![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What and is the purpose of The Clean Water Act of 1972?
|
To restore & maintain the chemical, physical, & biological integrity of the nation's water.
|
|
|
|
What is the minimum side water depth for a final settling tank clarifier at a activated sludge plant?
-10ft. -12ft -3ft -14ft |
12ft
|
|
|
|
According to OSHA, what depth in a trench is wall securing required?
-4ft -6ft -5ft -3ft |
5ft
|
|
|
|
Your anaerobic digester pH level dropped to low levels, what chemical do you -not- want to add?
-lime -sodium bicarbonate -alum -sodium hydroxide -aluminum sulfate |
aluminum sulfate
( or ferric chloride ) |
|
|
|
During nitrification process, converting 1mg/l of ammonia to nitrate consumes how much each, alkalinity and DO?
-3.3mg/l alk. & 3.6mg/l DO -8.24mg/l alk. & 7.1mg/l DO -7.14mg/l alk. & 4.6mg/l DO -7.9mg/l alk. & 7.48mg/l DO |
7.14mg/l alk. & 4.6mg/l DO
- note: answer could be in #'s if question refers #'s |
|
|
|
To make a BOD Test valid the DO uptake should be at least ________mg/l & the amount of DO that remains should be ________mg/l.
-2.0 & 1.0 -1.0 & 3.0 -1.0 & 2.0 -3.0 & 2.0 |
2.0mg/l uptake & 1.0mg/l remains for a valid BOD Test
|
|
|
|
What can be said of a anoxity zone?
- oxygen deficient and nitrate deficient - oxygen deficient and nitrate available - oxygen available and nitrate available - oxygen available and nitrate deficient |
Oxygen deficient (below 1mg/l DO) and
nitrate available (combined oxygen available) |
|
|
|
What is an inverted siphon in a sewer system?
- conveys water over or under a depression in a road or canal - siphons wastewater from a wet well to a higher elevation - siphons wastewater from a higher elevation to a well |
Conveys water over or under a depression in a road or canal
|
|
|
|
What is the best control of the nitrification process? (in aeration process)
- va/alk ratio - SRT & f/m ratio - SRT & va/alk ratio - wasting withdrawal |
-SRT & f/m ratio
|
|
|
|
When a sewer / interceptor is laid flat, what will happen?
- increase in velocity and settling of organics and inorganics causing odor problems - decrease in velocity and settling of organics and inorganics causing odor problems - waste water flow enter the plant slowly - velocity and settling will be normal |
Decrease in velocity and settling of organics and inorganics causing odor problems
|
|
|
|
When it is said wastewater is high in organics, you can also state it is high in __________.
-pH -TSS -DO -BOD |
BOD
|
|
|
|
What process in which air is added and settling also takes place?
- plug - step - facultative - sequential batch reactor - combine mixing |
Sequential Batch Reactor
(mainly used for denitrification and CBOD removal, but are also being used to remove nutrients, nitrogen/phosphorus) |
|
|
|
What is the max surface overflow rate during peak flow on a conventional FST ?
-1000 gpd/ft2 -1200 gpd/ft2 -1200 #/ft2 -1500 gpd/ft2 |
1200 gpd/ft2
|
|
|
|
Which sludge process has the lowest solids loading rate to a final settling tank?
- step - plug - extended aeration - combine mixing |
Step
|
|
|
|
What happens in a 2 stage nitrification process?
- stops nitrification occurring in a FST - CBOD and nitrate removal occur at same time - carbonaceous oxidation removal (CBOD) and nitrification occurs in two separate tanks - nitrification occurs more rapidly |
- carbonaceous oxidation removal (CBOD) and nitrification occurs in two separate tanks |
|
|
|
What test is best method to determine amount of organics in wastewater?
-pH - chlorine residual -TSS - biochemical oxygen demand/CBOD |
- biochemical oxygen demand/CBOD
|
|
|
|
What does organics turn into?
- water, hydrogen sulfide, & cell tissue - water, cell tissue, & carbon dioxide - water, cell tissue, & inorganics - water, gasses, carbon monoxide |
- water, cell tissue, & carbon dioxide
|
|
|
|
If bioassay tests confirms plant effluent is toxic, what is the next course of action?
- upgrade plant - resample and retest to confirm results - conduct a TRE ( toxic reduction evaluation ) - nothing, plant will correct issue overtime |
conduct a TRE (toxic reduction evaluation)
|
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a camera on a perimeter fencing of a plant besides survalance?
