![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
392 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Water rights to a water supply that is acquired for the beneficial use of water by following a specific legal procedure are called? |
Appropriative |
|
|
|
A natural underground layer of porous, water bearing materials usually capable of yielding a large amount of water is called? |
An Aquifer |
|
|
|
A connection between a drinking water system and an unapproved or non-potable water supply is called? |
Cross-connection |
|
|
|
The theoretical time it takes for a small amount of water to pass through a tank at a given flow rate is called? |
Detention Time |
|
|
|
The drop in the water table or level of water in the ground when water is being pumped is called? |
Drawdown |
|
|
|
When is the drawdown taken? |
When the pump is running |
|
|
|
What do you call the process by which water becomes a gas? |
Evaporation |
|
|
|
The process by which water vapor passes into the atmosphere from living plants is call? |
Evapotranspiration or Transpiration |
|
|
|
The actual time in hours, minutes, or seconds that a small amount of water is in a basin or tank is called? |
Detention Time |
|
|
|
A detailed description of all underground features discovered during the drilling of a well is called? |
Geological Log |
|
|
|
What do you call the process of evaporation of water into the air and it's return to earth by precipitation? |
Hydrologic Cycle |
|
|
|
Water that contains objectionable pollution, contamination, minerals, or infective agents is called? |
Non-potable Water |
|
|
|
Water that is free from objectionable tastes, odors, color, and turbidity and is at a desirable temperature is called? |
Palatable Water |
|
|
|
Disease causing organisms are called? |
Pathogens |
|
|
|
Water that does not contain objectionable pollution, contamination, minerals, or infective agents and is considered safe to drink is called? |
Potable Water |
|
|
|
Water rights which are acquired by diverting water and putting it to use in accordance with specific procedures are called? |
Prescriptive Rights |
|
|
|
Water rights which are acquired together with title to the land bordering a source of surface water are called? |
Riparian Rights |
|
|
|
When was the Safe Drinking Water Act put into law? |
1974 |
|
|
|
When was the SDWA last amended? |
1996 |
|
|
|
The annual quantity of water that can be taken from a source of supply over a period of years without depleting the source permanently is called? |
Safe Yield |
|
|
|
A condition that occurs in water tanks or basins that causes the water entering the tank to flow on a direct path from the inlet to the outlet is called? |
Short-Circuiting |
|
|
|
What is one method of fixing the problem in question 21? (Short-Circuiting) |
Adding Baffles to the tank or basin |
|
|
|
The formation of separate layers of temperature, plant, or animal life in a lake or reservoir is called? |
Stratification |
|
|
|
The cloudy appearance of water caused by the presence of suspended and colloidal matter is called? |
Turbidity |
|
|
|
Nephelometric units are used to measure what parameter? |
Turbidity |
|
|
|
What is the upper surface of the zone of saturation of groundwater in an unconfined aquifer called? |
Water Table |
|
|
|
The quantity of water that can be collected for a given use from surface or ground water sources is called? |
Yield |
|
|
|
Approximately how many feet of water evaporate annually from oceans? |
6 Feet |
|
|
|
What percent of treated water has groundwater as it's supply source? |
25% |
|
|
|
What percent of treated water has surface water as it's supply source? |
75% |
|
|
|
When do reservoirs or lakes destratify? |
Spring or Fall |
|
|
|
Do algal blooms occur during the winter? |
Yes, but are less likely to occur |
|
|
|
The porous materials just above the water table containing water is called? |
Capillary Fringe |
|
|
|
A branch of medicine which studies epidemics is called? |
Epidemiology |
|
|
|
The largest cause of water borne illnesses in the United States is? |
Cross Connection |
|
|
|
Name five physical characteristics of water? |
Color, Taste, Odor, Turbidity, and Temperature |
|
|
|
A water system that has at least 15 service connections or regularly serves an average of at least 25 individuals daily at least 60 days of the year is called? |
Public Water System |
|
|
|
A water system that has at least 15 service connections used by year-round residents or regularly serves at least 25 year round residents is called? |
Community Water System |
|
|
|
Any public water system that is not a community water system is classified as a? |
Non-Community Water System |
|
|
|
The three basic objectives of a water treatment plant operator are? |
Produce potable and palatable water at a reasonable cost |
|
|
|
What is the first priority for operating a water treatment? |
Production of potable water free of harmful bacteria and toxic materials; Health and Welfare of the consumer |
|
|
|
The Gathering of a liquid or gas on the surface or interface Zone of another material is called? |
Adsorption |
|
|
|
What do you call an electrical system designed to prevent rust, corrosion, or pitting of metallic surfaces that are in contact with water or soil? |
Cathodic Protection |
|
|
|
What is the indicator organism that is found in the intestines of warm-blooded animals including man and also in Plants, soil, air, and water? |
Coliform |
|
|
|
The development of vertical mixing within a lake or Reservoir to eliminate separate layers of temperature, plant, or animal life is called? |
Destratification |
|
|
|
In direct filtration, which treatment process is omitted? |
Sedimentation |
|
|
|
