 |
|
|
What degree should the lip clearance be on a twist drill?
|
8 to 12 degrees
120101g pg 24 |
|
|
What are the three safety precautions when using grinders?
|
–wear safety glasses
–Ensure appropriate grinding wheel –ensure tool rest and guards are properly adjusted 120101g pg 25 |
|
|
What are two ways to modify a drill point?
|
–change the point angle and clearance angle
–thin the chisel edge 120101g pg 26 |
|
|
What is a common ratio for a cutting Lubricant?
|
one part oil to 25 parts water
120101g pg 27 |
|
|
what is the primary function of plate rolls?
|
Roll flat stock into cylindrical and oval shapes
120101g pg 28 |
|
|
what is a power break used for?
|
Bending material at sharp angles using various combinations of rams and dies
120101g pg 30 |
|
|
why do you always attach the ground clamp directly to the material in a machine?
|
to prevent any electrical current from passing through any bearings or bushings on the machine
120101g pg 30 |
|
|
What is a power bender used to bend?
|
–pipe
–bar stock –structural shapes 120101g pg 31 |
|
|
Where do power benders have an advantage?
|
Where multiple compound bends are required
120101g pg 31 |
|
|
What are presses useful for?
|
–bending and straightening metal
–pressing bearings and gears onto and off of shafts 120101g pg 31 |
|
|
Why would you use a cage with a hydraulic press?
|
to minimize the kick out hazard
120101g pg 32 |
|
|
Pneumatic presses are dangerous due to what?
|
the ram generally moves very fast
120101g pg 32 |
|
|
What press has the highest capacity?
|
Electric presses
120101g pg 32 |
|
|
What are trip hammers used for?
|
shape metal (sharpening of bucket and ripper teeth)
120101g pg 33 |
|
|
What is a chipping guns and impact guns a related version of?
|
a trip hammer
120101g pg 33 |
|
|
What are the two common plate shears?
|
–mechanical shears
–hydraulic shears 120101g pg 34 |
|
|
What are mechanical shears powered by?
|
An electric motor power a large flywheel to perform the cutting operation
120101g pg 34 |
|
|
How often is the hold down device tightened on mechanical shears? what does this prevent?
|
–tightened for each cut
–prevents shear blade breakage 120101g pg 34 |
|
|
How do hydraulic shears differ from mechanical shears?
|
hold downs are run by hydraulic rams
–shear blades are powered by hydraulic pump 120101g pg 35 |
|
|
On hydraulic shears when you adjust the blade clearance what are you adjusting for?
|
Material thickness and type
120101g pg 35 |
|
|
What three processes does an ironworker machine do?
|
–punching
–shearing –notching 120101g pg 36 |
|
|
What can an Ironworker be run by?
|
hydraulic ram or large flywheel
120101g pg 36 |
|
|
What material is an Ironworker designed to work on?
|
–mild steel
–annealed medium carbon steel and abrasion resistant steels(within limits) 120101g pg 36 |
|
|
What are the three steps to consistent shearing?
|
–place material
–place the hold–down –depress the foot pedal 120101g pg 37 |
|
|
What is a rod shear used for?
|
cutting round bar and square bar stock
120101g pg 37 |
|
|
What are the two type of shape shears?
|
L and C shape shears
120101g pg 37 |
|
|
what are cut off saw used for?
|
for square or miter cutting on structural shapes and smaller diameter pipe
120101g pg 39 |
|
|
How should you clamp L shapes when cutting?
|
clamp so one side is against the stationary block
120101g pg 39 |
|
|
How high should vertical band saw guides be set above the work?
|
so they just clear the work piece
120101g pg 41 |
|
|
What are the three most common positioners?
|
–manual
–power –turning rolls 120101g pg 43 |
|
|
Is oxygen by itself flammable?
|
No
120101h pg 2 |
|
|
What process produces oxygen for cutting?
|
air liquefaction
120101h pg 2 |
|
|
What two thing does air liquefaction produce?
|
nitrogen and oxygen
120101h pg 2 |
|
|
What is the minimum percentage is the pure oxygen is produced through air liquefaction?
|
Minimum 99.5%
120101h pg 2 |
|
|
Oxygen + oil = ?
|
EXPLOSION
120101h pg 3 |
|
|
In the case of a fire what order should you shut gases off?
|
stop the Oxygen
stop the fuel gas (then extinguish the Fire) 120101h pg 3 |
|
|
What are you causing the metal to do at a rapid rate when cutting with OAC?
|
Rust
120101h pg 3 |
|
|
At what percentage can you smell acetylene?
|
1%
120101h pg 3 |
|
|
How is acetylene produced?
|
mixing calcium carbide and water in an acetylene generator
120101h pg 3 |
|
|
How does oxygen effect your flames heat?
|
the more oxygen the hotter the flame
120101h pg 3 |
|
|
Where should your flames inner cone be positioned when cutting?
|
just above the surface of the material to be cut
120101h pg 3 |
|
|
What must a suitable flame have to be used for cutting and heating?
|
–high flame temperature
–high rate of flame propagation –adequate heat content –little to no chemical reaction with the base metal 120101h pg 4 |
|
|
what is the explosive range of acetylene in air?
|
2.5%–80%
120101h pg 4 |
|
|
what is the critical point of acetylene at 21.0°C?
|
193kPa(28psi)
120101h pg 4 |
|
|
what is the max safe working load pressure of acetylene gas?
|
103kPa(15psi)
120101h pg 5 |
|
|
The high BTU content makes propane good for what?
|
cutting materials 150mm(6”) or greater
120101h pg 5 |
|
|
Propane requires how many times its volume of preheat oxygen during cutting?
|
4–4½ times
120101h pg 5 |
|
|
What volume of oxygen to propylene is required for a neutral flame?
|
2.6 to 1
120101h pg 6 |
|
|
Why is natural gas used for cutting?
|
low cost and readily available
120101h pg 6 |
|
|
What does a liquid oxygen tank pressure rarely exceed?
|
1655kPa(240psi)
|
|
|
How does a small and large cylinders pressure and volume generally line up?
|
same pressure but different volume
120101h pg 8 |
|
|
What do you mark on an empty tank?
|
MT
120101h pg 8 |
|
|
How long till the first time a cylinder is tested after being used in the industry? How often after that?
|
10 years
every 5 years after its first test 120101h pg 8 |
|
|
What process is use to test oxygen cylinders?
|
hydrostatically tested
120101h pg 8 |
|
|
What hand threads are oxygen tanks?
|
right handed
120101h pg 9 |
|
|
Do oxygen tanks have a fixed draw limit?
|
No
120101h pg 9 |
|
|
What does a metal rupture disk protect against?
|
Extreme pressure rise due to fire
120101h pg 11 |
|
|
At what pressure does a rupture disk burst?
|
22 063kpa (3200psi)
120101h pg 11 |
|
|
What has the ability to stabilize acetylene?
|
acetone
120101h pg 12 |
|
|
Why is acetylene mixed with acetone?
|
to store acetylene safely under pressure
120101h pg 12 |
|
|
What is the purpose of the porous material in the acetylene tank?
|
to keep the acetylene dissolved in the acetone
120101h pg 12 |
|
|
What does the calcium–silicate cause?
|
lighter cylinder weight and increased cylinder capacity
120101h pg 12 |
|
|
At what percentage of volumetric capacity is an acetylene cylinder weighed and stamped?
|
40%
120101h pg 13 |
|
|
What are the two types of valves?
|
–key type(requires a T wrench)
–wheel type 120101h pg 14 |
|
|
What is the only accurate method of determining how much acetylene is left in the cylinder?
|
Weighing it
120101h pg 15 |
|
|
What is the draw limit of an acetylene cylinder? Why?
|
No faster than 1/7 of it volumetric capacity per hour
To prevent drawing of acetone 120101h pg 15 |
|
|
When using a manifold system what must the cylinder be?
|
of equal pressure
120101h pg 17 |
|
|
What is a acetylene manifold system filled with to break down the large volumes?
|
–stainless steel welding rod
–steel shot –silica sand 120101h pg 17 |
|
|
What name must appear on a gas cylinder?
|
The trade name or chemical name of the gas
120101h pg 18 |
|
|
What must fittings on acetylene equipment be made of?
|
–yellow brass
–iron –steel (as approved by CGA) 120101h pg 18 |
|
|
What two things does a regulator do?
|
reduce the source pressure to a working level
–maintain a constant delivery pressure 120101h pg 20 |
|
|
What are the three main parts of a regulator?
|
–spring
–diaphragm –valve/seat assembly 120101h pg 21 |
|
|
What are regulators classified by?
|
–service(acetylene or oxygen)
–type(single or two stage) 120101h pg 21 |
|
|
What can sudden pressure do to a bourdon tube?
|
deform it
120101h pg 24 |
|
|
What do the two gauges on most regulators tell you?
|
–cylinder pressure
–working pressure 120101h pg 24 |
|
|
What is the minimum bursting pressure of oxyfuel cutting hoses?
|
2800kPa(400psi)
120101h pg 25 |
|
|
what color are? a)fuel gas hoses
b)oxygen hoses |
a)red
b)green 120101h pg 26 |
|
|
what is regulator Creep?
|
when the valve on the high pressure side does not seat properly
120101h pg 29 |
|
|
Tips should never be?
|
–reamed
–used as hammers –bent to form a new angle –overheated 120101h pg 30 |
|
|
What are three basic malfunctions with oxyfuel equipment?
|
–backfires
–burnbacks –flashbacks 120101h pg 35 |
|
|
Name two things that can cause a backfire?
|
–to little gas speed
–a dirty tip –partial obstruction of gas flow –loose or faulty seat connections –a hot tip 120101h pg 36 |
|
|
What three things can cause a burnback?
|
–a hot tip
–tip orifices are enlarged –faulty torch body seats 120101h pg 36 |
|
|
What can cause a flashback?
|
–Grossly unequal pressure
–mildly unequal pressure –faulty manipulation of the valves –failure to purge each hose 120101h pg 37 |
|
|
What is gas speed?
|
Speed at which premixed gases leave the tip
120101h pg 38 |
|
|
What is speed of flame propagation?
|
The speed at which the flame travels or spreads in premixed gases
120101h pg 38 |
|
|
What are the three flame types?
|
–carbonizing flame
–neutral flame –oxidizing flame 120101h pg 40 |
|
|
What is the temperature of a neutral flame?
|
3090°C(5600°F)
120101h pg 40 |
|
|
What is the kindling point range of most steels?
|
760°C–870°C(1400°F–1600°F)
120101i pg 2 |
|
|
What is Drag?
|
The amount the bottom of the kerf line lags behind the top of the kerf line
120101i pg 2 |
|
|
What is heat energy(heat value or heat of combustion)?
|
Overall heat a flame produces
120101i pg 2 |
|
|
What is heat energy measured in?
|
–Mega–joules per cubic meter (MJ/m3) |
|
|
What is Kerf?
|
the width of the cut produced during a cutting process
120101i pg 2 |
|
|
What is torch inclination?
|
The angle of the torch in relation to the direction of travel
120101i pg 2 |
|
|
What are the three categories of oxyfuel equipment?
|
–combination welding and cutting
–standard or heavy duty cutting torches –machine cutting torches 120101i pg 3 |
|
|
Why is combination welding and cutting torch the most popular unit?
|
it comes with a series of welding or heating tips as well as cutting attachments
120101i pg 3 |
|
|
What are Standard or heavy duty cutting torches only meant for?
|
cutting only
120101i pg 4 |
|
|
What is a standard or heavy duty torch better at than a combination torch?
|
–Cutting material 150mm(6”) or greater
–work in rough service enviroments 120101i pg 4 |
|
|
What is the two tube torch design known as?
|
premixing type cutting torch
120101i pg 4 |
|
|
What are three tube mixing torches known as?
|
Tip mixing type torch
120101i pg 5 |
|
|
What are the tree types of machine cutting tracing systems?
|
–manual machine tracers
–magnetic tracers –electronic tracers 120101i pg 6 |
|
|
What does CNC stand for?
|
Computer Numerical Control
120101i pg 9 |
|
|
What does a CNC machine allow for?
|
high consistency and accuracy and less turnaround time
120101i pg 9 |
|
|
What are the four types of cutting tips?
|
–Straight
–Scarfing –Gouging –Heavy duty rivet/bolt 120101i pg 10 |
|
|
For straight and bevel cutting what tip do you use?