- detour possible trespassers - to keep track of employees start time |
- detour possible trespassers
|
|
|
|
Which one is not occurring in a successful activated sludge plant?
- clear effluent - good settleability - ability for biological growth - inability for biological growth |
- inability for biological growth
|
|
|
|
math question: determine what is the detention time of solids in clarifier with data below?
|
- they wanted SRT or MCRT-- not detention
time |
|
|
|
What changes occur when the temperature of wastewater increases?
viscosity biological activity solids settleability chlorine retention DO retention density pH |
temp. increase
viscosity - increases biological activity - increases solids settleability - increases chlorine retention - decreases DO retention - decreases density - decreases pH - decreases*as biological activity increases |
|
|
|
What does NPDES stand for?
|
national pollutant discharge elimination system
|
|
|
|
In good settling sludge, list in decreasing order the microorganisms?
|
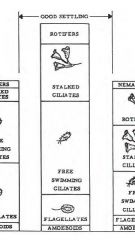
free swimming ciliates
stalked ciliates crawling ciliates flagellates rotifers amoeboids |
|
|
|
What is the organic loading range for a roughing filter? ( highest organic loading of all filters )
- 40 to 100lbs. BOD/1000FT3/DAY - 100 to 300lbs. BOD/1000FT3/DAY - 300 to 500lbs. BOD/1000FT3/DAY - 5 to 25lbs. BOD/1000FT3/DAY |

- 100 to 300lbs. BOD/1000FT3/DAY (40-65%BOD removal)
|
|
|
|
Raising the DO in the aeration tanks to 2 to 4mg/l would have which effect?
- increase nitrification rate - decrease nitrification rate - increase de-nitrification rate - decrease de-nitrification rate - increase cost |
- increase nitrification rate
( also reduces filamentous growth ) |
|
|
|
Increasing return activated sludge will have what effect on the following:
- detention time of aeration - hydraulic loading to clarifier - solids loading rate to clarifier |
- detention time of aeration / decrease
- hydraulic loading to clarifier / increase - solids loading rate to clarifier / increase |
|
|
|
What are biological selectors?
- chemicals to remove solids - chemicals to remove nutrients - reactor along with separate zones to remove solids - reactor along with separate zones to remove nutrients |
- reactor along with separate zones to remove nutrients
nutrients = nitrogen and phosphorus removal separate zones = anaerobic, anoxic, oxic |
separate zones = anaerobic, anoxic, oxic
|
|
|
Which of the following groups of microorganisms are found in good mlss?
- rotifers, stalked ciliates, & free swimming ciliates - flagellates, free swimming ciliates, stalked ciliate - stalked ciliates, rotifers, & flagellates - nematodes, flagellates, & stalked ciliates |
rotifers, stalked ciliates, & free swimming ciliates
|
|
|
|
Which heavy metal is the most stringent for land application?
- copper - zinc - lead - mercury |
mercury
|
|
|
|
Turbidity in waste water is caused by:
- color - dissolved calcium - finely divided suspended material - hardness |
finely divided suspended material
|
|
|
|
The valid number of total colonies on Petri plates when calculating total count is:
- 1 to10 sheens - 20 to 80 sheens - 20 to 60 sheens - 1 to 100 sheens |
20 to 80 sheens
|
|
|
|
Which of the following chemicals would be the most effective in achieving a pH adjustment of 8.4 so that nitrification can take place in an RBC?
- sulfuric acid - sodium hydroxide - soda ash - none of the above |
sodium hydroxide
|
|
|
|
The BOD removal in your activated sludge Plant (raw to final) is 96% is this removal...
- average - higher than normal - lower than normal |
average
|
|
|
|
What is the normal BOD removal of a primary clarifier expected to be?
- 15 % to 25 % - 25 % to 30 % - 40% to 60% - 85% to 95% |
25 % to 30 %
|
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a secondary settling tank?
- reduce SVI - remove biological solids - increase sludge age - grease floatation |
Remove biological solids by settling
|
|
|
|
Which is the most effective at killing bacteria?
- combined chlorine - free chlorine - chloramines - residual chlorine |
chloramines
|
|
|
|
Head in a pumping system is...
- the suction side of a pump - a pipe between the pump and check valve - a man in charge of a lift station - the head wall of a discharge structure - the pressure in terms of water column height |
The pressure in terms of water column height
|
|
|
|
One of the differences between extended aeration and the conventional aeration sludge system is...
