![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endocrine and exocrine glands are derived from?
|
embryonic epithelium
|
|
|
Do endocrine or exocrine glands loose conncetion with epithelium of orgin?
|
Endocrine glands
|
|
|
What two ectoderm primordia derive the pituitary gland
|
Oral extoderm (Rathke's Pouch) and Neural Ectoderm (Infundibulum)
|
|
|
What week does Rathke's pouch lose its connection with the oral cavity
|
Week 8
|
|
|
Remnants of Rathke's pouch (pharyngeal hypophysis) may lead to?
|
Carniopharyngioma
|
|
|
Midline invagination of pharyngeal endoderm
|
Thyroid orgins
|
|
|
What week is the thyroid first visible?
|
week 4
|
|
|
Found anywhere along path of thyroid displacement, commonly at base of tongue
|
Aberrant thyroid tissue
|
|
|
Parathyroid gland forms from what pharyngeal pouches?
|
3 and 4; superior pair originate from dorsal wing of 4th pouch and inferior pair form from dorsal wing of 3rd pouch
|
|
|
What week are parathyroid glands recognizable
|
week 5
|
|
|
Thyroid follicular cells are derived from
|
Thyroid diverticulum (endoderm)
|
|
|
Parafollicular cells (C cells) are derived from
|
Neural crest from ultimopharyngeal body
C-cells produce calcitonin which decrease serum Calcium |
|
|
The infundibulum of Rathke's pouch forms
|
Pituitary stalk and posterior lobe
|
|
|
The posterior wall of Rathke's pouch forms
|
Pars intermedia
|
|
|
Superior extension (of anterior lobe) of Rathke's Pouch forms; What week does this form
|
Pars tuberalis; week 11
|
|
|
Anterior wall of Rathke's pouch forms
|
Anterior lobe, pars distalis
|
|
|
Precursor of Pituitary Gland
|
Ectoderm
|
|
|
Precursor of thyroid gland
|
Endoderm of pharynx, displaced ventrally (C cells from neural crest)
|
|
|
Precursor of Parathyroid gland
|
Endoderm of pharynx displaced ventrally
|
|
|
Precursor of Adrenal Gland
|
Mesoderm (Cortex) (the medulla is from neural crest)
|
|
|
The fetal adrenal cortex is stimulated by
|
HcG from the trophoblasts
|
|
|
When does the definitive adrenal gland reach normal size?
|
when the Child is 2
|
|
|
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
|
enzyme (commonly 21-hydroxylase) needed to make cortisol and/or aldosterone is mutated so steroid pathway is shunted toward androgens --> enlarged adrenal cortex (due to incr ACTH), boys get early devo of secondary sex characteristics, girls get enlarged clitoris/ambiguous genitalia
|
|
|
At what week is LH/FSH, GH present
|
week 10
|
|
|
What week is the Pouch connection with oral cavity lost?
|
week 8
|
|
|
At what week are the thyroid follicles visible?
|
Week 10
|
|
|
What week is thyroid hormone produced?
|
week 12
|
|
|
What week does the throglossal duct close?
|
Week 11
|
|
|
At what week does the adrenal cortex forn
|
Week 4
|
|
|
A cells
|
Glucagon
|
|
|
B cells
|
Insulin
|
|
|
D cells
|
Somatostatin
|
|
|
F cells
|
Pancreatic Polypeptide
|
|
|
Chief cells in parathyroid
|
More abundant than oxyphil cells
Make PTH |
|
|
Follicular cells histology
|
Simple cuboidal wall of colloid follicle
|
|
|
Histology of thyroid with low TSH
|
squamous epithelium, high colloid (colloid goiter)
|
|
|
Histology of thyroid with High TSH
|
Columnar epithelium, low colloid (parenchymatous goiter)
|
|
|
Zona glomerulosa
|
primary controlled by renin angiotensin
Secretes aldosterone |
|
|
Zona fascuculata
|
Controlled by ACTH and CRH
Secretes cortisol and sex hormones |
|
|
Zona Retucularis
|
Stains dark
Controlled by ACTH and CRH Secretes Sex hormones |
|
|
Adrenal Medulla
|
Controlled by Pre-ganglionic sympathetic fibers
Secretes Norepinephrine and Epinephrine |
|
|
For group 1 hormones (aka steroids, iodothyronines)
List: solubility, transport, 1/2 life, receptor location, and mediator |
Lipophilic
Transport proteins Long (hrs-days) Intracellular receptor Receptor-hormone complex |
|
|
For Group 2 hormones (polypeptides, proteins, catecholamines, glycoproteins)
List: solubility, transport, 1/2 life, receptor location, and mediator |
Hydrophilic
NO transport proteins Short half life Plasma membrane receptor cAMP, cGMP. Ca++,kinase cascades |
|
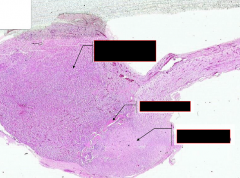
List the parts of the pituitary
|
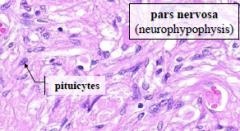
From top to bottom:
Pars distalis (adenohypophysis) (more blood vessels) Pars intermedia Pars nervosa (neurohypophysis) (has pituicytes present) |
|

|
Pancreatic islet (of Langerhans)
|
|
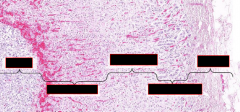
|
From left to right: medulla, zona reticularis, zona fasciculata, zona glomerulosa, capsule
|
|
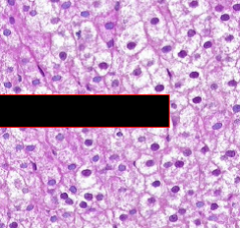
What part of the adrenal cortex?
|
Zona fasciculata
|
|
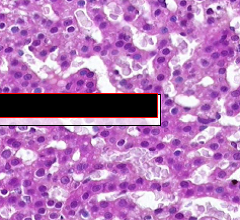
What part of the adrenal cortex?
|
Zona Reticularis
|
|
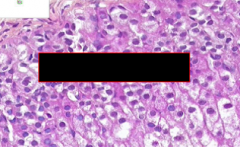
What part of the adrenal cortex?
|
Zona Glomerulosa
|
|
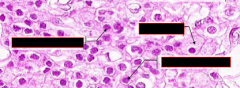
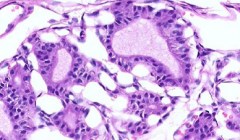
Name cells from left to right
|
In parathyroid
Two Chief cells Oxyphil cell |
|
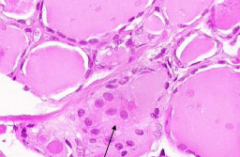
In thryroid
|
C-cell cluster
Pink centers are colloid that are surrounded by follicular cells |
|
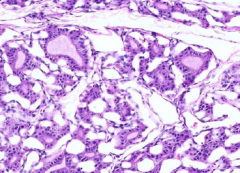
follicular epithelium?
amount of colloid? Treatment? |
Columnar (normal is cuboidal)
Low colloid Treated with propylthiouracil (blocks thyroperoxisase activity) |
|
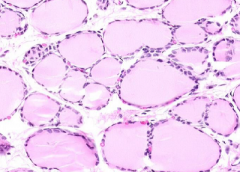
follicular epithelium?
amount of colloid? Treatment? |
Squamous
High colloid One month after pituitary removal (no TSH-->no T4 release from thyroid colloid) |