|
Straight tip
120101i pg 10 |
|
|
For removing minor imperfections and during foundry and casting work what tip would you use?
|
Scarfing tip
120101i pg 10 |
|
|
What cutting tip performs the same function as carbon arc cutting electrodes?
|
Gouging tips
120101i pg 10 |
|
|
What is the heavy duty rivet and bolt cutting tip good for?
|
Cutting rivet and bolt heads without damage to the parent metal
120101i pg 10 |
|
|
What are two piece splined tips used for?
|
propane or natural gas cutting
120101i pg 10 |
|
|
What does 15% drag mean?
|
The exit point of the cut is 15% behind the entry point of the cut
120101i pg 15 |
|
|
What do you examine to determine if you are cutting to fast?
|
The Kerf lines
120101i pg 15 |
|
|
What happens to the torch inclination when working on thinner material?
|
the thinner the material the more forehand inclination required
120101i pg 16 |
|
|
When cutting shapes what inclination is required?
|
None [steel 75mm(3”) or thicker you may need to use a slight backhand inclination]
120101i pg 16 |
|
|
What does cutting with a slight bevel ensure?
|
Slag will collect on the scrap material
120101i pg 17 |
|
|
What are the two methods to prevent molten slag and oxide from blowing back?
|
still torch method and the traveling torch method
120101i pg 18 |
|
|
What does the still torch method work best for doing?
|
small holes in a heavy plate
120101i pg 18 |
|
|
Where is the traveling torch method faster than the still torch method?
|
materials 12.7mm( ½“) thick or less
120101i pg 19 |
|
|
what prevents Cast iron form cutting?
|
–The refractory oxide
–carbon graphite flakes –iron carbide 120101i pg 20 |
|
|
For demolition purposes what methods can you use to sever cast iron?
|
–Carburizing flame and mild steel rod method
–oxygen lance method 120101i pg 20 |
|
|
What is the Carburizing flame and mild steel rod method?
|
uses a carburizing flame with a feather as long as the as the thickness of the cast iron you are cutting
120101i pg |
|
|
How does an oxygen lance work?
|
preheat metal then add pure oxygen and the intense heat then produced burns a path through the cast iron
120101i pg |
|
|
What elements in stainless steel slow down progressive burning?
|
chromium and nickel
120101i pg 21 |
|
|
What two methods exist to cut stainless steel?
|
–Introduce mild steel into the cut by adding a mild steel rod
–use a specially designed torch that injects iron powder or a flux into the cut 120101i pg 21 |
|
|
What has replace oxyfuel cutting methods of cutting stainless steel?
|
Plasma Arc Cutting (PAC)
120101i pg 21 |
|
|
What does to large of a nozzle cause?
|
The kerf edges melting back together behind the cut
120101i pg 22 |
|
|
What does to small of a cutting tip cause?
|
difficulty cutting fully through material
120101i pg 22 |
|
|
What are three factor to consider when selecting a cutting tip for the job?
|
–Depth of the cut
–The type of material –The condition of the material –The type of cut to be made –Quality of cut desired –Speed of cutting requires –cleanliness of the tip 120101i pg 24 |
|
|
What can happen if you use to small of a tip cleaner?
|
can cause damage to the orifices by filing them out of round
120101i pg 25 |
|
|
What can happen if you use to large of a cleaning tip?
|
you run the risk of getting it stuck
120101i pg 25 |
|
|
What are three methods of controlling the torch?
|
–Across cut
–Push cut –Pull cut 120101i pg 26 |
|
|
What are two type of machine–Guided cutting torches?
|
–Radiagraph
–Pipe Beveller 120101i pg 38 |
|
|
What is the temperature of a oxidizing flame?
|
3470°C(6300°F)
120101h pg 40 |
|
|
Define High Frequency Current.
|
AC current with an operating frequency of thousands of cycles per second
120101j pg 2 |
|
|
Define Ion.
|
An atom, molecule that has either gained or lost electrons
120101j pg 2 |
|
|
Define non–transferred arc.
|
An arc established between the electrode and the torch tip
120101j pg 2 |
|
|
Define Pilot arc.
|
low current high voltage arc established between the electrode and the torch tip.(establishes pathway for main arc)
120101j pg 2 |
|
|
Define Plasma.
|
a gas that has been heated to an extremely high temperature by an electric arc
120101j pg 2 |
|
|
Define stand–off distance.
|
The distance between the torch nozzle and the work
120101j pg 2 |
|
|
Define transferred arc.
|
current flow between the electrode in the torch and the work piece
120101j pg 2 |
|
|
What does plasma cutting rely on to work?
|
high temperature arc to melt the metal and a high velocity jet of plasma gas to blow the metal away
120101j pg 3 |
|
|
What is the temperature range of a plasma arc stream?
|
10,000°C to 14,000°(18,000°F–25,000°F)
120101j pg 3 |
|
|
What type of process is PAC and what current does it use?
|
PAC is an erosion process that operates on direct current straight polarity(DCSP)
120101j pg 3 |
|
|
What does the use of a secondary shielding gas with PAC provide?
|
protection of the kerf walls from oxidization and isolates the plasma stream from the atmosphere
120101j pg 4 |
|
|
That does a dual flow torches have?
|
separate passageways for the plasma and shielding gases
120101j pg 4 |
|
|
What does PAC have in its smoke that make it more dangerous than OAC?
|
very small fume particles
120101j pg 5 |
|
|
What do you have to worry about if plasma cutting under water?
|
Water breaking down into hydrogen, without proper ventilation an explosion hazard is present
120101j pg 6 |
|
|
What can Plasma arc cutting machines power supply range from?
|
35 amp to 750 amps
120101j pg 7 |
|
|
Power supplies designed for PAC are what?
|
DCSP rectifier or inverter–type constant current machine with an open circuits ranging from 120 to 400 volts
120101j pg 7 |
|
|
What does the torch do?
|
Transfers current to a fixed non–consumable electrode and directs the flow of plasma and shielding gas
120101j pg 7 |
|
|
Hafnium has a high oxidation resistance making it good for use with compressed air and oxygen plasma cutting systems.
A)True B)False |
A)True
120101j pg 7 |
|
|
Adapting a PAC torch for gouging operations involves changing nozzle that does what?
|
reduces arc constriction resulting in lower arc stream velocity
120101j pg 8 |
|
|
What are two methods for starting the arc when cutting?
|
edge and pierce start
120101j pg 8 |
|
|
What does PAC underwater eliminate?
|
–fumes
–gases –reduces noise levels 120101j pg 9 |
|
|
What are typical cutting variables for PAC cutting stainless steel?
|
–amperage
–metal thickness –travel speed 120101j pg 10 |
|
|
What determines your travel speed with PAC?
|
Type and Thickness of the metal
–orifice diameter –output of the power source 120101j pg 10 |
|
|
What is standoff distance in PAC?
|
The distance between the end of the torch nozzle and the work
120101j pg 10 |
|
|
What should the standoff for PAC cutting be for most applications?
|
6.4mm–10mm(1/4”– 3/8”)
120101j pg 10 |
|
|
What can improper standoff cause with PAC?
|
–excessive nozzle wear
–poor quality cuts –slow cutting speeds 120101j pg10 |
|
|
When gouging what determines the depth of the gouge?
|
travel speed and standoff distance
120101j pg 11 |
|
|
What are the two type of PAC torches?
|
compressed air torches and dual flow torches
120101j pg 12 |
|
|
What is generally the shielding gas used for a dual flow PAC torch?
|
carbon dioxide or nitrogen
120101j pg 11 |
|
|
Due to high temperatures and fast cutting speeds PAC a narrow what along the kerf?
|
Heat–affected zone(HAZ)
120101j pg 12 |
|
|
What is Dross?
|
Re–solidified oxidized molten metal that does not blow away during cutting
120101j pg 13 |
|
|
What can cause dross?
|
–Incorrect cutting speeds
–Incorrect amperage settings –Incorrect standoff distance –A worn nozzle 120101j pg13 |
|
|
What is Arc Cutting?
|
thermal cutting process where melting the base metal is accomplished using an electric arc established between the base metal and an electrode
120101j pg 15 |
|
|
When selecting an arc cutting process what must you consider?
|
–effectiveness of each cutting process
–limitations of the process –type of power source and auxiliary equipment –necessary precautions to avoid personal injury and damage to property 120101j pg 15 |
|
|
What are the two most used arc–cutting processes?
|
–air carbon arc cutting(CAC–A)
–plasma arc cutting(PAC) 120101j pg 15 |
|
|
How does Air Carbon Arc cutting work?
|
metals are melted by carbon electrode arc. Jet stream of compressed air blows molten metal away
120101j pg 15 |
|
|
What can air carbon arc cutting be used to do?
|
–gouging
–cutting –beveling –washing operations 120101j pg16 |
|
|
In CAC–A low heat input minimizes what in the base metal?
|
Warpage and Distortion
120101j pg 16 |
|
|
What equipment does air carbon arc cutting require?
|
–power source
–electrode holder –carbon electrodes –compressed air supply 120101j pg 18 |
|
|
What percentage of duty cycle may be required for automatic or semi–automatic cutting?
|
100% duty cycle
120101j pg 18 |
|
|
What happens if you use a constant voltage power source with an electrode smaller than 7.9mm(5/16”) for arc cutting?
|
can cause excess carbon deposits in the metal
120101j pg 18 |
|
|
Why is it recommended that PAC systems have overload protections?
|
to prevent damage to the power source during high current surges
120101j pg 18 |
|
|
In PAC where rectifier units do not have sufficient current output what can you do?
|
to rectifiers may be hooked up in parallel, double the current output
120101j pg 18 |
|
|
Carbon electrodes used in arc welding consist of what?
|
Carbon and graphite rod
120101j pg 21 |
|
|
What are the three types of arc cutting and gouging electrodes?
|
–DC copper–coated
–DC plain –AC copper coated 120101j pg 21 |
|
|
What can copper coated electrodes do better than plain electrodes(arc cutting)?
|
last longer and can carry higher currents
120101j pg 21 |
|
|
DC plain electrodes are cheaper then copper coated electrodes and do not have a coating(arc cutting)
A)True B)False |
A)True
120101j pg 22 |
|
|
Over what diameter do DC Plain Electrodes not perform well(Arc cutting)?
|
10mm(3/8”)
120101j pg 22 |
|
|
AC electrodes have rare earth materials added to do what(arc cutting)?
|
Stabilize the Arc
120101j pg 22 |
|
|
What do AC electrodes work well on (arc cutting)?
|
–copper
–nickel –cast iron 120101j pg 22 |
|
|
What pressure of air in normally required for air carbon arc gouging?
|
550kpa to 700kpa(80psi to 100psi)
120101j pg 22 |
|
|
What are the two most common problems encountered with air carbon arc gouging?
|
–carbonization of the base metal
–surface hardening 120101j pg 23 |
|
|
When does carbonization occur(arc cutting)?
|
When your air is not blowing away the molted metal
120101j pg 23 |
|
|
On what metals does surface hardening happen with arc air gouging? What helps reduce this hardness?
|
–Cast iron and higher carbon steels
–preheating your metal 120101j pg 23 |
|
|
What should the electrical stick–out for air arc gouging not exceed?
|
180mm(7”) all metals except aluminum[100mm(4”)]
120101j pg 25 |
|
|
How short can you let your electrode get?
|
50mm(2”)
120101j pg 25 |
|
|
Before you start an arc what must you make sure is on?
|
the air stream
120101j pg 25 |
|
|
The progression and quality of a air arc cut depends on what?
|
–type of base metal
–electrode size –current settings –available –experience of the operator 120101j pg 25 |
|
|
When air arc cutting what inclination angle gives you a shallow groove and faster travel speed?
|
30° forehand
120101j pg 25 |
|
|
When air arc cutting what inclination produces a deep narrow groove requiring a faster travel speed?
|
90° forehand
120101j pg 25 |
|
|
What inclination is used for most:
A)air arc cutting operations B)air arc gouging operations |
A)90°
B)30° 120101j pg 25 |
|
|
What do slight changes in you electrode angle help with in air arc cutting or gouging operations?
|
direct slag away from cut or gouged area
120101j pg 26 |
|
|
In Addition to PAC and CAC–A what are three other arc cutting process?
|
–shielded metal arc cutting
–carbon arc cutting –oxygen arc cutting 120101j pg 29 |
|
|
What can happen if you don’t level a crane?