- type of wastewater treated - the amount of settable solids in the influent - the presence or absence of a primary clarifier - the presence or absence of a communitor - what type of biological growth in the tanks |
The presence or absence of a primary clarifier
extended aeration does -not- have a primary clarifier |
|
|
|
The rise in SVI indicates...
- the density of sludge is increasing - the volatile sludge is decreasing - the sludge is settling faster - there is a danger of bulking sludge |
There's a danger of bulking sludge
|
|
|
|
Nitrification is the process of converting:
- nitrates to nitrogen gas - ammonia to nitrates - ammonia to nitrogen gas - ammonia to nitrites |
Ammonia to nitrates
|
|
|
|
Which of the following would not be a legitimate reason for bypassing your plant?
- extended power outage causing loss of influent - a broken shaft on the digester mixer - flows in excess of influent capacity - ruptured line between comminuter and primary tank - all of the above - none of the above |
A broken shaft on the digester mixer
|
|
|
|
Sludge gas from a typically operated digester contains...
- a negligible amount of carbon dioxide - about 20% carbon dioxide and 80% methane - about 30 % methane and 70% carbon dioxide - about 70% methane and 30% carbon dioxide |
About 70% methane and 30% carbon dioxide
|
|
|
|
On a bright sunny day the pH in a secondary treatment lagoon will generally...
- increase - decrease - neither |
Increase
|
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a dosing siphon in a trickling filter plant?
- removes excess grit - equalizes flow - provides head to operate distributor - allows ventilation through media |
provides head to operate distributor
|
|
|
|
The BOD in an aeration tank is oxidized in what order?
- nitrogenous then carbonaceous - solids then soluble - nitrosomonas then Nitrobacter - carbonaceous then nitrogenous |
carbonaceous then nitrogenous
|
|
|
|
What is the purpose of zoogleal mass on a fixed growth secondary process?
- to filter the suspended solids - to add dissolved oxygen to the wastewater - to oxidize the BOD - to filter the BOD out of the system |
to oxidize the BOD
( accumulates & oxidizes organic matter ) |
|
|
|
Ohio EPA is switching from _________ colonies to ________ colonies for permit limits.
- ecoli / fecal - fecal / protozoan - fecal / ecoli - nematodes / flagulates |
fecal / ecoli
|
|
|
|
What is the incubation temperature and the time duration of the ecoli test?
- 35 degrees Celsius +-.5 / 24 hours - 35 degrees Celsius +-.5 / 36 hours - 32 degrees Celsius +-.5 / 24 hours - 32 degrees Celsius +-.5 / 36 hours |
35 degrees Celsius +-.5 / 24 hours
|
|
|
|
Plates with colonies exceeding __________ are to be identified as Too Numerous To Count (TNTC) when calculating ecoli.
- 100 - 200 - 300 - 400 |
200 colonies
|
|
|
|
Ecoli results are calculated the same as fecal coliform. Colonies of bacteria per _________mL.
- 50 ml - 100mL - 150 mL - 200 mL |
100mL
|
|
|
|
Westerly permit limits are switching from 1000 fecal monthly to 126 ecoli monthly .
(2000 fecal Wkly to 284 ecoli Wkly) |
Westerly permit limits are switching from 1000 fecal monthly to 126 ecoli monthly .
(2000 fecal Wkly to 284 ecoli Wkly) |
|
|
|
According to the recommended standards for wastewater facilities, what is meant by the invert of a pipe?
- the bottom inside edge - the fight when it turned over - the bottom of a pipe - the pipe turned 180 degrees |
The bottom inside edge
|
|
|
|
When installing sewer lines near a water line, what distance must be kept between them?
- 18 inches - 2 feet - 10 feet - 36 inches |
10 feet
|
|
|
|
Filamentous organisms thrive best under which of the following conditions?
- high nutrient levels - low pH conditions - low oxygen conditions - sudden drop in temperature |
Low oxygen conditions
|
|
|
|
At what pH range does hydrogen sulfide cause the most serious problems?
- below 5.0 - 5.0 to 7.0 - 7.0 neutral - 7.0 to 9.0 |
Below 5.0 (highly acidic & corrosive)
|
|
|
|
Treatment tanks' or basins' drains:
- must be higher than the receiving sump to allow for gravity flow out of the basin - must be lower than the receiving sump to allow for gravity flow out of the basin and into the sump - need not be valved closed if the drain is higher than the receiving sump - need not be maintained because it is always faster to pump a treatment basin into the receiving sump |
Must be higher than the receiving sump to allow for gravity flow out of the basin
|
|
|
|
What is the explosive range of sewer gas?