Reservoirs and lakes that are rich in nutrients and very productive in terms of aquatic animal and plant life are called? |
Eutrophic |
|
|
|
The vertical distance in feet equal to the pressure (PSI) at a specific point is called? |
Head |
|
|
|
What do you call the lowest layer in a thermally stratified lake or Reservoir? |
Hypolimnion |
|
|
|
What do you call the portion of a body of fresh water extending from the Shoreline Lakeward to the limit of occupancy of rooted plant life? |
Littoral Zone |
|
|
|
What is the strip of land along the shoreline between the high and low water levels? |
Littoral Zone |
|
|
|
A reservoir or lake that has a moderate amount of nutrients is called? |
Mesotrophic |
|
|
|
Methyl Orange is used to measure what water parameter? |
Alkalinity |
|
|
|
What is the middle layer of a thermally stratified lake or Reservoir called? |
Metalimnion or Thermocline |
|
|
|
Lakes and reservoirs that do not freeze during the winter and are relatively deep and generally undergo a single stratification and mixing cycle are called? |
Monomictic |
|
|
|
Lakes and reservoirs that are nutrient-poor and contain little plant or aquatic plant or animal life are called? |
Oligotrophic |
|
|
|
What do you call the spontaneous mixing of all layers of water in a thermally stratified lake or Reservoir? |
Destratification; Overturn; Turnover |
|
|
|
What term is used to express the intensity of the basic or acidic condition of water (liquid)? |
pH |
|
|
|
The logarithm (base ten) of the reciprocal of the hydrogen ion activity is called? |
pH |
|
|
|
What is the numerical range of pH? |
0-14 |
|
|
|
What do you call the process by which organisms with the aid of chlorophyll (green plant enzyme) convert carbon dioxide (CO2) and inorganic substances into oxygen and additional plant material, using sunlight for energy? |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
|
What compounds react with chlorine to form THMs? |
Naturally occurring volatile organics |
|
|
|
Why is air added to a lake or Reservoir? |
To replenish DO |
|
|
|
A flat, white disc lowered Into Water by a rope until it is just barely visible is called? |
Secchi Disc |
|
|
|
The point at which the secchi disc is barely visible is called? |
Secchi Disc Transparency |
|
|
|
The minimum odor of a water sample that can be detected after successive dilutions with odorless water is called? |
Threshold Odor Number (TON) |
|
|
|
The greatest dilution of a sample with odor free water that still yields a just-detectable odor is called? |
TON |
|
|
|
Small, usually microscopic animals (such as protozoans) found in lakes and reservoirs are called? |
Zooplankton |
|
|
|
What change takes place in a lake or Reservoir during daytime when there is an algal bloom? |
ph goes up |
|
|
|
After Sundown, what change takes place in a lake or Reservoir that has experienced an algal bloom? |
pH goes down |
|
|
|
When is the pH at its lowest level in a lake or Reservoir? |
Just before sunrise (5 AM, 6 AM) |
|
|
|
After Sundown, plants give off carbon dioxide which drastically reduces the dissolved oxygen level in a lake or Reservoir. The oxygen depletion can cause what event? |
Fish Kill |
|
|
|
Regulations enacted for land areas that surround a source of water are called? |
Watershed |
|
|
|
What is another name for copper sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4 5H20)? |
Bluestone |
|
|
|
What affects the efficiency of Bluestone? |
Alkalinity, pH, suspended matter, water temperature |
|
|
|
If the total alkalinity of a lake or Reservoir is less than 50 mg/L, the effective dosage of copper sulfate is? |
0.9 lb/acre-foot |
|
|
|
If the total alkalinity of a lake or Reservoir is more than 50 mg/L, the effective dosage of copper sulphate is? |
5.0 lbs/acre-foot |
|
|
|
Which acid when added to Bluestone, will delay the precipitation of copper sulfate from the Bluestone solution? |
Aliphatic Hydroxy Acid (such as citric acid) |
|
|
|
What term is used to define a well or underground basin, in which the water is under pressure greater than atmospheric and will rise above the level of its upper confining surface if given the opportunity? |
Artesian |
|
|
|
When is the drawdown of a well taken? |
When the pump is running |
|
|
|
What term is used to define a detail evaluation and/or inspection of a source of water supply and All conveyances, Storage, treatment and distribution facilities to ensure protection of the water supply from all pollution sources? |
Sanitary Survey |
|
|
|
The Gathering of a gas or liquid on the surface or interface zone of another material is called? |
Adsorption |
|
|
|
What do you call small, usually microscopic plants, such as algae, found in lakes and reservoirs? |
Phytoplankton |
|
|
|
What do you call small, usually microscopic animals (such as protozoans) found in lakes or reservoirs? |
Zooplankton |
|
|
|
When a reservoir freezes, what action is necessary to protect structures and embankments? |
Lower the Reservoir water level |
|
|
|
When a reservoir freezes, ball floats for level control become virtually useless. What other level device can be used in place of the ball floats? |
Blubber tube or manometer |
|
|
|
To protect the blubber tube from Ice formation, the tube should be equipped with what device? |
Pyrotenax Cable (heating tape) |
|
|
|
What type of device is usually used for withdrawing water from a lake or Reservoir? |
Multi-level intake |
|
|
|
Lakes or reservoirs are classified according to what parameter? |
Depth |
|
|
|
What type of lakes or reservoirs are operators more likely to encounter? |
2nd Order Classification |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a screen or trash rack on a multi-level intake structure? |
Prevent fish, leaves, debris, etc from entering the WTP |
|