|
crane may tip over
120101k pg 4 |
|
|
What are the three methods to check if a crane is level?
|
–the cabs target level
–carpenters level –checking the hoist line 120101k pg 4 |
|
|
What are the factors that affect the lifting of a load?
|
–total weight of the load and rigging
–the shape of the load –the height to which the load is to be raised –the final position of the load when raised 120101k pg 5 |
|
|
What is load radius deflection?
|
The horizontal distance measured from the rotation centre of the crane to the load hook while the boom is under load
120101k pg 5 |
|
|
What should be taken into consideration when traveling with a load(crane)?
|
–type of terrain
–the presence of overhead power lines –the boom length –the stopping and starting momentum 120101k pg 6 |
|
|
What precautions should you follow during pick up and carry operations(crane)?
|
keep the load as close to carrier as possible
–keep the boom as short as possible –keep the boom as low as possible –carry load in line of travel –carried close to the ground and controlled 120101k pg 6 |
|
|
How should materials be stored?
|
so that they are easily accessible, and protected from harm and pose no threat to people in the vicinity
120101k pg 6 |
|
|
What are the rolls of the signalman?
|
–only on signalman |
|
|
What is a knot?
|
formed when two ends of a rope intertwines within a section of rope
120101k pg 9 |
|
|
What is a bend?
|
formed by intertwining two rope ends
120101k pg 9 |
|
|
What is a Hitch?
|
formed by fastening a rope to an object
120101k pg 9 |
|
|
What is a splice?
|
made by joining the ends of two ropes
120101k pg 9 |
|
|
What percentage is a ropes strength reduced by when a knot is put in it?
|
50%
120101k pg 10 |
|
|
What percentage is a ropes strength reduced by when a bend is put in it?
|
50%
120101k pg 10 |
|
|
What percentage is a ropes strength reduced by when a hitch is put in it?
|
25%
120101k pg 10 |
|
|
What percentage is a ropes strength reduced by when its spliced?
|
20%
120101k pg 10 |
|
|
Wire rope is a common material used for construction of slings?
A)true B)false |
A)True
120101k pg 17 |
|
|
What does the lay of a rope indicate?
|
the direction of the rotation of the wires and the strands in the rope
120101k pg 17 |
|
|
Wire rope classification numbers always indicate the what?
|
Number of strands in the rope
120101k pg 18 |
|
|
Larger the wire size is, the worse the abrasion resistance of the rope is.
A)True B)False |
B)False
Abasion resistance gets better 120101k pg 18 |
|
|
The more wires there are in a strand what happens to the flexibility of that rope?
|
more wires per strand the more flexible it becomes.
120101k pg 18 |
|
|
To determine the size of a wire where do you measure?
|
across the wires diameter at its widest point
120101k pg 19 |
|
|
What does seizing do?
|
binds the ends of a non–preformed wire rope to prevent the wires and strands from fraying
120101k pg 20 |
|
|
What are snake skin connectors?
|
connector used to join two wire ropes
120101k pg 21 |
|
|
Why are synthetic fiber ropes stronger than those made of natural fibers?
|
there are no breaks in the threads or strands
120101k pg 22 |
|
|
What can synthetic ropes be manufactured from?
|
–nylon
–polypropylene –polyester –polyethylene 120101k pg 22 |
|
|
What synthetic rope is the strongest?
|
Nylon
120101k pg 22 |
|
|
What synthetic is most popular rope(cheap and serviceable)?
|
polypropylene
120101k pg 22 |
|
|
When lifting what factors does weight affect?
|
–which equipment to use
–the best rigging materials –best way to secure the load for lifting 120101k pg 23 |
|
|
Where can weight information normally be found?
|
–shipping documentation
–manufactures’ tags –design plans –catalogue data 120101k pg 23 |
|
|
What do structural steel drawings normally include?
|
–size of each steel beam
–weight per meter or per foot –actual length of each member 120101k pg 23 |
|
|
What can you estimate
a)one meter cubed of steel weighs b)one foot squared of 1 inch thick steel weighs |
a)7850kg appoximatly
b)40lb 120101k pg 23 |
|
|
If you don’t know where the centre of gravity is what method can you use to find it?
|
Trial and error(lift it a little if its not right put it down adjust and try again)
120101k pg 25 |
|
|
What is the working load limit(WLL)?
|
the weight that can be safely lifted by a wire rope
120101k pg 26 |
|
|
What is safety factor?
|
a ratio that provides a margin for extra strength for if extra stresses are placed on a rope
120101k pg 26 |
|
|
What formula can you use to estimate the Working Load Limit of a wire rope sling with a safety factor of 8:1?
|
WLL = D¬2 x 8
120101k pg 26 |
|
|
What formula can you use calculate the Working Load Limit of a wire rope sling with a safety factor of 5:1?
|
WLL = D2 x 5
120101k pg 27 |
|
|
What do safety factors allow for?
|
–reduced rope capacity
–extra load imposed by shock loading –extra load due to sheave friction –inability to accurately guess the weight of objects –bending stress on fibers passing over sheaves 120101k pg 28 |
|
|
Name two advantages of synthetic slings.
|
–non–sparking |
|
|
What is a plate clamp designed with to do what?
|
serrated jaws to grip plate metal for hoisting
120101k pg 30 |
|
|
What is strongly recommended you plate clamp has for safety?
|
locking lever so your clamp doesn’t accidently open up when you set you metal down
120101k pg 30 |
|
|
How many plates can you lift with a plate clamp at one time?
|
one only
120101k pg 30 |
|
|
What should you check on your plate clamp before using it?
|
–serrated jaws and lifting eye for wear
–buildup of paint, mill scale, or corrosion – lifting line is directly over head – use care in cold or wet conditions 120101k pg 31 |
|
|
Why do you not use plate clamps on stainless steel?
|
The jaws damage the surface of the steel
120101k pg 31 |
|
|
What are the two types of wire rope clips?
|
–double saddle and bolt(safety or fist–grip)
–U–bolt and saddle(Crosby) 120101k pg 31 |
|
|
When wire rope clips are applied properly how much of the wire strength is kept?
|
80%
120101k pg 31 |
|
|
What two advantages does a double saddle and bolt clip have?
|
–wide bearing surface for maximum strength and higher holding power
–cannot be installed incorrectly 120101k pg 31 |
|
|
What saying can you use to remember how to put on a U–bolt and saddle wire rope clip?
|
Never saddle a dead horse
120101k pg 32 |
|
|
What is the rule of thumb for haw far apart wire rope clips should be placed apart?
|
rope diameter times(x) 6
120101k pg 33 |
|
|
How many trades and occupations are involved in the Alberta apprenticeship system?
|
50 plus
120104f |
|
|
What is the difference between a compulsory and voluntary certification trade?
|
Compulsory means one must be must be an apprentice or journeyman to work in the trade
120104f |
|
|
What is the total number of on the job hours a welder required to have per year?
|
1500
120104f |
|
|
What is the total number of technical training hours in the first year of welding?
|
240
120104f |
|
|
What is the total number of work experience hours required for a wire process operator apprenticeship second year?
|
1800 |
|
|
Who is responsible for determining the course outline for the welder and wire process operator trade?
|
the Provincial Apprenticeship Committee
120104f |
|
|
What is the purpose of the learning outcomes in a trade course outline?
|
the outcomes are what you must be able to do or know. the outcomes guide the objectives in the course outline.
120104f |
|
|
How are the final apprenticeship written exams formulated?
|
they are keyed to the objectives in the trade course outline
120104f |
|
|
Who are the major participants when entering into a contract of apprenticeship?
|
the apprentice, the employer, and Alberta Apprenticeship and Industry training
120104f |
|
|
Who is responsible for recommending that the apprentice receive time credit for any past experience in the trade?
|
the employer
120104f |
|
|
Who is responsible for notifying the Alberta Apprenticeship and Industry Training that the apprentice has changed employers?
|
The new employer and the apprentice |
|
|
Who is responsible for Blue Book security and accuracy of the information and sending it to Alberta Apprenticeship and Industry training when required?
|
the apprentice
120104f |
|
|
What are the three elements of each year of your apprentice ship? |
–technical training |
|
|
Arange in order from Largest to smallest
45/64, 5/8, 3/4, 11/16, 23/32 |
3/4, 23/32, 45/64, 11/16, 5/8 |
|
|
How do you use the calculator to get to lowest terms?
|
use the a a/b button press =
|
|
|
How do you use the calculator to get a mixed number to lowest terms?
|
Main number a a/b top number a a/b bottom number press = gives you answer |
|
|
Changed the mixed Number to an improper fraction(top heavy)
4 2/3 8 5/8 |
14/3 (4x3+2=14/3)(4–2–3 SHIFT a a/b =14–3) |
|
|
Change the improper fraction to a mixed number
23/8 107/9 |
3 ½ (28–8 a a/b = A)
15–2–7 (107–7 a a/b = A) 120104a pg 14 |
|
|
Determine the I.D. of a piece of steel tubing if the O.D. is 13/16” and has a wall thickness of 1/32” a)25/32
b)24/32 c)3/4 d)5/8 |
c)3/4
120104a pg 29 |
|
|
Define Equivalent Fractions
|
fractions that are equal in value to each other ex.½=2/4
120104a pg 2 |
|
|
Define mixed numbers
|
A whole number and a fraction ex 2 ½
120104a pg 2 |
|
|
Define Improper fractions (top heavy fractions) |
the top number is equal to or larger than the bottom number(denominator). ex 8/3
120104a pg 2 |
|
|
What do drawings do?
|
Conveys information to the fabricator and supplies a permanent record of the fabrication
120102a pg 4 |
|
|
Who draw up plans? |
The draftsman |
|
|
What are the copies of original drawing called?
|
Blueprints
120102a pg 4 |
|
|
What are working drawings?
|
The drawings created during the process of producing the blueprints before the final draft |
|
|
What do working drawings allow for?
|
Needed changes and revisions before the final draft is approved |
|
|
What is CAD?
|
Computer Aided Drafting |
|
|
What are specifications?
|
written instructions necessary for that particular job
120102a pg 5 |
|
|
When there is a conflict between the specifications and the drawings what do you assume is correct?
|
the information in the specifications is usually assumed to be correct(best to confirm with the engineer or architect |
|
|
What are the 5 divisions of working drawings and blueprints?
|
-architectural |
|
|
What are architectural drawings?
|
a line drawing that shows plan and/or elevation views of the proposed building for showing it’s overall appearance |
|
|
What are structural drawings?
|
All the drawings that describe the structural members of the building and their relationship to each other |
|
|
What drawings can structural drawings contain?
|
-foundation plans and details
-framing plans and details -wall sections -beam details 120102a pg 6 |
|
|
What are mechanical drawings?
|
they show all the required mechanical components of the building |
|
|
What items can Mechanical drawings include?
|
-heating
-air conditioning -sprinkler systems -plumbing fixtures -water supply and waste disposal lines -other supply and disposal lines 120102a pg 6 |
|
|
What are electrical Drawings?
|
they locate the various outlets, indicate the routing of circuits, show the location and size of panel boards and illustrate other electrical details
120102a pg 6 |
|
|
What are landscaping drawings?
|
They show the elevations of the ground that surrounds the building and location of trees and plants
120102a pg 6 |
|
|
What are the three basic elements found on a blue prints?
|
-lines |
|
|
What do lines convey?
|
-the shape of the object |
|
|
Dimensions give what information? |
sizes and locations
120102a pg 7 |
|
|
What do notes give information on? |
details of construction not shown by lines.(may be symbols or abbreviations) |
|
|
What are object lines?
|

(visible line) |
|
|
What are Hidden lines?
|
Broken lines that of medium thickness used to show edges and outlines not visible to the eye |
|
|
What are section lines?
|
-They represent different types of material when there is an imaginary cut surface |
|
|
What are centerlines?
|
-Thin broken line made up of a series of short and long dashes that are alternately spaced |
|
|
What are Extension lines?
|
-Thin lines that extend from the object with a slight break between |
|
|
What are dimension lines?
|
-Thin lines with arrowheads, unbroken except where the dimension is placed |
|
|
What are terminals?
|
arrows, slashes, or dots at the end of dimension lines |
|
|
What are leader lines?
|
-Thin straight line or a fine curved line |
|
|
What are cutting plane lines?
|
Indicates where an imaginary cut is made through an object |
|
|
What do the arrows on cutting lines indicate?