- 21.3% to 28.9% - 5.9% to 19.3% - 74.3% to 83.7% - 34.0% to 41.5% |
5.9% to 19.3%
|
|
|
|
Before free chlorine can exist as a residual, what must occur?
- the temperature of the water must be stabilized - all direct chemical actions must be satisfied - microorganism killed must be complete - effluent must be regulated |
All direct chemical actions must be satisfied
|
|
|
|
TKN (Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen) is the sum of:
- ammonia nitrogen plus organic nitrogen - organic nitrogen minus ammonia nitrogen - nitrites + nitrates - none of the above |
Ammonia nitrogen plus organic nitrogen
note: ammonia nitrogen = NH3 Organic nitrogen = nitrogen in amino acids and proteins |
|
|
|
Which one occurs in a anoxic zone?
- nitrification - denitrification - high levels of DO - none of the above |
Denitrification
|
|
|
|
What is occurring in denitrification process?
- ammonia to nitrates - nitrites to nitrates - nitrates to nitrogen gas - nitrates to nitrites |
Nitrates to nitrogen gas
anoxic zone nitrates (NO3) + heterotrophic bacteria = nitrogen gas (N2) & oxygen & alkalinity |
|
|
|
What is occurring in the nitrification process ?
- nitrites to nitrates - nitrates to nitrites - ammonia to nitrates - ammonia to nitrites |
Ammonia (NH3) to nitrates (NO3)
Ammonia NH3 + oxygen O2 + alkalinity + Nitrosomonas = nitrite NO2 Nitrite + oxygen + alkalinity + Nitrobacter = nitrate NO2 O2 NO3 |
|
|
|
Is nitrites (NO2) stable or unstable?
|
NO2 is the unstable form of nitrogen and is easily converted because it does not wish to be in this form.
|
|
|
|
The quantity of volatile solids in the content of the incoming sludge is an indirect measure of what?
- the food available for bacteria in the digester - the number of bacteria in the digester - the primary of fluid suspended solids - none of the above |
The food available for bacteria in the digestion
|
|
|
|
What happens when chlorine reacts with hydrogen sulfide gas?
-the hydrogen sulfide gas is amplified and expands - the gas is diluted - hydrogen sulfide is not affected by chlorine - it is made odorless due to being oxidized by the chlorine |
it is made odorless due to being oxidized by the chlorine |
|
|
|
What is affected first when the aerobic digestion process is starting to deteriorate?
- supernatant quality - temperature - volatile acid: alkalinity ratio - volatile solids concentration |
Volatile acid: alkalinity ratio
|
|
|
|
What is the proper interpretation of an SVI 120?
- 120 is the level of settled mixed liquor - excessive increase in volatile solids - 1 gram of sludge occupies 120 milliliters of space - the mixed liquor suspended solids are 120mg/l |
1 gram of sludge occupies 120 milliliters of space
SVI = 30 min. settling volume as mL/L ÷ MLSS concentration as mg/L x 1000 mg/g = mL/g |
|
|
|
After making a change in the operation of a biological treatment process, how long does it take to properly evaluate whether the change was beneficial?
- 1 MCRT interval - 2 to 4 days - 2-3 times the MCRT - until lab results are completed |
2 to 3 times MCRT
|
|
|
|
Besides chlorine, which of the following chemicals can be used to control or prevent odors?
- chlorophenol - dichloramine - hydrogen peroxide - arsenic |
Hydrogen peroxide
|
|
|
|
Other than hydrogen sulfide , what is another offensive inorganic gas odor that can be generated by a wastewater treatment plant?
- ammonia - methane - mercaptans - nitrogen |
Ammonia
|
|
|
|
Acceptable SVI levels are between 50 to 150mL/g, but are ideally less than :
- 140 mL/g - 120 mL/g - 100 mL/g - 60 mL/g |
100 mL/g
|
|
|
|
When you increase wasting at a activated sludge plant, what will occur to the following?(increase or decrease)
SVI F/M Ratio MCRT & SRT |
SVI increases F/M Ratio increases MCRT & SRT decreases |
|
|
|
True or false: low SVI = high SDI
|
True
SVI (sludge volume index) SDI (silt or sludge density index) |
|
|
|
What is the typical range of the SDI in a conventional activated sludge plants?