|
|
How can you minimize the entrance of silt into the intake system of a Reservoir? |
Install Baffles |
|
|
|
What do you call the clumping together of very fine particles into larger particles (floc) after the addition of a chemical? |
Coagulation |
|
|
|
Water Treatment Plant operators are mainly concerned with particles that have what type of charge? |
Negative Charge |
|
|
|
The capacity of water to neutralize acid is called? |
Alkalinity |
|
|
|
What parameter is measured when water is titrated with 0.2 N H2S04 to a pH of 4.5? |
Total Alkalinity |
|
|
|
Water color that includes not only the color due to substances in the water but suspended matter as well is called? |
Apparent color |
|
|
|
Water color of a sample that has had turbidity removed is called? |
True Color |
|
|
|
A polymer that has a positive charge is? |
Cationic Polymer |
|
|
|
A polymer that is often used as a filter Aid is called? |
Nonionic Polymer |
|
|
|
Where is the filter aid added? |
Filter influent |
|
|
|
A negatively charged polymer is called? |
Anionic |
|
|
|
A collection of individual samples obtained at regular intervals, usually every one or two hours during a 24-hour period and combined in proportion to the flow is called? |
Composite sample |
|
|
|
A contaminant formed by the reaction of disinfection chemicals with other substances in the water being disinfected is called? |
Disinfectant By-Product (DBP) |
|
|
|
The Gathering Together of fine particles after coagulation to form larger particles by a process of gentle mixing is called? |
Flocculation |
|
|
|
A single sample of water collected at a particular time and place, which represents the composition of the water only at that time and place, is called? |
Grab Sample |
|
|
|
What test is used to determine the correct chemical dosage during water treatment? |
Jar Test |
|
|
|
The sum of the atomic weights of the elements in a compound is used to determine? |
Molecular Weight |
|
|
|
A sample portion of water that is as nearly identical in content and consistency as possible to that in the larger body of water being sampled is called? |
Representative Sample |
|
|
|
A condition that occurs in tanks or basins when some of the flowing water entering a tank or basin flows along a nearly direct pathway from the inlet to the outlet is known as? |
Short-Circuiting |
|
|
|
The Cloudy appearance of water caused by the presence of suspended and colloidal matter is called? |
Turbidity |
|
|
|
What parameter is obtained when you measure the optical property of water based on the amount of light reflected by suspended particles? |
Turbidity |
|
|
|
What are the three types of solids found in water? |
Settable, Suspended, and Dissolved |
|
|
|
When the coagulant sodium aluminate is added to water what happens to the pH? |
pH goes up |
|
|
|
When aluminum sulfate (alum) is added to the water what happens to the pH? |
pH goes down |
|
|
|
When the alum dosage is decreased what generally happens with the lime dosage? |
Lime dosage decreases |
|
|
|
When the alum dosage is increased what normally takes place with the lime dosage? |
Lime Dosage Increases |
|
|
|
A physical and chemical reaction occurring between the alkalinity of the water and the chemical added which results in the formation of insoluble floc is called? |
Coagulation |
|
|
|
When using Alum as a coagulant, the most effective pH range for the water is? |
5-7 |
|
|
|
What is the best pH range for coagulation? |
It depends one the coagulant used |
|
|
|
What water treatment process is known as "flash mix"? |
Coagulation |
|
|
|
The coagulation process requires what amount of detention time? |
Less than a minute; a few seconds |
|
|
|
Reducing the speed of the mixers in each succeeding tank to lower the turbulence is called? |
Tapered energy mixing |
|
|
|
The flocculation process takes place in what length of time? |
5-30 minutes |
|
|
|
What type of Floc should be formed during Flocculation? |
Discreet and fairly dense; Popcorn flake |
|
|
|
What is considered the best chemical dosage obtained during coagulation? |
The dosage, which produces finished water that meets drinking water standards at the lowest cost. |
|
|
|
During the jar test, the floc starts to settle before the mixer is turned off, and 80% of the floc is settled within 1 - 2 minutes. What does this indicate? |
Overdosage |
|
|
|
Jar tests are useless unless? |
Applied and verified |
|
|
|
During a jar test, the floc start settling after the mixer is turned off and 80% of the floc settles within 15 minutes. What does this indicate? |
Good Settling/Dosage |
|
|
|
During a plant tour, the operator notices a small, well disperse floc throughout the flow. What action is needed? |
None. This is good treatment |
|
|
|
If the operator does not notice a small, well-dispersed floc, what is likely the cause? |
Chemical dosage or feed rate too low ; flash mixer not providing effective mixing |
|
|
|
The water treatment plant is using Alum as a coagulant. The floc being form is Tiny. What does this indicate? |
Under-dosage |
|
|
|
In the solids contact unit the water appears to have a bluish tint or milky color. What is the likely cause? |
Overdose of alum |
|
|
|
As the floc enters the flocculation basin, the size of the floc increases. As it flows through the basin the flow starts to break up. What is the likely cause? |
Flocculator/Floc mixer speed too high |
|
|
|
As the floc enter the flocculation basin the size of the floc increases. As it flows through the basin the flow starts to break up because the Flocculator/Flocculation mixer speed is to high. What action is needed to correct the problem? |
Reduce Flocculation speed or increase dosage |
|
|
|
