![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Water Quality |

Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, biological, and radiological characteristics of water. It is a measure of the condition of water relative to the requirements of one or more biotic species and or to any human need or purpose |
|
|
Fecal Coliform |

is a facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, gram-negative, non-sporulating bacterium. |
|
|
Secondary Treatment |
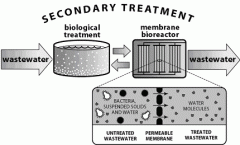
the further treatment of sewage effluent by biological methods following sedimentation. |
|
|
Wastewater Treatment |

Wastewater treatment is a process to convertwastewater - which is water no longer needed or suitable for its most recent use - into an effluent that can be either returned to the water cycle with minimal environmental issues or reused. |
|
|
Dead Zone |
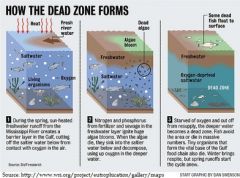
Dead zones are hypoxic (low-oxygen) areas in the world's oceans and large lakes, caused by "excessive nutrient pollution from human activities coupled with other factors that deplete the oxygen required to support most marine life in bottom and near-bottom water. (NOAA)." |
|
|
Aquifer |
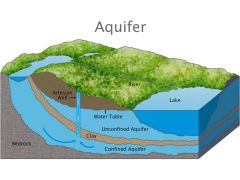
a body of permeable rock that can contain or transmit groundwater. |
|
|
Leachate |

water that has percolated through a solid and leached out some of the constituents. |
|
|
Biological Oxygen Demand |
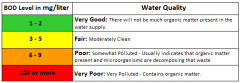
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic biologicalorganisms in a body of water to break down organic material present in a given water sample at certain temperature over a specific time period. The term also refers to a chemical procedure for determining this amount. |
|
|
Point Source Pollution |

Point source pollution, on the most basic level, is water pollution that comes from a single, discrete place, typically a pipe. The Clean Water Act specifically defines a "point source" in section 502(14) of the Act. |
|
|
Tertiary Treatment |
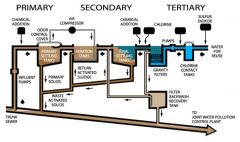
Tertiary treatment is the advanced treatment process, following secondary treatment of waste water, that produces high—quality water.Tertiary treatment includes removal of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen and practically all suspended and organic matter from waste water. |
|
|
Runoff |
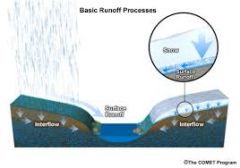
the draining away of water (or substances carried in it) from the surface of an area of land, a building or structure, etc. |
|
|
pH |
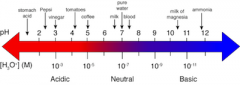
In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. |
|
|
Hypoxia |
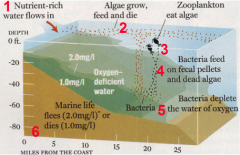
deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues. |
|
|
Environmental Law |

Environmental law is a body of law, which is a system of complex and interlocking statutes, common law, treaties, conventions, regulations and policies which seek to protect the natural environment which may be affected, impacted or endangered by human activities. |
|
|
Non-Point Source Poll |
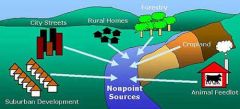
Non-point source (NPS) pollution refers to both water and air pollution from diffuse sources. Non-point source water pollution affects a water body from sources such as polluted runoff from agricultural areas draining into a river, or wind-borne debris blowing out to sea. |
|
|
Effluent Discharge |

The Compact Oxford English Dictionary defines effluent as "liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea". Effluent in the artificial sense is in general considered to be water pollution, such as the outflow from a sewage treatment facility or the wastewater discharge from industrial facilities. |
|
|
Watershed |
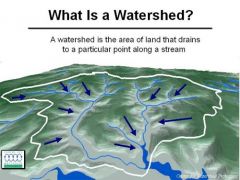
an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. |
|
|
Dissolved Oxygen |
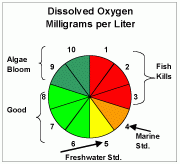
Dissolved oxygen (DO) refers to microscopic bubbles of gaseousoxygen (O2) that are mixed in water and available to aquatic organisms for respiration—a critical process for almost all organisms. Primary sources of DO include the atmosphere and aquatic plants. |
|
|
Methane Gas |
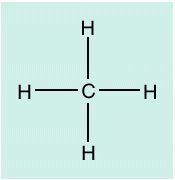
a colorless, odorless flammable gas that is the main constituent of natural gas. It is the simplest member of the alkane series of hydrocarbons. |
|
|
Contaminants |
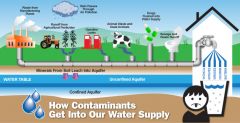
contaminant. CloseStyle: MLA APA Chicago. noun con·tam·i·nant \kən-ˈta-mə-nənt\ : something that makes a place or a substance (such as water, air, or food) no longer suitable for use : something that contaminates a place or substance. |
|
|
Primary Treatment |
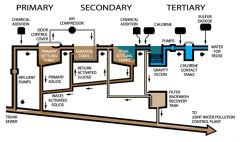
involves basic processes to remove suspended solid waste and reduce its biochemical oxygen demand |
|
|
Water Renovation |

to restore to good condition; make new or as if new again; repair. |
|
|
Water Conservation |

Water conservation refers to the preservation, control and development of water resources, both surface and groundwater, and prevention of pollution. |
|
|
Eutrophication |

excessive richness of nutrients in a lake or other body of water, frequently due to runoff from the land, which causes a dense growth of plant life and death of animal life from lack of oxygen. |
|
|
Chlorination |
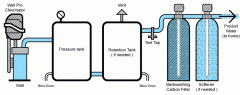
chlorination - Dictionary definition and meaning for wordchlorination. (noun) the addition or substitution of chlorine in organic compounds Definition. (noun) disinfection of water by the addition of small amounts of chlorine or a chlorine compound. |
|
|
Activated Sludge |
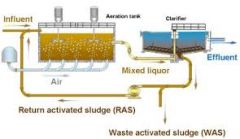
aerated sewage containing aerobic microorganisms that help to break it down. |