|
-The direction in which the section is to be viewed |
|
|
What are viewing lines?
|
line used outside an object to show the direction of viewing(similar to cutting plane lines) |
|
|
What are short break lines? |
-A thick irregular line drawn freehand to show where a portion of an object is broken away to show detail behind the object |
|
|
What are long break lines? |

-A thin straight light line with freehand zigzags |
|
|
What are phantom lines?
|

thin, broken line made up of a series of one long and two short dashes |
|
|
What are the three different ways of placing dimensions
|
-Unidirectional |
|
|
What are unidirectional dimensions?
|
Dimensions placed inside the arrows with numbers placed in the horizontal position |
|
|
What are aligned dimensions?
|
Dimensions placed inside arrows with numbers in the directions the arrows are running |
|
|
What are architectural dimensions?
|
Dimensions placed beside the arrows running the same way as arrows. Solid arrows |
|
|
What is the seam line?
|
the line between the shell and the vessel and the head of the vessel |
|
|
What is the tangent line?
|
the line that touches the curved head of a vessel at the highest point of the curvature |
|
|
What is the datum line?
|
The line that runs around the circumference of the shell of a vessel near one end of the shell |
|
|
What is the best line is best for reference on vessels?
|
The datum line |
|
|
What can notes provide?
|
-Details of constructions |
|
|
Where is a note placed?
|
near one of the views and a leader line indicates the exact point of reference |
|
|
Where is a general note placed?
|
Away from the views so that it can be readily seen
120102a pg 13 |
|
|
What is a note called if it specifies the materials required, the welding processto be used and the type and size of filler material?
|
A Specification |
|
|
Where is the title block normally located on a drawing?
|
Lower right corner |
|
|
Where is the bill of materials located on a drawing?
|
top right corner |
|
|
What are symbols on drawings used to draw your attention to? |
-corrections or revisions
-detail drawings 120102a pg 17 |
|
|
How are corrections shown on blueprints?
|

letters or numbers that have a circle or triangle drawn around them |
|
|
All changes must be initialed by authorized personnel and include the date of change.
a)True b)False |
a)True |
|
|
When an entire section of a drawing has been changed the section may be enclosed in what?
|
a revision cloud |
|
|
What is an as built drawing?
|
A drawing that represents the final project, which may differ from the original drawing because of field changes or other add ons |
|
|
What does a detailed drawing show?
|
larger scale drawing which clearly shows all information needed to complete a specific part of a larger whole |
|
|
When many pieces in a drawing need to be shown in detail what is done?
|
Each part is given a number or letter on the main drawing and detailed drawings are given similar letters or numbers |
|
|
What is an auxiliary view used for?
|
to show the true size and shape of a slanted surface |
|
|
What is a developed view show?
|
-Shows a part before bending, rolling, or any other fabrication method shapes it |
|
|
What does a revolved view do to an object?
|
A portion of the object is rotated to obtain a straight axis for better detail and dimensioning |
|
|
What is a sectional view?
|
any view seen when a portion of the object nearest the observer is imagined to be removed by means of cutting planes |
|
|
What is a full section view?
|
-A view of an object that is imagined to be cut through top to bottom |
|
|
What is a half section view?
|
-A view that is imagined to be only cut in halfway through |
|
|
When does an offset section have an advantage?
|
If you want to obtain certain details of the object |
|
|
If a true cross sectional is desired what section view do you use?
|
Revolved section view |
|
|
What is an aligned section view?
|
When a revolved projection is incorporated within a sectional view |
|
|
How do you write one hundred twenty six thousandths?
|
0.126
120104b |
|
|
What is 0.203 in 64’s?(round to whole number)
|
13/64 |
|
|
How do you write sixty three hundredths in decimal form?
|
0.63
120104b |
|
|
Round 14.2896 to the nearest thousandth
|
14.290
120104b |
|
|
A welder makes 37 table frames using 1” square tubing as shown
a)calculate the total length of square tubing required for the job b)Determine the total weight of square tubing if a 1’ length weighs 1.2408 lb. round your answer to three decimal places. |
a)10743.875
b)1110.917 120104b |
|
|
Convert 7.319 feet to feet and inches.
|
7’-3 53/¬64“ |
|
|
What is 0.203 in 64’s?(round to whole number)
|
13/64
120104b |
|
|
Convert 0.15 to a fraction.
|
3/20 |
|
|
If a welder can do 72 fillet welds in an 8 hour day how many can she do in 20 minutes?
|
3 per 20 minutes
120104c |
|
|
A welder receives an increase 63/4% in her hourly rate, which is currently $25.80 per hour. What is her new hourly rate?
|
$27.54
120104c |
|
|
What is the 1-inch in millimeters?
|
25.4mm
120104e |
|
|
What is 1 mile in kilometers?
|
1.609km
120104e |
|
|
What is 1 yard in feet?
|
3 feet(36”)
120104e |
|
|
What is 1 kilogram in pounds?
|
2.205lb
120104e |
|
|
What is the order of metric units that you need to know?
|
-kilo-(kids) |
|
|
When you go up the metric scale what do you do?
|
divide by 10
120104e |
|
|
When you go down on the metric scales what do you do?
|
multiply by 10
120104e |
|
|
When you convert 1m2 to cm2 what do you do?
|
multiply by 10 twice
120104e |
|
|
What is the formula for the perimeter of a circle?
|
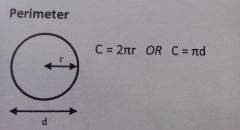
C=2πr
120104d |
|
|
What is the formula for the area of a triangle?
|
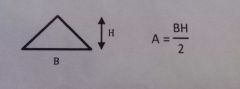
120104d |
|
|
What is the formula for the area of a Trapezoid?
|
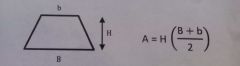
120104d |
|
|
What is the formula for the area of a parallelogram?
|
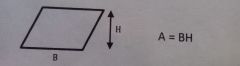
A=BH |
|
|
What is the formula for the area of a circle?
|
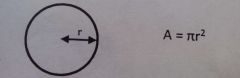
A=πr^2 |
|
|
What is the Formula for a cylinders volume?
|
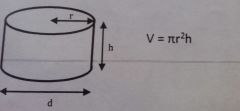
V=(π)(r^2)(h) |
|
|
What is the Formula for a cube?
|
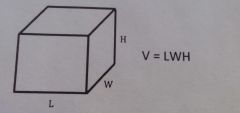
V=LWH |
|
|
What is the formula for Lateral Surface Area of a cylinder?
|
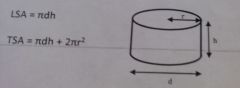
LSA= πdh |
|
|
What is the formula for Total Surface Area of a cylinder?
|
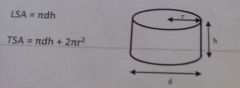
TSA= πdh + 2πr^2 |
|
|
What is the formula for Lateral Surface Area of a rectangle?
|
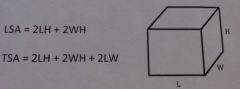
LSA= 2LH+2WH |
|
|
What is the formula for Total Surface Area of a rectangle?
|
TSA=2LH+2WH+2LW
120104d |
|
|
Metal is an element or mixture of elements that has all or most of what characteristics?
|
-solid at room tepurature
-opaque -conducts heat and electricity -reflects light when polished -expands when heated and contracts when cooled(except bismuth) -has a crystalline structure 120102c pg 2 |
|
|
What is ferrous metals main ingredient?
|
Iron |
|
|
What are the most common ferrous metals?
|
Carbon steels and cast irons |
|
|
What are tooled or high speed steels?
|
very high carbon steels used to make punches, dies, shear blades, cutting tools, and other components
120102c pg 2 |
|
|
What are most non-ferrous metals identifiable by? |
they are non-magnetic
120102c pg 3 |
|
|
What is the main ways to identify a metal?
|
-visual appearance and color |
|
|
The most practical method for identifying metals is what?
|
visual appearance and color
120102c pg 3 |
|
|
When looking at the fractured surface of a metal what are you looking at?
|
the exposed grain structure
120102c pg 4 |
|
|
What can relative weight be measured in?
|
g/cm3 or lb/ft3
|
|
|
When looking at your shape of a metal what can you see that tells you it’s been cast?
|
A cast seam is visible |
|
|
What does a rough outer texture of a metal object usually suggest?
|
a casting
120102c pg 6 |
|
|
If a solid metal has a smooth outer surface usually means it’s a formed product. a)True
b)False |
a)True
120102c pg 6 |
|
|
What are the four tests used for identifying metals?
|
-chip test |
|
|
When doing the spark test what pressure should you use on different test pieces?
|
constant equal pressure |
|
|
What sparks do low carbon steels give off?
|
bright long, straight and yellow
very little branching and few carbon bursts 120102c pg 8 |
|
|
What sparks do high carbon steels give off?
|
-burst and branch off more than low carbon steels
-darker yellow orange and burst nearer to the wheel |
|
|
What type of sparks are produced by cast iron?
|
red bursts near the grinder yellow bursts further out
-not as long as carbon steels -may require considerably more pressure 120102c pg 9 |
|
|
What sparks are created by high speed steel?
|
lines are orange with very little branching and end in ball shaps
120102c pg 10 |
|
|
What can you observe from a flame test?
|
-Speed of melting
-Changes in color -appearance and action of the slag -appearance of the molten puddle of -action of the molten puddle under the flame 120102c pg 11 |
|
|
What is the melting point of aluminum?
|
659°C (1218°F) |
|
|
What is the melting point of carbon steel?
|
1510°C (2750°F) |
|
|
What is the most accurate way to identify a metal?
|
A Mill Test Report
120102c pg 13 |
|
|
Where is the heat number identified?
|
specification tag and mill test report
120102c pg 14 |
|
|
Why are tag numbers used?
|
because there may be more than one bundle of metal all with the same heat number |
|
|
What are mechanical properties?
|
a materials ability to resist or withstand a particular kind of physical force
120102c pg 15 |
|
|
What is compressive strength?
|
the resistance of a material to a force that tends to deform or fail by crushing
120102c pg 15 |
|
|
What is shear strength?
|
the maximum load required to punch through a material
120102c pg 15 |
|
|
What is tensile strength?
|
the ultimate pull that a material will stand without fracture(measured in psi or MPa) |
|
|
What is yield strength?
|
-The stress point where deformation takes place
-point where force applied causes the metal to bend or deform and not return to it’s original shape 120102c pg 16 |
|
|
What is impact strength?
|
the ability of a metal to withstand a high velocity blow
120102c pg 17 |
|
|
What is ductility?
|
ability of a material to stretch or deform under a load without breaking
120102c pg 18 |
|
|
What is Brittleness?
|
The tendency of a material to fail suddenly by breaking without any permanent deformation before failure |
|
|
What is hardness?
|
a materials ability to resist penetration or indentation
120102c pg 19 |
|
|
What are the two common types of hardness tests? |
Rockwell and Brinell
120102c pg 19 |
|
|
What does a Rockwell test punch have on its punch tip?
|
diamond cone
120102c pg 19 |
|
|
What does a brinell test punch have on its punch tip?
|
ball
120102c pg 19 |
|
|
What is toughness?
|
-the ability of a metal to withstand a rapidly applied load without breaking |
|
|
What is Elasticity?
|
the ability of a metal to return to it’s original shape and dimension once the load has been removed
120102c pg 20 |
|
|
What is malleability?
|
metals ability to be cold worked without a great deal of resistance |
|
|
What are physical properties?
|
They describe the nature of the metal
120102c pg 22 |
|
|
What is Density?
|
a materials weight per unit of volume
120102c pg 22 |
|
|
What is corrosion resistance?
|
ability of a material to resist chemical attack by compounds or other elements that tend to waste is away |
|
|
What is electrical conductivity?
|
a materials ability to conduct an electrical current
120102c pg 23 |
|
|
What is thermal conductivity?
|
measure of rate at which heat travels through a material(higher the thermal conductivity the faster the heat loss)
120102c pg 23 |
|
|
What is thermal expansion?
|
the increase in physical dimension due to an increase in the material’s temperature
120102c pg 24 |
|
|
What is Melting point?
|
The point at which a material becomes a liquid
120102c pg 25 |
|
|
What is the electrical conductivity of copper?
|
100
120102c pg 23 |
|
|
What is the electrical conductivity of steel?