During a plant tour, the operator notices floc flowing over the laundering weirs. What is the likely cause? |
Floc too light for the detention time produced by the flow rate; Cougulant Underdosage; Alkalinity too low |
|
|
|
Alum is the coagulant being used. The floc is Tiny and has a very fine appearance. What is the likely cause |
Alum Underdosage; Correct by increasing the dosage |
|
|
|
If alkalinity is an important factor in coagulation, what parameter in the water must the operator measure? |
Alkalinity |
|
|
|
If the turbidity of the raw water increases, what action is usually taken to ensure good coagulation? |
Increase coagulant dosage |
|
|
|
When water temperature decreases, what action is needed to ensure good coagulation? |
Increase coagulant dosage |
|
|
|
In Enhance coagulation, when is the acid added? |
Prior to coagulation |
|
|
|
How many zones are there in a sedimentation tank? |
4 |
|
|
|
Which is the largest Zone in a sedimentation tank? |
Settling Zone |
|
|
|
In a conventional sedimentation tank, how long is the detention time? |
2-6 hours |
|
|
|
What is short-circuiting? |
When water takes a different path from the influent to the effluent without fully mixing with the contents of the tank |
|
|
|
What do you call the four zones in a sedimentation tank? |
Inlet; Settling; Sedimentation or Sludge, and Outlet |
|
|
|
What affects the settling process? |
Temperature and Turbidity |
|
|
|
What are the advantages of a solid contact unit? |
Save on land use, all processes take place in one tank, save on chemicals, ability to adjust the slurry, especially to deal with algal problems, capital and maintenance cost are reduced. |
|
|
|
For the volume over volume test, a ______ sample is taken from the _____ Zone, and allowed to settle for _____ minutes? |
100 mL, reaction zone, and 5 min |
|
|
|
What advise can you give to an operator at a neighboring plant who is experiencing high chemical cost? |
Recirculate chemicals |
|
|
|
When you took sludge samples, you determined that there was too much sludge in the tank. What will you do to correct this problem? |
Increase the number of blowdowns or increase the duration of the blowdowns, or both |
|
|
|
Observation of the treatment process indicated that there is not enough sludge in the treatment tank. What action is needed? |
Reduce the number of blow downs or their duration/ adjust recirculation rate |
|
|
|
How do you adjust the recirculation rate? |
Increase or decrease the flow (Some solid contact unit have a sludge recirculation device) |
|
|
|
By _____ the recirculation rate, a _____ amount of sludge will be held in the tank. |
Increasing, Larger |
|
|
|
If the recirculation rate is too high,_____ will be carried over to the _____. |
Sludge slurry, filter |
|
|
|
How are the bottoms of sedimentation tanks and solid contact unit configure to Aid in sludge removal? |
They are sloped toward the center |
|
|
|
What would you install to improve sedimentation? |
Tube settlers |
|
|
|
What affects the efficiency of tube settlers? |
High winds |
|
|
|
The Gathering of a liquid or dissolve substance on the surface or interface zone of another material is called? |
Adsorption |
|
|
|
An electrical system for the preventing of rust or corrosion of metal surfaces that are in contact with water is called? |
Cathodic protection |
|
|
|
In direct filtration, what process is omitted? |
Sedimentation |
|
|
|
A water treatment process in which solid particles settle out of water being treated is called? |
Sedimentation |
|
|
|
Put these processes in the correct order- flocculation, filtration, sedimentation, and coagulation. |
Coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration |
|
|
|
How do you prevent short-circuiting? |
Install baffles |
|
|
|
If an overdose of coagulant occurs, what happens in solids contact tank? |
Sludge settles too rapidly, and there is not enough sludge slurry recirculated |
|
|
|
How many sedimentation basins or solid contact units are needed in a water treatment plant? |
2 |
|
|
|
How does the operator of a solid contact unit control the performance of the unit? |
Adjusting the chemical dosage, recirculation rate, and sludge control |
|
|
|
A solid contact unit has a surface loading rate of 0.95 GPM/sq ft. what is the rise rate in feet per minute? |

|
|
|
|
What factors control the detention time? |
Flow and tank volume |
|
|
|
Lower temperatures cause what condition in solids contact tank? |
Slow settling |
|
|
|
Solids contact units are most unstable during what conditions? |
During rapid changes in temperature, flows and turbidity |
|
|
|
When there is a large increase in turbidity of the flow to a solid-contact unit, what action is needed? |
Jar test, increase coagulant dosage, change coagulant, increase alkalinity, adjust flash mixer/flocculator speed/ intensity |
JICIN |
|
|
What will happen if the recirculation rate is too low? |
Sludge will settle too fast and there will not be enough sludge recirculating |
|
|
|
How is pin floc removed? |
Filtration, recarbonation |
|
|
|
What is the best test to evaluate the water treatment process? |
Turbidity |
|
|
|
What is the best way to control chemical feed rates / dosage in a water treatment plant? |
Electronically Controlled Chemical Feeders |
|
|
|
A water treatment plant is having problems maintaining its sludge blanket. What action is needed? |
Adjust recirculation rate |
|
|
|
A water treatment solids contact unit is 75 ft long, 25 ft wide and 10 feet deep. What is the surface loading rate of the tank at a flow 6.5 MGD during the 3 p.m. to 11 p.m. shift? |

|
|
|
|
The release of dissolved air in saturated cold water due to a decrease in pressure causes which of the following? |
Air Binding |
|
|
|
The color of filtered water is called? |
True color |
