![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Frequency |
The amount of waves passing a point each second. |
|
|
|
Period |
The length of time it takes one wave to pass a given point. |
|
|
|
Wavelength |
The distance from a point on the wave from it's rest position |
|
|
|
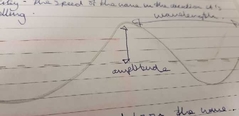
Amplitude |
Maximum distances of a point on the wave away from it's rest position. |
|
|
|
Velocity |
The speed of the wave in the direction it's travelling. |
|
|
|
Transverse wave |
Up and down the wave. |
|
|
|
Longitudinal wave |
Backwards and forwards the wave. |
|
|
|
Law of Reflection |
Angle of incidence is the same as angle of reflection. |
|
|
|
What is Refraction? |
Bending of a wave when it enters a medium where it's speed is different. |
|
|
|
What is the total internal reflection? |
Happens when light travels from a dense material to a less dense material. |
|
|
|
Reflected |
The wave bounces off. |
|
|
|
Transmitted |
The wave passes through the material and is not absorbed or reflected. |
|
|
|
Absorbed |
The wave disappears as the energy is transferred to a new material. |
|
|
|
Equation for calculating wave: |
Speed(m/s) = distance(m) ÷ time(s) |
|
|
|
Equation that links wave frequency and wavelength: |
Wavespeed(s) = frequency(Hz) × wavelength(m) |
|
|
|
Conditions for total internal reflection: |
-Angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. -The index of refraction must decrease across the boundary in the direction of light refraction. |
|
|
|
Uses of Total internal reflection: |
-Periscope. - optical fibre. -relfectors. |
|