|
3-15
120102c pg 23 |
|
|
What is the thermal conductivity of copper?
|
93
120102c pg 24 |
|
|
What is the thermal conductivity of Aluminum?
|
50 |
|
|
What is the thermal expansion coefficient of aluminum?
|
0.000013in/in/°F
120102c pg 24 |
|
|
What is the thermal expansion coefficient of steel?
|
0.0000065in/in/°F |
|
|
What is the melting temperature of mild steel?
|
1510°C(2750°F)
120102c pg 25 |
|
|
What is the melting point of stainless steel?
|
1449°C(2640°F) |
|
|
What is the melting point of aluminum? |
659°C(1218°F) |
|
|
What are the five basic joint types?
|
-Butt |
|
|
What are the four weld types?
|
-surfacing |
|
|
What is surface welding?
|
when a bead or beads are used in place a layer of weld metal over a surface
120102e pg 3 |
|
|
What is surface welding used for?
|
-Reclaim worn surfaces |
|
|
What are the two steps for surface welding?
|
1.Layer of softer less expensive weld metal returns metal to original thickness |
|
|
What joint are plug or slot welds commonly used with?
|
lap joints
120102e pg 4 |
|
|
What joints are fillet welds found on?
|
lap, Tee and corner joints
120102e pg 4 |
|
|
What is the size of a fillet weld determined by?
|
the largest equal leg triangle that may be drawn within the cross section of the weld |
|
|
What is a fillet welds strength determined by?
|
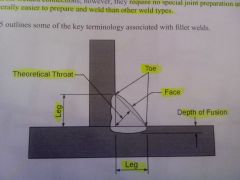
it’s effective throat dimension |
|
|
What can excessive convexity lead to on a fillet weld?
|
tends to produce a notch effect |
|
|
What can over welding a joint with a fillet weld lead to?
|
increased distortion
120102e pg 5 |
|
|
What is the size of an unequal leg fillet weld determined by?
|
it’s shortest leg |
|
|
What are the 4 variations of fillet welds?
|
-continuous |
|
|
The length and centre to centre distance of fillet welds is called what?
|
Pitch |
|
|
What joint types are groove welds commonly used with? |
butt joints
120102e pg 8 |
|
|
What is the size of a groove weld determined by?
|
The throat size |
|
|
Name two factors you use to determine what type of groove weld to use on a joint?
|
-intended service |
|
|
What are square groove welds generally restricted to due to limited penetration? |
Thin gauge material
120102e pg 9 |
|
|
Where is the bevel groove used most often?
|
Where you only have access to one member of the joint or where the joint is set in the horizontal position |
|
|
What is the most widely used groove joint for materials 9.6mm(3/8”) to 25.4(1”) thickness? |
Vee Grove
120102e pg 10 |
|
|
What is the advantage of a U-groove weld over a Vee groove?
|
smaller included angle which requires less filler metal
120102e pg 11 |
|
|
What advantage does a J groove weld have over a bevel groove?
|
J groove affords better access for welding, which promotes good penetration and fusion to the bottom of the joint
120102e pg 12 |
|
|
What is a corner joint used mainly on?
|
sheet metal fabrications |
|
|
To make a corner joint stronger what can you add to the inside of the joint?
|
a fillet weld |
|
|
What is an edge joint used extensively to do?
|
join light gauge sheet metal |
|
|
What advantages does edge joining light gauge sheet metal give you? |
-less danger of burn through |
|
|
What is the disadvantage of edge joints?
|
Cannot withstand dynamic loads |
|
|
How are thin gauge material edge joints generally welded?
|
autogenously(without the need for additional filler metals) |
|
|
What weld are Tee joints generally joined with?
|
fillet welds
120102e pg 15 |
|
|
What is the lap joint highly successful at joining?
|
Metals of different sizes |
|
|
Why are Lap joints preferred for soldering, brazing and braze welding operations?
|
Total joining surface area is greater than that of the butt joint |
|
|
Where maximum strength joint is needed what joint is used?
|
The butt joint
120102e pg 17 |
|
|
In the two digit code 1G what does the |
a)the position |
|
|
What are the primary considerations in deciding what joint and weld type to use? |
strength requirements and load conditions |
|
|
Define Alternating current.
|
Current that flows in one direction during any half cycle, then reverses and flows in the other direction during the next half cycle
120102b pg 2 |
|
|
What is Amperage?
|
-Electrical property that causes the electrode and/or parent metal to be melted together |
|
|
What is the Arc?
|
Created when there is enough amperage and voltage available at the electrode tip to overcome the natural resistance to the flow of electricity |
|
|
What is Arc Blow?
|
A condition encountered during DC welding when the arc flares uncontrollably from side to side. Caused by magnetic fields being set up around the work |
|
|
What is Arc voltage?
|
-The voltage output of the machine during welding. |
|
|
What is a Buzz Box?
|
Describes an AC transformer welding machine because of the typical buzzing sound made when welding with them |
|
|
What is a circuit?
|
Any system of conductors that is designed to complete the path of an electric current |
|
|
What is a core?
|
-The magnetic link between the primary and secondary coils of a welding transformer
120102b pg 3 |
|
|
What is a movable shunt?
|
A core that can be moved into different positions which will alter the magnetic link between the primary and secondary coils |
|
|
What is a conductor?
|
A material or substance that is capable of transmitting electricity |
|
|
What is current flow?
|
-the movement of electrons in an electrical circuit. |
|
|
What is a diode? |
A one way electrical valve
120102b pg 5 |
|
|
What is a diode used for in welding machines?
|
used to change AC current to DC current |
|
|
What is direct current?
|
-electrical current that flows in one direction only |
|
|
What is a cycle?
|
A complete rotation of a sine wave pattern |
|
|
What direction do electrons flow in?
|
Negative to Positive |
|
|
What is duty cycle?
|
percentage of time that a machine can run at maximum rated output current before over a 10 minute period before it must be cooled down |
|
|
What is an electron?
|
Negatively charged particle
120102b pg 6 |
|
|
What is frequency?
|
Relates to the speed at which alternating current changes it’s direction of flow |
|
|
What is a generator? |
a machine used to create electricity of sufficient volume for welding |
|
|
What are AC generators called?
|
Alternators |
|
|
What is inductance?
|
The ability of a conductor to transfer current onto a neighboring body without physical contact |
|
|
What is an insulator? |
Any material that does not allow current to flow through it |
|
|
What is an inverter? |
A device that changes DC to AC current |
|
|
What is line transformer? |
used to describe an AC transformer welding machine |
|
|
What is open circuit voltage? |
when a welding machine is turned on but no current is flowing in the circuit |
|
|
What does the primary coil do?
|
takes power directly from the AC input power line
-causes magnetic fields to form 120102b pg 7 |
|
|
What is a rectifier?
|
A device that changes AC to DC by allowing current to flow in one direction only |
|
|
What is a relay?
|
a switch that is operated by electro-mechanical force rather than by the application of external mechanical force |
|
|
What is resistance?
|
the property of an electrical conductor to oppose the flow of current, which causes electrical energy to turn into heat |
|
|
What does the secondary coil do?
|
Takes the magnetic field generated by the primary coil is then induced into the secondary coil |
|
|
What is a switch? |
a device with points of contact that can complete a circuit |
|
|
What is Voltage?
|
Electrical pressure of force that causes current to flow in a conductor or to cross an arc gap |
|
|
What is EMF?
|
Electromotive force
120102b pg 9 |
|
|
What is voltage responsible for in arc welding?
|
-starting the arc |
|
|
To maintain the arc what must be present?
|
Arc voltage |
|
|
What does arc voltage control in the weld puddle?
|
the width of the weld bead and the fluidity
120102b pg 9 |
|
|
What is an atom?
|
the smallest particle of any element that can exist
120102b pg 11 |
|
|
What does the selection of DCEP, DCEN, or AC depend on?
|
-filler metal type |
|
|
60 cycles per second(AC) changes direction how many time per second?
|
120 times per second
120102b pg 13 |
|
|
what does three phase allow for?
|
fewer gaps in the current flow
120102b pg 13 |
|
|
what are the three distinct advantages of three phase over single phase?
|
-constant power |
|
|
constant power from three phase results in what in machines?
|
less vibration and better performance |
|
|
What does a transformer do?
|
Takes electricity from the power grid and converts it into welding current |
|
|
How does a AC transformer convert voltage and amperage?
|
high voltage, low amperage to low voltage to high amperage suitable for welding
120102b pg 15 |
|
|
How does an adjustable coil transformer work?
|
moves the primary and secondary coils closer together or further apart |
|
|
How does a Metal shunt adjustable coil work?
|
-Moves a metal bar between the two coils |
|
|
What is one advantage of AC transformers?
|
-low initial cost |
|
|
What is one disadvantage of AC transformers?
|
-not portable
-no choice of polarity -limited electrode selection -more difficult to strike and maintain an arc -restricted welding process 120102b pg 17 |
|
|
What is an AC-DC Transformer-Rectifier?
|
welding machine that are AC transformers with an added rectifier(made up of diodes that are capable of allowing current to flow in one direction only, changing AC to DC)
120102b pg 18 |
|
|
What is one advantage of AC-DC transformer-Rectifiers?
|
-May have AC or DC output capability |
|
|
What is one disadvantage of AC-DC Transformer Rectifiers?
|
-Generally more costly than transformers
-Arc blow can be a factor with DC -Not portable -Requires a clean, cool enviroment 120102b pg 19 |
|
|
What do generators and alternators do?
|
convert mechanical energy into electrical energy
120102b pg 20 |
|
|
What type of current does a generator create?
|
DC
120102b pg 20 |
|
|
What type of current does an alternator produce?
|
AC
120102b pg 20 |
|
|
What does a basic generator consist of?
|
a wire loop that can rotate in a stationary magnetic field |
|
|
What is one advantage of AC Alternators?
|
-No arc blow
-May be portable - higher duty cycle rating than many transformers -can run power tools 120102b pg 23 |
|
|
What is one disadvantage of an AC Alternator?
|
-higher initial cost |
|
|
On DC generator there is a split ring that rectifies the current what it called?
|
a commutator |
|
|
What is one advantage of DC Generators and Alternators?
|
-choice of polarity |
|
|
What is one disadvantage of DC Generators and Alternators?
|
-high initial cost |
|
|
What is an inverter?
|
an electronic circuit that is capable of transmitting DC imput to AC output
120102b pg 27 |
|
|
What is one advantage of an Inverter?
|
-Small and lightweight |
|
|
What is a disadvantage of an Inverter?
|
-AC is very noisy |
|
|
What can an Inverter machine with transistors do? |
rectify incoming AC to DC and then transistors convert DC voltage into high frequency AC output which is then rectified back to an extremely a smooth DC welding current |
|
|
What is the heat affected zone(HAZ)?
|
It is the area on both sides of a weld directly adjacent to where the weld metal mixes with the parent metal
120102d pg 2 |
|
|
The HAZ consists of what four areas?
|
-the solid/liquid transition zone
-the grain growth zone -the recrystalized zone -the partially transformed zone 120102d pg 2 |
|
|
What is the end grain result in a multi-pass weld?
|
finer grain structure(finer grain=stronger weld)
120102d pg 3 |
|
|
Why must HAZ be controlled?
|
To maintain the required mechanical properties
120102d pg 4 |
|
|
A finer grain provides a higher _________ and __________ strength.
|
tensile and yield
120102d pg 4 |
|
|
A welding procedure that generates too fine a grain structure may result in the formation of a hard and brittle martensitic structure prone to what?
|
Cracking
120102d pg 4 |
|
|
Temperature refers to what?
|
a degree or intensity and is expressed in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or in degrees Celsius (°C)
120102d pg 5 |
|
|
What is heat as a volume measured in?
|
British Thermal Units(BTU) or Joules(J)
120102d pg 5 |
|
|
How do you convert BTUs to joules?
|
Multiply the number of BTUs by 1055.056
120102d pg 6 |
|
|
How do you convert joules to BTUs?
|
Multiply the number of joules by 0.000948
120102d pg 6 |
|
|
What are the three forms of heat transfer? |
radiation
-convection -conduction 120102d pg 7 |
|
|
What is radiation? |
heat that travels on light waves, such as ultraviolet and infrared rays from the sun or from the welding arc |
|
|
What is convection?
|
the transfer of heat from one body to another
120102d pg 7 |
|
|
What is conduction?