|
|
|
What is the final step for removal of suspended solids? |
Filtration |
|
|
|
Which FAC chapter addresses drinking water standards, monitoring, and Reporting? |
FAC 62-550 |
|
|
|
Inaccurate test results are generally due to? |
Poor sampling techniques |
|
|
|
What is the highest possible turbidity reduction expected when operating a filtration process under Optimum conditions? |
99.5% |
|
|
|
How is pinpoint floc removed? |
Filtration |
|
|
|
Direct filtration omits which process? |
Sedimentation |
|
|
|
What are the main removal mechanisms in a filter? |
Adsorption and sedimentation |
|
|
|
Sand drying beds are similar to what type of filters |
Gravity sand filters |
|
|
|
Which of the following coagulants is generally used as a filter Aid? |
Nonionic polymer |
|
|
|
What parameters are used to determine when to backwash a filter? |
Head loss, turbidity, and time |
|
|
|
Where is the application point for a filter Aid? |
Filter influent |
|
|
|
Before starting the backwash process, what must you check first? |
Water supply |
|
|
|
Mudballs are caused by which of the following? |
Improper backwash |
|
|
|
If mudballs are caused by improper backwash how do you correct the problem? |
Properly backwash the filter |
|
|
|
During a plant walkthrough, an operator discovers a filter is air bound. What action should she take? |
Backwash the filter immediately |
|
|
|
Media boils are caused by? |
High backwash rates |
|
|
|
What is the main goal of filtration? |
Removal of turbidity |
|
|
|
What is the 4th step in the backwash process? |
Start the surface scours |
|
|
|
How should an air bound filter be backwashed? |
Slowly |
|
|
|
The color in unfiltered water is called? |
Apparent color |
|
|
|
After backwashing a filter, there is a high initial head loss. What is most likely the cause? |
Insufficient backwash |
|
|
|
What causes air binding? |
Operating the filter at high head loss too long and the release of O2 in saturated cold water due to a decrease in pressure |
|
|
|
During a plant tour, an operator noticed that filter 16 has a sudden increase in head loss. What action should she take? |
Do a jar test |
|
|
|
What do you call the process of reversing the flow of water through filter media to remove trapped particles? |
Filter backwash |
|
|
|
The common boundary layer between two substyances such as water and a solid is called? |
Interface |
|
|
|
The difference between the water surface and the media surface is called? |
Submergence (Head) |
|
|
|
What is the filter rate in GPM/sq ft of slow sand filters? |
0.015-0.15 GPM/sq ft |
|
|
|
High water temperatures require what type of backwashing rates? |
Higher backwash rates |
|
|
|
The Filter Backwash Rule requires the backwash water to be sent where after dewatering the sludge? |
Upstream of all conventional or direct filtration systems (includes coagulation, filtration, and sedimentation) |
|
|
|
What is the ripening period of a filter? |
This occurs at startup of a new filter or after backwash of a filter |
|
|
|
A filter 12 feet long and 8 feet wide drops 3 inches in 90 seconds. What is the filtration rate in GPM/sq ft? |

|
|
|
|
What is the backwash rate in inches/ minute if the backwash flow rate is 35 GPM/sq ft? |

|
|
|
|
What is the backwash pumping rate in GPM for a filter 20 ft long x 30 ft wide with a desire backwash rate of 25 GPM/sq ft? |

|
|
|

How much water is needed to backwash the filter in question 35 for 8 minutes? |
120,000 Gallons (15,000 GPM x 8 min) |
|
|
|
During a filter run, flow through the filter was 12.8 MG. It took 120,000 gallons to backwash the filter. What percent of the filter's water production was used for backwashing? |
1% |
|
|
|
What Is the minimum treatment required for drinking water by the Surface Water Treatment rule (SWTR)? |
Filtration and Disinfection |
|
|
|
Where should you install a particle counter at a water treatment plant? |
As close as possible to the point of measurement |
|
|
|
The length of a sample line of a particle counter should be how long? |
A short as possible |
|
|
|
Pumping sample water to the particle counter may cause what problem? |
Air bubbles, which may be erroneously counted as particles |
|
|
|
What material is recommended for the sample line of a particle counter? |
Black nylon with Hytryl liner |
|
|
|
What is the final step for removal of suspended solids? |
Filtration |
|
|
|
Chlorine is how many times heavier than air? |
2.5 |
|
|
|
A quart of liquid chlorine will evaporate into how many quarts of gaseous chlorine? |
450 quarts |
|
|
|
At what temperature does a fusible plug melt? |
Between 158 degrees and 165 degrees Fahrenheit |
|
|
|
How many fusible plugs are there on a ton cylinder? |
6 |
|
|
|
How many fusible plugs are there on a 100 or 150 lb chlorine cylinder? |
1 |
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of a chlorine leak? |
Lead washer failure or failure to change lead washer |
|
|
|
What type of respirator is needed when entering a chlorine room? |
SCBA |
|
|
|
What is the IDLH for chlorine? |
10 |
|
|
|
How many PPM of chlorine in a room will bring death in seconds? |
1,000 ppm or 0.10% by volume |
|
|
|
What percentage of the air is oxygen? |
20.9% |
|
|
|
What chemical is used to oxidize iron from water? |
Chlorine |
|
|
|
How do you open a chlorine cylinder? |
With a 6 inch box wrench |
|
|
|
The iodometric test is used to test for what parameter? |
Ozone Residual |
|
|
|
What is the minimum free chlorine residual for the distribution system? |
0.2 mg/L |
|
|
|
What is the minimum combined residual? |
0.6mg/L |
|
|
|
What is the maximum residual disinfectant level? |
4mg/L |
|
|
|
What does the C in CT value mean? |
Concentration of the chlorine residual |
|
|
|
