![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
8.1 The importance of Water |
H |
|
|
|
8.2 Solutions and their Characteristics |
J |
|
|
|
8.3 The Dissolving Process |
G |
|
|
|
8.5 Solubility and Saturation |
Saturated solution: contains maximum quantity of solute at a given temperature and pressure
Unsaturated solution: more solute can dissolve at a given temperature and pressure
Supersaturated solution: contains more than the maximum quantity of solute it should at a given temperature and pressure
Solubility curve: graph of the Solubility of a compound over a range of temperatures
Thermal pollution: increase in water temperature, usually as a result of warm water being added to an aquatic ecosystem
Pressure: the force applied per unit area
Solubility of ionic compounds increase with rising temperature
Solubility curves of gases decreases as temperature rises Pressure has little to no effect on solids and liquids. However, gases are significantly affected by changes in pressure. The solubility of a gas in a liquid increases as the pressure of the gas is increased |
|
|
|
8.6 Concentration |
Stock solution: a concentrated solution that is used to prepare dilute solutions for actual use
Standard solution: solution that is carefully prepared in a laboratory for which the precise concentration is known
Amount concentration = amount of solute (in mol) / volume of solution (in L) c=n/V M = mol/L M = molarity |
|
|
|
8.7 Preparing Dilutions |

Dilution is the process of reducing the concentration of a solution by adding more solvent.
During a dilution: - the amount of solute does not change - concentration decreases because volume of solution increases
Dilution Equation: - ccVc=cdVd - c1V1=c2V2 |
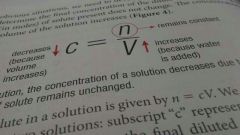
Concentration and volume are inversely related to one another. |
|
|
8.8 Concentration and Consumer Products |

cv/v = Vsolute/Vsolution × 100% cw/v = msolute/Vsolution × 100% cw/w = msolute/ msolution × 100% cppm = msolute/msolution × 106ppm cppb = msolute/msolution×109 ppb cppt = msolute/ msolution × 1012 ppt |
|