|
The transfer of heat within a body
120102d pg 7 |
|
|
What is expansion?
|
increasing in size or swelling and is usually associated with a rise in temperature
120102d pg 9 |
|
|
What is solid expansion?
|
occurs when the metal is in a solid condition and has not reached its transition temperature
120102d pg 9 |
|
|
When does transition expansion occur?
|
Above the transition temperature
120102d pg 9 |
|
|
Where does fluid expansion occur?
|
Molten metal
120102d pg 9 |
|
|
What is free expansion and contraction?
|
metal is allowed to expand and contract in all directions
120102d pg 9 |
|
|
What is restrained expansion and free contraction?
|
the longitudinal expansion is prevented so that expansion upon heating only occurs on the height and width of the bar
120102d pg 10 |
|
|
What method can you use to remove broken studs? |
Dimensional upset
120102d pg 12 |
|
|
What are the two methods of preheating?
|
-a local preheat on a small surface area
-total preheat of the material 120102d pg 13 |
|
|
What does preheating prevent?
|
high stress or cracking
-reduces or prevents hardness 120102d pg 15 |
|
|
What arc characteristics does preheating make easier?
|
striking the arc
120102d pg 15 |
|
|
What effects does preheating have?
|
-lowers the tensile strength
-reduces residual hardness -improves ductility -increases the notch toughness 120102d pg 15 |
|
|
What do preheat temperatures usually range from?
|
40°C to 250°C(100°F to 400°F)can be as high as 425°C(800°F)
120102d pg 15 |
|
|
What is postheating ?
|
the application of heat immediately after welding
120102d pg 16 |
|
|
What is the primary purpose of postheating?
|
to slow the cooling process
120102d pg 16 |
|
|
Name two specific purposes of post heating?
|
-prevention of hydrogen-induced cracking
-reduction or prevention of martensite formation in the weld metal or HAZ -relief of residual stress -reduction of the preheat temperature 120102d pg 16 |
|
|
How does postheating prevent hydrogen-induced cracking?
|
Postheating allows hydrogen trapped in the HAZ to come to migrate out of the metal
120102d pg 16 |
|
|
How does post heating prevent martensite formation?
|
Postheating slows down the cooling rate and allows the carbon to escape to the grain boundary and not become trapped
120102d pg 17 |
|
|
The higher the postheat temperature the ________ the residual stress is.
|
Lower
120102d pg 17 |
|
|
Postheating allows for a what in your preheat temperature?
|
reduction
120102d pg 17 |
|
|
Temperature for postheating depends on what three factors?
|
-Material thickness
-carbon and other alloy content -weather the material was subjected to heat treatment when it was manufactured 120102d pg 17 |
|
|
What two categories can postweld heat treatments be divided into?
|
high temperature heat treatments and low temperature heat treatments
120102d pg 19 |
|
|
What is transformation temperature (lower critical temperature)?
|
When a metal begins to change to it’s crystalline form
120102d pg 19 |
|
|
What is upper critical temperature?
|
The transformation from one crystalline form to another
120102d pg 19 |
|
|
What is one postweld heat treatment that involves temperature above the upper critical limit?
|
-normalizing
-annealing -hardening 120102d pg 19 |
|
|
Normalizing heat treatment is heated above the upper critical temperature by how many degrees and how is it cooled?
|
-10°C to 40°C (50°F to 100°F)
-allowed to cool in still air at room temperature 120102d pg 20 |
|
|
What is annealing?
|
The process of softening a material or bringing it to its softest, toughest, weakest state.
120102d pg 21 |
|
|
For the annealing process how far above the upper critical temperature does the material get heated and how is it cooled?
|
About 40°C(100°F)
- cooled through the use of an oven or other means 120102d pg 21 |
|
|
What are two of the main purposes of annealing?
|
softens the steel so it can be more readily formed or cold worked
-aid in machining -refine the grain structure -removes residual stresses 120102d pg 22 |
|
|
Annealing improves softness and toughness but what does it lower in the material? |
Tensile strength
120102d pg 22 |
|
|
Hardening is an immediate process to tempering and to combat wear. |
a)True
120102d pg 22 |
|
|
What is one facto that influences the desired degree of hardness? |
-The composition of the steel
-the recommended quenching temperature -the degree of hardness required -the proper quenching medium 120102d pg 22 |
|
|
What is the most severe quenching media in hardening? |
iced brine
120102d pg 23 |
|
|
What are the two temperature hardening processes that use quenching are? |
-flame hardening
-induction hardening 120102d pg 24 |
|
|
What is flame hardening? |
The process of hardening the outer surface of the material without hardening the material within
120102d pg 24 |
|
|
What is induction hardening? |
The process of hardening through the use of high-frequency magnetic resonance that is set up between a water-cooled magnetic heating coil and the work
120102d pg 26 |
|
|
What are the two types of post weld heat treatments that involve temperatures below the lower critical temperature? |
stress relieving and tempering
120102d pg 27 |
|
|
When stress relieving you must control the rising and lowering of what? |
Temperature
120102d pg 27 |
|
|
What does Tempering do? |
Reduces hardness and promotes toughness
120102d pg 28 |
|
|
The process of tempering involves a thermal cycle after hardening that includes what? |
reheating below lower critical limit
-subsequent cooling in a liquid or in air 120102d pg 28 |
|
|
How is the temper heat determined? |
By the impact the object will be subjected to |
|
|
What is the most common temperature-indicating devices? |
temperature indicating crayons and pellets |
|
|
What is the range of temperature indicating crayons come in? |
40°C-815°C(100°F-1500°F) increments of 50°F |
|
|
Thermocouples provide what when heating treating? |
continuous indication of the material’s temperature |
|
|
What do welding symbols provide? |
A shorthand method for conveying complete welding information from the designer to the welder |
|
|
Weld symbols represents what? |
-types of desired welds |
|
|
Supplementary weld symbols are necessary to what? |
proper weld completion |
|
|
What are three elements of a welding symbol? |
-reference line
-arrow line -basic welding symbols -dimension and other data -supplementary symbols -finish symbols -tail -specifications, process or other references 120102f pg 4 |
|
|
What is the reference line? |
forms the base for welding symbols (always drawn horizontally)
120102f pg 5 |
|
|
What side of the reference line is the |
a)the bottom |
|
|
When is a broken Arrow line used? |
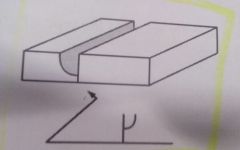
Used with J groove and bevel groove preparation when it is necessary to indicate which member of the joint is to be prepared |
|
|
When drawing a surface welding symbol what side is it always on? |

The arrow side |
|
|
What symbol is an isosceles drawn with the left leg perpendicular to the reference line? |
Fillet weld symbol |
|
What does a dotted U or J indicate? |
The preparation of the groove by the carbon arc-air process |
|
|
When a backing welding symbol is put on a single reference what is indicated by the note? |
whether it should be welded before or after the weld |
|
|
In the AWS letter designation for joints with backing what does M mean? |
materials to be located in the tail |
|
|
In the CSA letter designation what is does each letter mean? |
a)material identification(by means of assigned letter
b)material identification, but remover after welding c)steel or other material as specified d)The same as S, but removed after welding e)Tape f)Flux 120102f pg 12 |
|
|
What are the three contour symbols? |

-flat |
|
|
Each letter mean the contour means it should be finished how?a)M
b)C d)G e)H f)R g)U |
a)machine |
|
|
When reference is made to what a tail added to the end of a reference line?
|
-specification data |
|
|
Multiple reference lines provide information relative to what? |

-the sequence of welding operations |
|
|
What dimensions are shown on a plug and slot weld symbol? |
-diameter of the hole
-depth of the fill -center to centre spacing(pitch) -the degree of countersink 120102f pg 20 |
|
|
Where is the length of a fillet weld located? |
to the right of the weld symbol |
|

What is this symbol? |
plug or slot weld |
|

What is this symbol? |
Square Groove weld |
|
What is this symbol? |
Vee Groove weld |
|
What is this symbol? |
U Groove weld
120102f pg 9 |
|

What is this symbol? |
Bevel Groove weld |
|
What is this symbol? |
J Groove
120102f pg 10 |
|
What does this weld symbol mean? |
the joint requires welding all around one side(or both sides, if shown)
120102f pg 10 |
|

What is this weld symbol? |
Field weld |
|
What is this symbol and what does the R mean? |
Joints with backing |
|
What is this symbols general classification? |
joint with spacer |
|

What does the solid black semi circle in this symbol mean? |
Melt through(full penetration is required) |
|
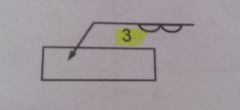
What does this symbol mean? |
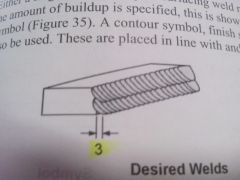
a 3mm deep surface is needed on the whole face of the object |
|
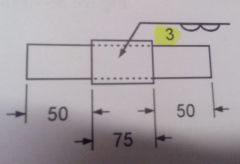
What does this symbol mean? |
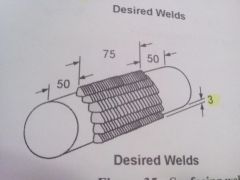
a 3mm deep surface weld is only required to the 75mm section |
|
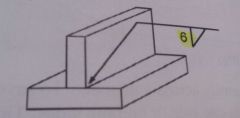
What does this symbol mean? |
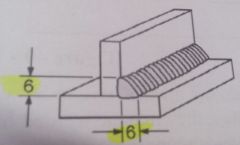
Fillet weld is an equal leg fillet weld |
|
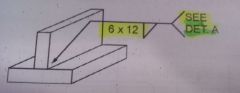
What does this symbol mean? |
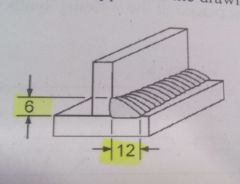
Fillet weld with unequal legs |
|
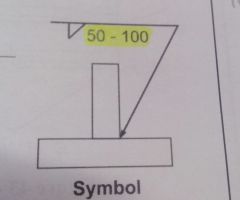
What does this symbol show? |
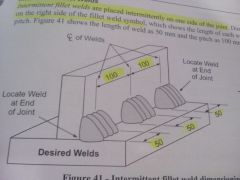
a intermittent fillet 50mm weld with a pitch of 100mm |
|
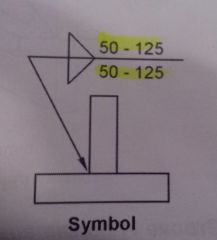
What does this symbol show? |
A chain intermittent 50mm fillet weld with a pitch of 125mm |
|
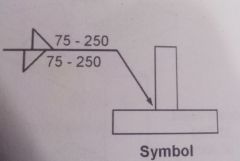
What does this symbol mean? |
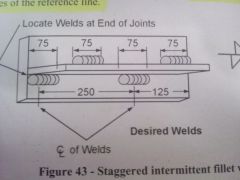
A staggered 75mm fillet weld with a pitch of 250mm |
|
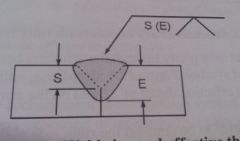
A)What is S? |
A)effective throat size |
|
In this picture what is 3 the measurement of and what is the 50°? |
The root measurement and the bevel angle
120102f pg 25 |
|
What does this symbol indicate? |
direction of radiation(in relation to the weld joint |
|

What does this symbol show? |
the percentage of a weld to be tested with a radiographic test |
|
What does this symbol show? |
weld test is to be done in the field all around the weld with a penetrant test |
|
|
What is distortion the result of?
|
stresses being set up in the work through heating, coupled with factors such as expansion, upset and contraction
120102g pg 6 |
|
|
Where is angular distortion? |
rotation around the weld line
120102g pg 6 |
|
|
Where is it most angular distortion most prominent? |
Tee joints and butt joints that are welded on one side only
120102g pg 6 |
|
|
Angular distortion causes what?
|
Warpage
120102g pg 6 |
|
|
Transverse and longitudinal distortions are sometimes classed as what?
|
Dimensional distortions |
|
|
Where is Transverse distortion? |
perpendicular to the weld line |
|
|
Transverse distortion refers to what?
|
-The tendency in butt joints for the plates to draw together
-can also refer to a change in dimension caused by weld shrinkage 120102g pg 7 |
|
|
How can Transverse distortion be prevented?