What is measure from the chlorine application point to the point where the chlorine residual is taken? |
Time |
|
|
|
How many pounds of chlorine can you withdraw from a ton cylinder in a day? |
400 pounds |
|
|
|
How many pounds of chlorine can you draw from a 100 or 150 pound cylinder in a day? |
40 pounds |
|
|
|
When chlorine is used to disinfect drinking water, the chlorine cylinders are placed on what device to measure usage? |
Scale |
|
|
|
What is a device used to measure the flow rate of liquid or gasses? |
Rotameter |
|
|
|
The chlorine scale reading does not equal the rotameter setting for the past 24 hours. What is the most likely cause? |
Air leak Downstream of the chlorinator |
|
|
|
Pumping air into a container or cylinder to assist with the withdrawal of a liquid or gas is called? |
Air padding |
|
|
|
What is an open or vertical drop or space that separates a potable drinking water supply from an unapproved water or nonpotable water called? |
Air gap |
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of waterborne illnesses in the US? |
Cross-connection |
|
|
|
What method is considered the most reliable in measuring chlorine residuals? |
Amperometric Titration |
|
|
|
The addition of chlorine until the demand is satisfied and, thereafter, every drop of chlorine added is free residual is called? |
Breakpoint chlorination |
|
|
|
What is the disadvantage of breakpoint chlorination? |
THM formation |
|
|
|
Substances which cause cancer are called? |
Carcinogens |
|
|
|
What do you call a substance that changes the speed or yield of a chemical reaction without being consumed or chemically change? |
A catalyst |
|
|
|
What parameter is determined by this formula? Cl2 dosage - residual =? |
Demand |
|
|
|
What do you call the indicator organism that is found in the intestines of warm-blooded animals, including human beings, and in Plants, soil, water, and air? |
Coliform |
|
|
|
What is DPD used for? |
Measuring chlorine residuals |
|
|
|
Why is chlorine added to drinking water? |
To disinfect the water |
|
|
|
How many pounds of chlorine can you withdraw from a cylinder in 24 hours? |
Depends on ambient temperature (8 pounds per degree Fahrenheit) |
|
|
|
Disease-causing organisms are called? |
Pathogens |
|
|
|
What does HTH mean? |
High-test hypochlorite |
|
|
|
What does OCl mean? |
Hypochlorite |
|
|
|
What does HOCl mean? |
Hypochlorous acid |
|
|
|
What is NaOCl? |
Sodium hypochlorite (bleach) |
|
|
|
An increase in the heterotrophic plate count indicates? |
Nitrification |
|
|
|
What do the initials MPN mean? |
Most Probable Number |
|
|
|
What bacteria break down ammonia nitrogen to nitrites? |
Nitrosomonas |
|
|
|
Which bacteria break down nitrites to nitrates? |
Nitrobacter |
|
|
|
Which are the ideal conditions for nitrification to take place? |
A dark environment, temperature between 25 - 30°C, a pH of 7.5 - 8.5, and free ammonia available |
|
|
|
What is used to detect a chlorine leak? |
Ammonia |
|
|
|
What is used to detect a sulfur dioxide leak? |
Ammonia |
|
|
|
What is used to detect an ammonia leak? |
Hydrochloric acid |
|
|
|
If your plant is pre-chlorinating and you find that you are exceeding the MCL for THM's, what should you do? |
Stop pre-chlorinating |
|
|
|
Naturally occurring volatile organic compounds react with chlorine and form what cancer-causing compound? |
THMs |
|
|
|
A pure chemical substance that is used to make new products or is used in chemical test to measure, detect, or analyze other substances is called? |
A reagent |
|
|
|
The concentration of chlorine present in water after the chlorine demand has been satisfied is called? |
Residual |
|
|
|
What is this formula used to detect? Demand + residual=? |
Dosage |
|
|
|
The dosage is 5 PPM and the residual is 3 PPM. What is the demand? |
2 PPM |
|
|
|
What do you call the process of adding a chemical reagent in small increments until completion of a reaction, as signaled by the end point? |
Titration |
|
|
|
What do you call the Cloudy appearance of water caused by the presence of suspended and colloidal matter? |
Turbidity |
|
|
|
Why are water plant operators concerned with turbidity? |
Turbidity interferes with disinfection |
|
|
|
What is the MCL for turbidity? |
0.5 Nephelometric units |
|
|
|
Name four bacteria found in contaminated water? |
Typhoid, Cholera, Dysentery, and Salmonella |
|
|
|
Name two parasites that are found in contaminated water? |
Cryptosporidium and Giardia lamblia |
|
|
|
What determines the number of coliform samples that a water system has to take? |
Population served |
|
|
|
What is the MCL for coliform? |
Presence or absence |
|
|
|
If a sample tests positive for coliform what actions should be taken? |
Retest at the site within 24 hour notification of the positive test and Sample one site upstream and downstream from the positive site. |
|
|
|
If a water systems samples 40 or more sites for coliform, how many positive samples are allowed? |
2 or 5% |
|
|
|
If a water system samples 39 or fewer sides for coliform, how many positive samples are allowed? |
1 |
|
|
|
What are the optimum conditions for disinfection? |
High Cl2 concentration, long contact time, low pH, and low turbidity |
|
|
|
Why is turbidity of the water important? |
High turbidity interferes with disinfection and coagulation |
|
|
|
Ultraviolet rays are used to disinfect water. What limits the UV rays efficiency? |
No residual; also, if a pathogen is caught between two particles, the Rays have no effect on the pathogen. |
|
|
|
What color is chlorine gas? |
Greenish-yellow |
|
|
|
Chlorine cylinders are filled to what capacity? |
85% to allow for the expansion of the liquid into the gaseous state |
|
|
|
How many parts per million of chlorine is needed to oxidize one ppm of H2S to Elemental sulfur? |
