![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Three types of ways we get our water supply? |
A vehicle Reticulated supplies (hydrants) Static supplies (dam) |
|
|
Types of mains? |
Trunk mains - original sources, dams to reservoirs, 3m in diameter Distribution mains - reservoirs to subdivided areas - suburbs - 450mm Service mains - feed off distribution and supply individual streets and structures, supply water to meet consumers - 75mm to 150mm |
|
|
Consider two factors when using mains? |
Pressure and flow |
|
|
Types of hydrants and what is the distance between hydrants? |
Millcock Rural standpipe L type Pillar
City shopping areas - 50 to 100m Residential or suburban - 150 to 200m Rural - >200 m |
|
|
Below ground hydrant? |

Ground ball hydrant |
|
|
Division A standpipe? |
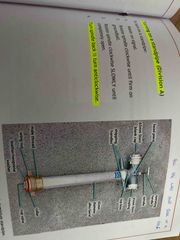
Spindle thread is fine therefore requires more turns |
|
|
Division B standpipe? |
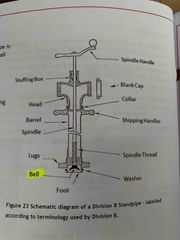
Rotate clockwise slowly three times and bell will make full contact to dome of ground ball
Spindle thread is coarse therefore requires less turns |
|
|
Black top hydrant? |
We don’t use, high pressure or dry. |
|
|
Two types of Hydrant indicators? |
Metal - nailed to wooden poles Vinyl - spray adhesive to metal or concrete poles |
|
|
Primary and secondary markers? How far above the ground? |
Primary - indicate a hydrant between yourself and the indicator - square shape Secondary - indicate a hydrant beyond the indicator - rectangle shape Needs to be 2m high |
|
|
Hydrants are used to supply? |
Supply water to a fire appliance or to a branch via a hose |
|
|
How to ship a standpipe? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Inspection and testing of hydrants? |
Ensure hydrant marking is readily visible Below ground hydrants ensure lid is accessible Check hydrant box and clear debris if needed Slowly open and flush hydrant slowly close hydrant |
|
|
Shipping a standpipe? |
1. Don appropriate PPC and PPE 2. Remove cover from fire plug/ground ball check no snakes, spiders or insects when removing hydrant pit 3. Remove any obstruction from hydrant pit 4. Grasp spindle with one hand and the bottom boss with the other hand 5. Place the standpipe across your knee whilst kneeling on one leg 6. Check spindle is fully up, the wing nut/lugs are fully down and the washer is present 7. Place standpipe in fire plug/ground ball 8. Turn clockwise to engage wing nut/lugs under clutches of ground ball 9. Lift standpipe vertically to ensure wing nut/lugs are locked under the clutches 10. Maintain standpipe in a vertical position with one hand and rotate clockwise using the shipping handles until fully engaged 11. Finally go down on one knee, harden the joint with both hands on handles. Always rotate the head piece clockwise in order to avoid the possibility of disengaging the wing nut/lugs from hydrant clutches 12. Flush standpipe before connecting the hose to the standpipe |