|
-Tack welds placed at both ends
-wedge ahead of the joint 120102g pg 7 |
|
|
Where is longitudinal distortion? |
Parallel to the weld line |
|
|
Longitudinal Distortion refers to what?
|
Distortion or shrinkage along the length of the weldment
120102g pg 8 |
|
|
How can you reduce longitudinal distortion? |
-keeping the reinforcement on groove welds
-convexity of fillet welds to a minimum -somewhat controlled if the heat input is evenly distributed on both sides of the weld 120102g pg 8 |
|
|
What are the tree ways of controlling distortion?
|
-mechanical |
|
|
What does pre-setting allow for?
|
shrinkage due to heat in the welds
120102g pg 9 |
|
|
How does pre-bending differ from pre-setting?
|
Pre-bending usually involves using clamps set up along the weld seam
120102g pg 9 |
|
|
What is ridged clamping and fixturing?
|
Weldments are rigidly clamped to heavy slabs or bases during welding
120102g pg 10 |
|
|
What is Residual stress?
|
refers to the buildup of internal stresses within the weld or the parent metal
120102g pg 10 |
|
|
What is a jig?
|
a fixture or device made for the express purpose of aligning and holding parts or components of a weldment
120102g pg 10 |
|
|
What does a jig ensure?
|
-accuracy and dimension
-uniformity of product -cost reduction by speeding up production 120102g pg 10 |
|
|
What is a skeleton frame?
|
is an internal frame or skeleton around which parts are clamped or otherwise held in place for welding
120102g pg 10 |
|
|
What is a strongback?
|
is heavily built, high strength object placed opposite the parts to be welded
120102g pg 11 |
|
|
What are chill strips?
|
Heavy strips of metal that are placed on either side of the weld shoulders and are generally clamped to a heavy backer
120102g pg 12 |
|
|
What are chill strips most often used on?
|
light gauge sheet metal fabrications
120102g pg 12 |
|
|
What are backing strips?
|
strips of metal or other material that are placed at the back (root) side of groove weld joint preparations
120102g pg 13 |
|
|
What is it called when an object it is broken down into parts to be welded?
|
Sub-Assembly
120102g pg 13 |
|
|
What is a welding sequence?
|
The order in which the welds of a structure or project are completed
120102g pg 14 |
|
|
When you are planning a weld so one welds pull is counteracted another welds pull what are you doing?
|
working around the neutral axis
120102g pg 15 |
|
|
What is the neutral axis?
|
The theoretical centre of an object or an imaginary line where neither tension nor compression would exist if the object were bent
120102g pg 15 |
|
|
What is the principle involved in stagger welding?
|
spreading of heat throughout the joint
120102g pg 17 |
|
|
How does skip welding work?
|
weld deposits are applied in increments on each side of the centre of the joint
120102g pg 17 |
|
|
What is the back stepping method of welding?
|
The first weld begins a short distance from the end with the direction of travel towards that end and the following welds use the same process
120102g pg 18 |
|
|
How does Tack welding parts help control distortion?
|
it preheats the metal and holds the joint in alignment
120102g pg 19 |
|
|
What one of the four guidelines when deciding on the number and frequency of tack welds?
|
-thinner the material, closer together the tack welds must be
-Narrow strips require more tack welds than wide strips -flat objects require more tack welds than curved or cylindrical pieces -tack welds should be neat clean and small enough to fuse into the finished weld 120102g pg 19 |
|
|
Why do you decide if pre set is required?
|
to prepare the joint properly so that travel in welding is not slowed down for wide sections or speeded up for narrow sections
120102g pg 19 |
|
|
Why should you avoid to many passes when welding?
|
the heating and cooling leads to higher distortion, particularly on welds that may be subjected to transverse shrinkage
120102g pg 20 |
|
|
To avoid distortion why should you weld at a fast even rate?
|
to keep the heat affected zone narrow and to prevent to much heat from creeping ahead of the weld
120102g pg 20 |
|
|
Local preheating can alleviate what?
|
stress and distortion
120102g pg 20 |
|
|
A water jet cutting machine is a form of what that minimizes distortion?
|
specialized equipment
120102g pg 21 |
|
|
Good welding design uses what?
|
-smooth flowing lines
-few or no rapid changes in direction or cross-section 120102g pg 21 |
|
|
To capitalize on strength and minimize the number of welds what can you use?
|
rolled or formed sections(shapes, beams, and tubing)
120102g pg 22 |
|
|
Welding in the flat position allows what?
|
high heats and larger electrodes allowing for increased welding speed
120102g pg 22 |
|
|
What does the use of rounded corners prevent?
|
Prevents a rapid change in direction of the stress flow lines, which cause a notching effect
120102g pg 22 |
|
|
What can welding across a frame cause?
|
high stresses that can lead to cracking when the frame is stress loaded
120102g pg 22 |
|
|
Why is weld seams that line up a poor design?
|
concentration of heating and cooling is localized to the area where the weld joins
120102g pg 23 |
|
|
What are two design methods of distortion control?
|
-minimizing the number of pieces |
|
|
What are two procedural methods of controlling distortion? |
-planning the welding sequence |
|
|
What are two mechanical methods of minimizing distortion?
|
-pre-setting and pre-bending |
|
|
What are the three weld defects general classifications?
|
–dimensional defects
–structural discontinuities –defective properties 120102h pg 3 |
|
|
Satisfactory welds depend upon maintaining specified dimensions related to what?
|
–preparation and fit up
–the size and shape of completed welds –the finished dimensions of a welded assembly 120102h pg 3 |
|
|
Dimensional defects include what?
|
–poor or incorrect material preparation
–poor or incorrect fit–up –incorrect weld size and profile –distortion and warping 120102h pg 3 |
|
|
When are structural discontinuities in the weld zone generally caused?
|
During the welding process
120102h pg 3 |
|
|
Structural discontinuities can ultimately lead to the failure of the weld while in service.
A)True B)False |
A)True
120102h pg 3 |
|
|
What are two structural discontinuities weld faults?
|
–porosity
–slag inclusion –oxidation –lack of fusion –incomplete penetration –cracking –stray arc strikes 120102h pg 3 |
|
|
How are structural discontinuities normally tested for?
|
Through non–destructive testing
120102h pg 3 |
|
|
What are Defective properties?
|
Any departure from the specified mechanical and chemical requirements
120102h pg 3 |
|
|
What is intergranular carbide precipitation?
|
A serious metallurgical condition that leads to a loss of corrosion resistance in the area adjacent to the weld zone
120102h pg 4 |
|
|
When does the notch effect occur?
|
Whenever a notch is placed or formed within the cross section of a material creating a point of weakness or as a result of:
–poor joint design –poor weld profile –structural discontinuities in the weld zone 120102h pg 6 |
|
|
What are stress flow lines?
|
imaginary lines that run through an object when stress is applied to it
120102h pg 6 |
|
|
When joints are to be made between parts of unequal thickness what should you do to prevent severe notching effect and possible failure of the weldment?
|
taper the transition
120102h pg 7 |
|
|
What is a good taper ratio to use?
|
3:1
120102h pg 7 |
|
|
Excess what in a lap weld can lead to a severe notching effect?
|
–concavity or convexity
120102h pg 8 |
|
|
What on frames and support structures provides a more gradual flow in stress lines?
|
Gussets and corner braces
120102h pg9 |
|
|
Weld craters at the end of a weld should always be?
|
filled and apply a wash coat if necessary
120102h pg 9 |
|
|
What are the three types of faults that occur before welding?
|
incorrect preparation and fit up
–irregularities in the surface of the joint preparation –surface discontinuities 120102h pg 10 |
|
|
What can poor material preparation and fit up cause?
|
–difficulty in maintaining dimensions
–high stresses –structural discontinuities –defective properties within the weld zone 120102h pg 11 |
|
|
Surface discontinuities can lead to what types of weld faults?
|
–sheared surfaces
–flame–cut surfaces –gouged surfaces 120102h pg 11 |
|
|
Depending on the condition of the shear blades various undesirable foreign materials may become embedded on the joint edges possibly leading to what?
|
–porosity
–slag entrapment –lack of fusion 120102h pg 11 |
|
|
How can flame cut surfaces lead to weld faults?
|
notches and irregularities may occur when flame cutting and slag may adhere to these leading to slag entrapment, porosity, lack of fusion or chemical composition defects
120102h pg 11 |
|
|
What can Carbon arc gouging operations leave leading to weld fault defects?
|
deposits of carbon, copper, and/or oxidized metal in the joint area
120102h pg 11 |
|
|
What are the two general types of faults that can occur after welding?
|
–distortion and warpage
–incorrect weld profile 120102h pg 13 |
|
|
What is one cause of distortion?
|
–lack of control over heat imput
–inadequate control of weld pass sequencing –inaccurate preparation of the joint –inadequate control of fit up –incorrect joint design 120102h pg 13 |
|
|
What are the effects of distortion?
|
welded components so badly out of shape that extensive work is needed to straighten them or they may need to be replaced
120102h pg 13 |
|
|
How can you control distortion?
|
–ensuring accuracy during preparation
–strict adherence to welding specifications and procedures –using jigs, braces, and supports when required 120102h pg 13 |
|
|
What are the four types of incorrect weld profiles?
|
–convex reinforcment
–insufficient throat or leg –overlap –undercut 120102h pg 13 |
|
|
The convexity of a weld or individual surface bead shall not exceed 0.0___ times the actual face width of the weld or individual face bead, respectively plus 1.6mm (1/16 inch)
|
0.07
120102h pg 14 |
|
|
The Reinforcement of a groove weld shall not exceed what?
|
3mm
120102h pg 14 |
|
|
Excessive convexity tends to produce what in multi–pass welds?
|
notch effect
120102h pg 15 |
|
|
Why is excessive weld reinforcement undesirable?
|
It can lead to increased shrinkage stresses and to create a notch effect
120102h pg 15 |
|
|
What is a cause of convexity and excessive reinforcement?
|
–travel speed to slow
–incorrect electrode angle –incorrect electrode filler size –incorrect welding technique –insufficient current 120102h pg 15 |
|
|
What are effects of convexity?
|
–distortion
–points of high stress –poor weld profile that can cause a notch effect 120102h pg 15 |
|
|
How can you avoid convexity and excessive reinforcement?
|
–increased travel speeds
–use appropriately sized electrodes and filler metals –use recommended welding techniques –preheat if requires –use the proper current settings for the electrode 120102h pg 15 |
|
|
What is excessive concavity is more often associated with what type of weld?
|
fillet welds
|
|
|
When is a concave fillet weld not a weld fault?
|
when the drawing calls for it
120102h pg 16 |
|
|
What is a cause of insufficient throat or leg size?
|
–travel speed to fast
–insufficient number of passes or layers –incorrect welding technique –excessive groove angle 120102h pg 16 |
|
|
What problems can insufficient throat or leg cause?
|
–weld size does not meet specification
–strength is low –notch effect occurs –excessive groove angle 120102h pg 16 |
|
|
What can you do to remedy insufficient throat or leg?
|
–use proper joint preparation
–maintain correct current settings –use recommended welding techniques –visually inspect weld 120102h pg 16 |
|
|
Poor profile may be detected with visual examination or with a what?
|
With suitable gauges
120102h pg 17 |
|
|
What is overlap?
|
a condition in which an excess of weld metal exists at the toe of a weld beyond the limits of fusion
120102h pg 17 |
|
|
What can cause overlap?
|
–incorrect electrode angle
–incorrect travel speed –excessive passes or layers –incorrect welding techniques 120102h pg 18 |
|
|
What are the effects of overlap?
|
–weld size does not meet specification
–strength is low –Notch effect occurs(in more severe cases) –poor weld metal appearance results 120102h pg 18 |
|
|
What can you do to remedy overlap?
|
–use proper joint preparation
–maintain correct current settings –use recommended welding techniques –use recommended electrode angles –do not over–weld 120102h pg 18 |
|
|
What is under cut?
|
the melting away of the parent material during the welding process
120102h pg 18 |
|
|
Elongated slag lines as a result of undercut left in the weld between the root bead and the fill pass are known as what?
|
Wagon Tracks
120102h pg 19 |
|
|
Undercut of the side walls of a groove weld does not affect the completed weld if what?
|
sufficient care is taken to correct the condition before depositing the next bead
120102h pg 19 |
|
|
What is a cause of undercutting?