2.08 mg/L |
|
|
|
How many parts per million of chlorine is needed to oxidize one ppm of H2S to sulfates? |
8.32 mg/L |
|
|
|
If sulfur dioxide comes into contact with a person's mucous membrane, what can happen? |
The formation of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) |
|
|
|
What does this chemical reaction indicate? H2S + Cl2 + O2- ➡️ S⬇️ + H2O + 2 Cl |
Oxidation of H2S by chlorine to elemental sulfur |
|
|
|
What does this chemical reaction indicate? H2S + 4 Cl2 + 4 H2O ➡️ H2SO4 + 8 HCl |
Oxidation of H2S by chlorine to sulfate or sulfuric acid (H2SO4) |
|
|
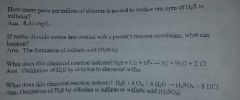
In the last four questions, what do you call the oxidation process that took place? |
Sub-residual chlorination |
|
|
|
In the normal pH range of drinking water, what is the usual form of chlorine? |
Monochloramines |
|
|
|
When you add ammonia to chlorine you form? |
Chloramines |
|
|
|
When chlorine is added to water what is the usual first reaction? |
Chlorine is used up ( destroyed) by reducing compounds (viruses, bacteria, solids, parasites, Etc) |
|
|
|
After the reduction of the chlorine dosage, what reaction takes place? |
Chlororganics and chloramines are formed- residual is present |
|
|
|
What is the next reaction in the chlorination chain? |
Residual is reduced- Chlororganics and chloramines destroyed |
|
|

After the reaction in question 85, what takes place? |
Breakpoint chlorination |
|
|
|
What causes the swimming pool taste and odor in water? |
Low chlorine residual-plant did not use breakpoint chlorination |
|
|
|
What is the best residual for disinfection? |
Free available chlorine |
|
|
|
At water pH levels of 4.0 or lower, what form will chlorine take? |
Trichloramine |
|
|
|
Above pH of 7.5 chlorine is found as? |
Monochloramines |
|
|
|
Dichloramines and monochloramines exist together at what PH range? |
5.5 - 7.5 |
|
|
|
Dichloramines and trichloramines are associated with what water complaint? |
Tastes and odors |
|
|
|
If chlorine is used to treat an odor cause by phenols (Benzene), what happens? |
The odor and taste are intensified |
|
|
|
Customers are complaining of a sweet, aromatic, medicinal taste in the water. What is the likely cause? |
Phenols |
|
|
|
What is the best method to remove taste and odors caused by phenols? |
GAC |
|
|
|
To avoid THM formation, what options are available to the Water Treatment Plant? |
Switch disinfectants, remove the precursors, or form THMs and remove them after they are formed |
|
|
|
What is the most common alternate disinfectant used to avoid the formation of THMs? |
Chloramines |
|
|
|
What is the highest chlorine to ammonia ratio by weight? |
5 ppm Cl2 as free residual to 1 PPM of NH3 |
|
|
|
When measuring combined chlorine residuals (chloramines) in the field, what is the process? |
Analyze for total chlorine (no free chlorine should be present at Cl2 - NH3 ratios of 3:1 to 5:1) |
|
|
|
What is the MCL for nitrites? |
1 |
|
|
|
What is the MCL for nitrates? |
10 |
|
|
|
What is the combined MCL for nitrites and nitrates? |
10 |
|
|
|
Before moving a chlorine cylinder, what should you do? |
Replace the protective cap |
|
|
|
The chlorine cylinders have iced up. What is the likely cause? |
Too rapid a withdrawal |
|
|
|
In what direction do you turn a chlorine valve to open the cylinder? |
Counterclockwise |
|
|
|
How many turns does it take to open the cylinder valve fully? |
One complete turn opens the tank fully |
|
|
|
If the bottom valve of a cylinder is leaking, what should you do? |
Rotate the tank so the leak is at the top |
|
|
|
A minimum PSI at the injector should be? |
50 PSI |
|
|
|
When a direct-mount chlorinator, water is showing in the metering tube. What is the likely cause? |
Check valve failure |
|
|

What action is needed in question 110? |
Clean or replace valve |
|
|
|
Ona direct-mount chlorinator, water is venting into the atmosphere. What is the likely cause? |
Excess water PSI |
|
|

What action is needed in question 112? |
Remove vacuum regulator |
|
|
|
On a direct-mount chlorinator, there is no indication on Flow Meter when a vacuum is present. What is the likely cause? |
Vacuum leak |
|
|
|
On a direct-mount chlorinator, there's an indication on the flow meter, but air is present, not chlorine gas. What is likely the cause? |
Gasket leaks |
|
|
|
If the DPD test is taken on water that has a combined residual, what error can take place? |
False positive reading- precipitate forms and gives sample appearance of having color |
|
|
|
Chlorinator will feed OK at maximum output, but there is no control at lower feed rates. What is the problem? |
Vacuum regulating valve |
|
|
|
Chlorinator will not reach maximum Point. What's the problem? |
Faulty injector |
|
|
|
Variable vacuum control will not go below 30% feed. Signal OK. What is causing the problem? |
CPRV |
|
|
|
Variable vacuum control reaches full speed, but will not go below 50% feed rate. CPRV OK. What is causing the problem? |
Signal vacuum too high |
|
|
|
Variable vacuum Control won't go to full feed. Gas pressure OK. CPRV OK. What's causing the problem? |
Plugged restrictor |
|
|
|
Low injector vacuum reading. What is the problem? |
Flow restricted |
|
|
|
There is an increase in the coliform level. What is the cause? |
Low chlorine residual |
|
|
|
There is a sudden drop in the chlorine residual. What causes this? |
Increase in chlorine demand or drop in chlorine feed rate |
|
|
|
How and what is used to detect a chlorine leak? |
Soak a rag with chlorine and hold it near connections. Also, Polyethylene spray bottle can be used to spray ammonia Vapors near the connections. A white cloud indicates a leak |
|
|
|
