![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Water Pollution
|
contamination of water bodies
|
|

Fecal Coliform
|
most common microbiological contaminants of natural waters. Fecal coliform live in the digestive tracks of warm-blooded animals, including humans, and are excreted in the feces
|
|
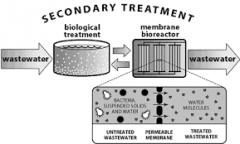
Secondary Treatment
|
treatment of sewage effluent by biological methods following sedimentation
|
|
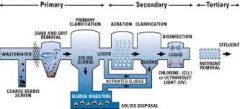
Wastewater Treatment
|
process to convert wastewater into an effluent that can be either returned to the water cycle with minimal environmental issues or reused
|
|
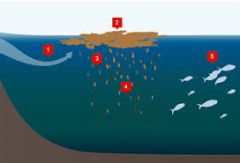
Dead Zone (in a body of water)
|
hypoxic (low-oxygen) areas in the world's oceans and large lakes, caused by excessive nutrient pollution from human activities
|
|
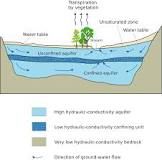
Aquifer
|
underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock, rock fractures or unconsolidated materials
|
|
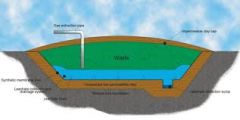
Leachate
|
water that has filtered through a solid and drained out some of the constituents
|
|

Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD)
|
amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic biological organisms in a body of water to break down organic material present
|
|
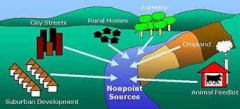
Point Source Pollution
|
any single identifiable source of pollution from which pollutants are discharged, such as a pipe, ditch, ship or factory smokestack
|
|
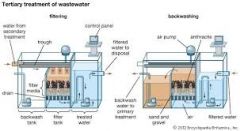
Tertiary Treatment |
final treatment stage to further improve the effluent quality before it is discharged to the receiving stream |
|

Runoff |
flow of water that occurs when excess stormwater, meltwater, or other sources flows over the earth's surface |
|
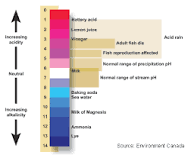
pH |
numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution |
|
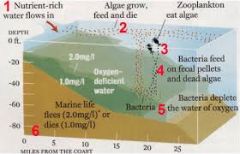
Hypoxia |
oxygen deficiency in a biotic environment |
|

Environmental Law |
network of treaties, statutes, regulations, and common and customary laws addressing the effects of human activity on the natural environment |
|

Non-Point Source Pollution |
rainfall or snowmelt moving over and through the ground |
|

Effluent Discharge |
outflowing of water or gas from a natural body of water, or from ahuman-made structure |
|
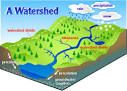
Watershed |
area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas |
|

Dissolved Oxygen |
amount of oxygen that is present in the water |
|

Methane Gas |
gas from sludge digester in wastewater treatment plant |
|

Contaminants (water) |
undesirable material that makes water unfit |
|
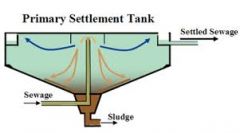
Primary Treatment |
temporarily holding the sewage in a basin where heavy solids can settle to the bottom |
|
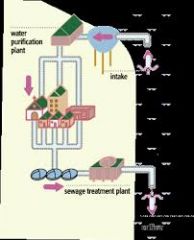
Water Renovation and Conservation |
water is treated and returned to the environment |
|
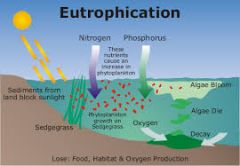
Eutrophication |
enrichment of an ecosystem with chemical nutrients, typically compounds containing nitrogen, phosphorus, or both |
|

Chlorination |
process of adding chlorine to water; is used to kill certain bacteria and other microbes |
|
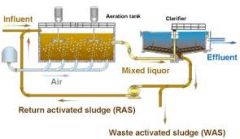
Activated Sludge
|
microorganisms cultivated in the treatment process to break down organic matter into carbon dioxide, water, and other inorganic compounds |