|
Poor joint preparation
–incorrect travel speed –improper electrode angles –incorrect electrode selection –improper welding techniques –wrong electrode diameter –improper current settings –impurities –poor joint accessibility 120102h pg 20 |
|
|
What are the effects of undercutting?
|
notch effect
–lack of strength –structural discontinuities –poor weld appearance 120102h pg 20 |
|
|
What is a remedy to undercut?
|
–remove all impurities from the weld zone
–maintain the correct electrode angle angle –use correct settings a and polarity for the electrode –use proper welding technique –remove internal undercut between passes by grinding or melting out with successive passes –external undercut should be filled in with another pass and blended in by grinding if necessary 120102h pg 20 |
|
|
What are the two categories of structural distortion?
|
–surface defects
–internal defects 120102h pg 20 |
|
|
What do surface defects include?
|
–surface porosity
–badly shaped surface ripples –excessive spatter –craters –stray arc strikes 120102h pg 20 |
|
|
The welder is responsible for surface defects as a result of what?
|
improper base metal preparation
–incorrect technique –improper current setting 120102h pg 21 |
|
|
Why are bead irregularities a defect?
|
they constitute a change of cross–section and may create a notch effect
120102h pg 21 |
|
|
What does spatter indicate?
|
improper welding technique
120102h pg 21 |
|
|
What do stray arc flashes cause?
|
They create a quenched, hard brittle condition(often called a metallurgical notch)
120102h pg 21 |
|
|
What is a stray arc flashed area prone to?
|
cracking
120102h pg 21 |
|
|
What are the two categories of internal discontinuities?
|
spherical and laminar
120102h pg 22 |
|
|
Spherical faults are serious if they are what?
|
present in large quantities or are positioned in line
120102h pg 22 |
|
|
What are the three spherical faults?
|
–porosity
–slag inclusion –other inclusions 120102h pg 22 |
|
|
What are the three types of laminar faults?
|
–lack of fusion
–incomplete penetration –cracking 120102h pg 22 |
|
|
What is porosity?
|
gaseous voids trapped within the weld metal
120102h pg 22 |
|
|
What are the causes of porosity?
|
–moistuer in the electrodeor parent metal
chemistry and structure of the parent metal –surface impurities and contaminants –faulty electrodes, fluxes, insufficient gas shielding , trapped slag –incorrect welding techniques 120102h pg 23 |
|
|
What surface contaminants cause porosity?
|
(DOGROMP)
–Dirt –Oil –Grease –Rust –Oxides –Mill scale –Paint 120102h pg 24 |
|
|
Insufficient flux covering in submerged arc welding may cause what?
|
scattered surface porosity
120102h pg 25 |
|
|
How can porosity be avoided?
|
–properly prepare and clean joints
–select correct filler metal –good condition filler metal –set up welding equipment properly –adhere to recommended welding procedures 120102h pg 25 |
|
|
What are slag inclusions?
|
oxides and other non–metallic solids that are sometimes found as elongated or irregular shaped inclusion in welds
120102h pg 25 |
|
|
What can cause slag inclusion?
|
high viscosity of weld metal
–rapid solidification –to low temperature –current setting too low improper manipulation of the electrode –undercut from previous passes –foreign material trapped in weld 120102h pg 26 |
|
|
Slag inclusions have much the same effect as porosity.
a)true b)false |
a)true
120102h pg 26 |
|
|
Majority of slag inclusions may be prevented by what?
|
–proper preparation of the joint
–correct filler metal selection –correct current settings –complete removal of slag between passes –proper welding techniques 120102h pg 26 |
|
|
How can you prevent oxidation on the inside of a pipe or tube?
|
purge it with an inert shielding gas
120102h pg 28 |
|
|
Lack of fusion(cold lapping)describes what?
|
the failure to fuse the weld metal to the base material or adjacent layers of weld metal to each other
120102h pg 28 |
|
|
Lack of fusion is normally only detectable by what non–destructive test?
|
Ultrasonic testing
120102h pg 29 |
|
|
What does incomplete penetration (IP) describe?
|
failure of the deposited weld metal to fuse fully and completely with the parent material at the root of the weld
120102h pg 29 |
|
|
How can you remedy incomplete penetration?
|
–prepare the joint properly
–select correct filler metal –use the correct current settings –use the correct voltage settings –use proper welding technique 120102h pg 30 |
|
|
Why is cracking the most serious of all faults?
|
–difficult to detect
–usually lead to a complete failure of the joint –can occur after all welding operations are complete 120102h pg 30 |
|
|
What are the two categories of cracking causes?
|
–metallurgical
–mechanical 120102h pg 30 |
|
|
What are the metallurgical causes of cracking?
|
–hydrogen–induced cold cracking
–solidification cracking –hot cracking –crater cracking 120102h pg 30 |
|
|
Cold cracks develop when?
|
after the weld metal has cooled(weld metal or HAZ)
120102h pg 31 |
|
|
What steels are more susceptible to cold cracks?
|
higher carbon steels
120102h pg 32 |
|
|
What causes solidification cracking?
|
contraction strains across the weld
120102h pg 32 |
|
|
What causes hot cracking?
|
combined effects of metallurgical and mechanical factors
120102h pg 32 |
|
|
What causes crater cracking?
|
improper termination of the welding arc
120102h pg 32 |
|
|
What is a mechanical cause of a crack?
|
–high restraint on the joint |
|
|
How do you remedy cracks?
|
identify the reason for the crack |
|
|
What are the purposes of hard facing?
|
-combat wear
-prolong the life of the object -reduce costly down time -reduce the cost of replacement parts 120102i pg 2 |
|
|
What is spalling?
|
The breaking away of the weld metal from the base metal
120102i pg 2 |
|
|
What does ABR stand for?
|
Abrasive resistant material
120102i pg 5 |
|
|
In Pulsed DC GMAW surfacing allows for better control of electrode melting rate and bead shape.
True or False |
True
120102i pg 6 |
|
|
What is the advantage of MCAW surfacing?
|
has a large variety of alloy classifications
120102i pg 7 |
|
|
With SAW what are coiled trip electrodes most commonly used for?
|
corrosion resistant surfacing
120102i pg 8 |
|
|
When using SAW for surfacing full properties of the surfacing metal are not attained until when?
|
two or more layers are deposited
120102i pg 8 |
|
|
SMAW surfacing is popular, low cost, and convenient.
true or false |
true
120102i pg 9 |
|
|
What current can be used with SMAW surfacing?
|
DC or AC
120102i pg 9 |
|
|
What positions can SMAW surfacing be used in?
|
all positions
120102i pg 9 |
|
|
GTAW surfacing has what type of deposition rate that produces high quality deposit with minimum dilution and low distortion?
|
low deposition rates
120102i pg 10 |
|
|
Low temperature limits the base metal dilution in what surfacing methods?
|
OAW
120102i pg 10 |
|
|
What is critical when thermal spray surfacing?
|
Distance and heat input
120102i pg 11 |
|
|
How is a hardfacing material determined for a specific task?
|
the type of wear that the base metal is subjected to
120102i pg 12 |
|
|
Define abrasion.
|
a sliding/scraping type of wear that removes metal by gouging or grinding
120102i pg 12 |
|
|
What causes abrasions?
|
continuous exposure of metal parts to rubbing friction against earth, sand, gravel or other gritty substances
120102i pg 12 |
|
|
Define impact.
|
A pounding or battering type of wear that splits, breaks, chips, mushrooms or otherwise deforms the metal surface
120102i pg 13 |
|
|
Define erosion.
|
a gouging type of wear that washes away or grooves out the metal surface
120102i pg 13 |
|
|
What can cause erosion?
|
steam, water, liquids, or solids moving rapidly across or against a metal surface
120102i pg 13 |
|
|
Define Metal to metal wear.
|
the seizing or galling(wearing away by friction) that rips and tears out portions of a metal surface
120102i pg 14 |
|
|
Define corrosion.
|
the type of wear that pits, perforates and eventually dissolves metal parts
120102i pg 14 |
|
|
What can cause corrosion?
|
acid and acid fumes, gas fumes and salts can cause corrosion
120102i pg 14 |
|
|
Define oxidation.
|
a special form of corrosion that takes place when some metals are exposed to a combination of heat and air
120102i pg 15 |
|
|
Define compression?
|
a squeezing type of wear usually cause by a heavy static load or by loads that gradually increase pressure on a metal surface
120102i pg 15 |
|
|
What does thermal shock refer to?
|
cracking or splitting wear caused by exposing metal parts to temperature extremes such as rapid heating and cooling cycles
120102i pg 16 |
|
|
What is the hardest and most abrasive-resistant of all hard surfacing filler metals?
|
tungsten Carbide
120102i pg 19 |
|
|
What filler metal is slightly superior to tungsten carbide for impact resistance?
|
chromium carbide
120102i pg 19 |
|
|
What are martensitic stainless steels filler metal are used for?
|
metal to metal wear applications
120102i pg 19 |
|
|
Semi-austenitic steels are probably the most widely used filler metal.
True or false |
true
120102i pg 19 |
|
|
Austenitic manganese steels filler metals are good alloys of resistance to what?
|
Impact
120102i pg 20 |
|
|
Austenitic Stainless Steels filler metals provide a tough ductile coating with good resistance to what?
|
chipping and corrosion
120102i pg 20 |
|
|
Heat treatable steels are high carbon steels, medium carbon alloy steels or tool and die steels
true or false |
true
120102i pg 20 |
|
|
What filler metal is good for salt water resistance?
|
copper alloys
120102i pg 20 |
|
|
Define dilution?
|
the mixing of the base metal with the hardfacing filler metal
120102i pg 22 |
|
|
What are five common hardfacing problems?
|
-dilution
-spalling -stress failure -underbead cracking -distortion 120102i pg 22 |
|
|
If there is to dilution what can happen to the hardfacing material characteristics?
|
They are watered down by the softer base metal
120102i pg 22 |
|
|
How can you avoid excessive dilution?
|
-use low current settings
-use slower rate of travel -use correct polarity -change welding position -use more overlap between beads -use weave beads -select a shielding gas that produces minimum dilution 120102i pg 22 |
|
|
Define spalling.
|
when the weld metal breaks away from the base metal
120102i pg 23 |
|
|
How can spalling be avoided?
|
-prepare the surface
-Control the cooling rate -limit deposit thickness -if thicker deposit is necessary, build up the object with a filler metal that matches the chemistry of the base metal before hard surfacing -use a base layer for brittle hardfacing deposits -apply a base layer of austenitic stainless steel -when surfacing high manganese steels(12% to 14% manganese), keep interpass temperatures below 260°C(500°F) 120102i pg 24 |
|
|
Define stress failure?
|
occurs when welding stresses are added to parts that contain high retained internal stresses
120102i pg 24 |
|
|
How can stress failures be avoided?
|
-preheat slowly and uniformly
-controlled heating and slow cooling to achieve specified preheat tempuratures -avoid interuptions during the weld process -cool the part slowly and evenly 120102i pg 24 |
|
|
Define underbead cracking.
|
occurs in the base metal just under the weld.cracks may not be visible but can lead to more serious defects such as spalling or weld cracking
120102i pg 25 |
|
|
How can you prevent underbead cracking?
|
make sure material is at 21°C-38°C(70°F-100°F)
-preheat metal to the specified preheat temperature -slow the cooling rate 120102i pg 25 |
|
|
Define Distortion?
|
occurs when unbalanced stresses are created during uneven expansion and contraction
120102i pg 25 |
|
|
What are ways to avoid surfacing distortion?
|
-allow distortion forces to work positively
-balance the stresses -Do not overheat the part -relieve internal stresses 120102i pg 25 |
|
|
What temperature should materials be at before hardfacing?
|
21°C-38°C(70°F-100°F)
120102i pg 27 |
|
|
Medium to high carbon and low alloy steels may require a higher what?
|
preheat
120102i pg 27 |
|
|
How can you control the cooling rate when hardfacing?
|
-preheat the materials
-maintaining the correct interpass temperature -retaining the heat by insulating the surface 120102i pg 28 |
|
|
What does the waffle pattern work well for?
|
earth moving equipment(built up dirt and sand provide additional base metal protection
120102i pg 28 |
|
|
What does the dot pattern works well on?
|
base metals that should not be overheated during welding
|
|
|
What hardfacing pattern is used when larger pieces of ore, rock or slag?
|
Stringer beads |

