![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the: Source Watershed Tributary Mouth Confluence |
Source= Where the river starts Watershed= Boundary of a drainage basin Tributary= Stream or small river that flows into a bigger one Mouth= End of river Confluence= A small river joins a larger one |
|
|
Drainage Basin/ Hydrological Cycle |
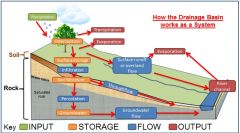
|
|
|
Types of Erosion |
Abrasion (Corrasion)- Rubbing Attrition- Smashing Solution (Corrosion)- Dissolving Hydraulic Action- Pressure/Force |
|
|
Transport Processes |
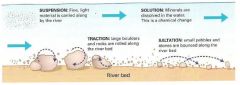
Traction- Rolling Saltation- Bouncing Suspension- Light material carried Solution- Dissolved material |
|
|
Concept of Deposition |
When a river loses its energy to carry material it deposits its load. Heaviest material is put down first and the lightest last. |
|
|
Key Terms: Gradient Velocity Discharge Channel Shape Valley Shape |
Gradient= Slope/angle of river Velocity= Speed of which the river flows Discharge= Volume of water passing a particular point in a given time (cumecs) Channel Shape= The bit the river actually occupies Valley shape= The whole valley, not just the river |
|
|
The Long Profile of a River |
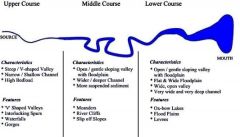
|
|
|
Formation of a Waterfall |
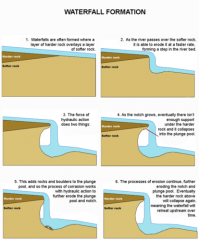
|
|
|
V Shaped Valley and Interlocking Spurs |
Steep sided valleys from vertical erosion. River has to go around hard rock and the vertical in the upper course creates a V-shaped valley. |
|
|
Meanders |
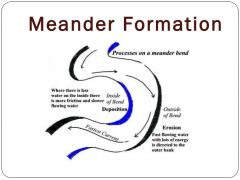
|
|
|
Ox-Bow Lakes |
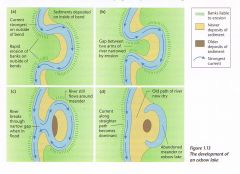
|
|
|
Levees |
In the lower course of the river some meanders form levees. Levees are high banks of silt along the banks of a river. Gradually, the river bed increases until its higher than the land around. After repeated floods the height of the levee increases. Levees are formed by deposition. It deposits the heaviest material first. |
|
|
Floodplain |
The floodplain is very fertile for crops because when the river floods it leaves behind a silt called alluvium. Many thousands of years ago the sea level was higher. This meant that the rivers didn't have to cut down so far to reach the sea. Due to the sea level dropping and the river having to cut down further it has left terraces in the floodplain. |
|
|
Estuaries |
Wide, deep mouth. These are very useful for shipping, so they usually have ports and factories along them. |
|
|
Deltas |
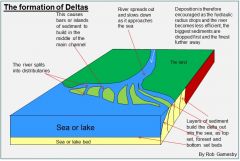
|
|
|
Volume |
Amount of water in the river system. Use a cross section of the river, measure in square meters. |
|
|
Flood Hydro-graphs |
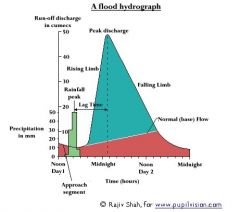
There is less lag time in urban areas as there are more impermeable surfaces such as brick and glass. |
|
|
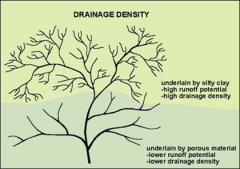
High Drainage Density |
|

