![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lamarck's inheritance of acquired characteristics
|
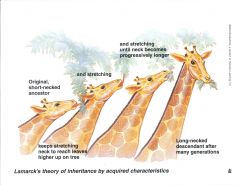
new characteristics arise because of needs and, somehow, the characteristics are passed on
|
|
|
Artificial Selection
|
sweeter corn or seedless watermelon
|
|
|
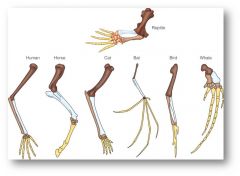
Homologous structures
|
look different but are actually the same
|
|
|
Homologous structures
|
|
|
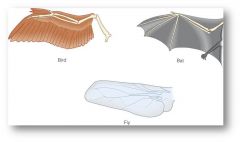
Analogous structures
|
|
|
Analogous structures
|
look the same but are actually different
|
|
|
Convergent Evolution
|
unrelated animals no where near each other have evolved to occupy similar environments
|
|
|
Vestigial structures
|
remnants of structures
|
|
|
Genetic variation
|
Individuals in all species’ possess variations, such as size, speed, agility, color, etc.
|
|
|
Overproduction of species
|
More animals are born than reach maturity, yet the adult population remains constant.
|
|
|
Struggle for existence
|
Competition for resources results in high mortality rate, which limits population size.
|
|
|
Differential survival
|
favorable variation may give a “competitive edge” in getting resources.
|
|
|
Adaptation
|
Specialized features that allow an organism to excel in its environment
|
|

|
Camouflage, is an example of an adaptation.
|
|
|
How does variation occur?
|
Sexual recombination through reproduction and mutations
|
|
|
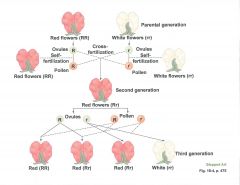
Gregor Mendel
|
|
|
genes
|
hereditary determinants in all organisms.
|
|
|
Mutation
|
random change in genetic information resulting from chemicals, radiation, extreme temperatures, or randomness.
|