How do you reduce high chlorine residuals before the water leaves the plant? |
GAC or Sodium Bisulfate |
|
|
|
If there is a leak around the chlorine valve stem, what action is needed? |
Tighten the nut or stem by turning it clockwise |
|
|
|
What chemicals can be used to neutralize chlorine? |
Caustic Soda; Soda Ash; Lime |
|
|
|
What kit is used to repair a defective ton cylinder? |
B Kit |
|
|
|
What kit is used to repair a 100 or 150 pound cylinder? |
A kit |
|
|
|
What is the maximum temperature that chlorine cylinders should be stored at? |
100° C |
|
|
|
ORP probes are used to measure what? |
Direct measure of the disinfecting power of chlorine |
|
|
|
Where should the ORP probe be located? |
6.5 minutes Downstream from the injection point |
|
|
|
In rooms where there is chlorine or carbon dioxide present, what type of respirators should not be used? |
Gas mask |
|
|
|
What should you give someone who has inhaled chlorine? |
Milk or peppermint spirits |
|
|
|
What causes UV systems to be ineffective? |
Scaling or fouling of the quartz sleeves. Also, high flow velocities; turbidity; and decline in lamp output |
|
|
|
If 30 pounds of chlorine are used during an average week at a WTP, how many 150 pound cylinders will be used per month? |

0.86 Cylinder |
|
|
|
A water system treats 12.8 MGD. It doses the water with 5 PPM of chlorine. How many pounds of chlorine will the WTP use in 30 days? |

16,013 lbs |
|
|
|
If the free chlorine residual leaving the plant is less than 0.2 mg/L, what action is needed? |
WTP/system is allowed up to 4 hours to correct problem |
|
|
|
A heterotrophic plate of less than 500 colonies/mL is considered equivalent to? |
Equivalent to a detectable disinfectant residual |
|
|
|
Bacteria found in the intestines of warm-blooded animals, including human beings, and also in Plants, water, soil, and air are called? |
Coliform |
|
|
|
Name three disease-causing bacteria found in water? |
Salmonella, cholera, and typhoid |
|
|
|
Which tablet is always found in a coliform sampling Twirl bag? |
Sodium Thiosulfate |
|
|
|
Why is a space left in the twirl bag? |
To allow for mixing |
|
|
|
If the sample site is contaminated and you have no other sample site available, what should you do? |
Swab the spigot with an NaOCl solution |
|
|
|
What is the minimum amount needed to test for coliform? |
100 mL |
|
|
|
How long can you hold a sample collected for coliform? |
6 hours |
|
|
|
What test is also taken when the coliform samples are collected? |
Chlorine residual |
|
|
|
What causes blue babies? |
Nitrites |
|
|
|
What do heterotrophic organisms use for their growth? |
Organic matter |
|
|
|
Which substance in water increases the chlorine demand? |
Nitrites |
|
|
|
An increase in the heterotrophic plate count (HPC) indicates what process is taking place? |
Nitrification |
|
|
|
A HPC of less than 500 is an indication that there is a ____? |
Chlorine residual |
|
|
|
When taking samples for analysis by the lab, which of the following protocols must be followed? |
Must fill out Chain of Custody Report |
|
|
|
Greensand treated with potassium permanganate is used to remove ______ from water? |
Iron and manganese |
|
|
|
An iron bacteria that will oxidize iron in water and use the energy for reducing carbon dioxide to organic forms is a? |
Crenothrix, Thiothrix |
|
|
|
What is the best method to test for iron in the water? |
Atomic absorption (AA) |
|
|
|
When testing for iron, if there is clay or visible rust you should not _____ the sample? |
Acidify; also ask the lab to analyze immediate |
|
|
|
Polyphosphate should always be added to the water prior to? |
Chlorine |
|
|
|
Never use a polyphosphate over _____ old? |
48 hours |
|
|
|
A WTP using polyphosphate to control iron corrosion is getting calls because of red water in the distribution system. What is the likely cause of the red water? |
Iron bacteria, polyphosphate reverted to orthophosphate |
|
|
|
Soluble iron can be oxidized to insoluble precipitates by _____ and remove by sedimentation and filtration? |
Clorine; Aeration; Potassium Permanganate |
|
|
|
When using aeration to oxidize iron from the water, increasing the _____ will improve the removal efficiency? |
pH |
|
|
|
What chemical is commonly used to dechlorinate large amounts of water? |
Sodium Bisulfite |
|
|
|
Potassium permanganate is used with _____ to remove iron and manganese from water. |
Greensand Filtration |
|
|
|
What is used to regenerate a manganese green sand filter? |
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) |
|
|
|
, What causes pink water? |
Overdose of KMnO4 |
|
|
|
A WTP with greensand treatment is receiving red water complaints from its customers. What is the likely cause? |
Iron Bacteria; Greensand needs to be regenerated with KMnO4 |
|
|
|
Electromedia iron and manganese removal systems use what chemical to remove sulfur compounds causing taste and odor problems? |
Small dose of sulfur dioxide |
|
|
|
The influence to a manganese green sand filter has a pinkish/orange color. What does this indicate? |
Normal and will be removed by the filter |
|
|
|
A pink color in the greensand filter effluent indicates? |
Overdose of KMnO4 |
|
|
|
Greensand filter effluent has a yellow to Brown brownish color. Effluent has high iron and manganese content. What is the problem? |
High Alkalinity |
|
|

How would you correct the problem in question 18? |
Reduce Alkali feed; maintain pH during Cl2 addition between 6.2 - 6.5 |
|
|
|
How would you get rid of the red water that is in the distribution system? |
Flush fire hydrants |
|
|
|
Filter effluent clear, iron level low, and manganese level higher than raw water. What is the most likely cause? |
Manganese leaching from greensand; bed is insufficiently regenerated |
|