- 3.0 to 4.4 - 2.5 to 3.5 - 1.0 to 2.5 - none of the above |
1.0 to 2.5
SDI = MLSS % ÷ x 100 % volume occupied by MLSS 30min. settling |
|
|
|
What is the common return rate for RAS at a wastewater plant?
- 10 to 20% influent - 20 to 40 % influent - 50 to 70 % influent - none of the above |
20 to 40% influent
|
|
|
|
What is the typical sludge age in days (SAD) at a conventional activated sludge plant?
- 1 to 4 days - 10 to 20 days - 3 to 15 days - 15 to 30 days |
conventional = 3 to 15 days
note:extended aeration activated plant=15 to 30 days |
|
|
|
What will occur in a grit channel when too much air is added and also when too little air is added as well?(above & below design guidelines) |
above design guidelines - poor grit removal
below design guidelines - excessive organics settle out with grit
Excessive quantities of air can cause the roll velocity to be too high resulting in poor grit removal. Insufficient quantities of air result in low roll velocities and excessive organic matter will settle with the grit. |
|
|
|
If large amounts of organic matter is settling out in grit tanks, what should be done to correct issue?
- add additional tanks to the process - remove tanks from the process - turn off all air to the grit tanks - turn off collectors |
Remove tanks from the process to increase velocity.
|
|
|
|
The key to successful process control of enhanced biological systems is...
- BOD reduction - coliform kill - liquid/solids separation - nutrient removal |
liquid-solids separation
|
|
|
|
If nitrification application slows, what other effects would you see?
- decrease in ammonia & alkalinity, increase in & DO - decrease in ammonia & acidity, increase & alkalinity & DO - increase in ammonia & alkalinity, decrease in acidity & DO - increase in ammonia & acidity, decrease alkalinity & DO |
increase in ammonia & alkalinity, decrease in acidity & DO
|
|
|
|
What is lost when denitrification takes place?
- alkalinity - ammonia - organic nitrogen - nothing |
Ammonia
|
|
|
|
In severe cold weather in a activated sludge plant, the biological activity in the aeration tanks will decrease. What should an operator do to correct the situation?
- decrease sludge age - increase MLSS - decrease blower output - none of the above |
Increase MLSS ( less wasting )
|
|
|
|
Which of the following would you not use to determine wasting rate?
- MCRT - sludge condition - sludge age - SRT |
Sludge condition
|
|
|
|
Along with nitrates, what else is removed during denitrification?
- phosphorus - alkalinity - oil and grease - nocordia - none of the above |
Phosphorus
|
|
|
|
How does carbon dioxide affect an anaerobic digesters sludge?
- no change - raises pH - lowers pH - reduces volatile solids |
Lowers pH
|
|
|
|
Residual ammonia remains after biological treatment can be removed by...
- re carbonation and airstretching - ion exchange and re carbonation - activated carbon and filtration - breakpoint chlorination and air stripping |
breakpoint chlorination and air stripping
|
|
|
|
Methane would be produced when what is decomposed?
- starches and fats - ammonia and carbohydrates - grease and carbohydrates - nitrates and starches |
Grease and carbohydrates
|
|
|
|
Which group of elements are necessary to achieve the BOD in wastewater?
- C, N, P - Can, NH3, H2SO4 - O, N, P - H, N, O |
O, N, P
|
|
|
|
Which of the following is the best choice as a definition of denitrification?
- aerobic biological reduction of nitrate nitrogen gas causing the removal of TKN from a system - oxidation of TKN that finalizes the process of nitrogen removal - anaerobic biological reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas causing the removal of TKN from a system - facultative digestion of TKN causing the total removal of nitrogen from a system |
anaerobic biological reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas causing the removal of TKN from a system |
|
|
|
Which of the following are the most important operational considerations for process control?
- ammonia, alkalinity, and BOD - suspended solids, BOD, and pH - BOD, pH, and temperature - BOD, flow, and suspended solids |
BOD, flow, and suspended solids
|
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes a venturi tube?
- turbine blower - flow meter - level indicator - head pressure meter |
Flow meter
|
|
|
|
Ozone is a good disinfectant because...
- it is easy and cheap to produce - small amounts can kill any bacteria - it forms less carcinogenic compounds when it reacts with wastewater than other disinfectants - it has a metallic holder |
it forms less carcinogenic compounds when it reacts with wastewater than other disinfectants
|
|
|
|
Under which of the following circumstances should sludge wasting normally be increased?
- mixed liquor settles to slowly - large billows of white foam starts forming on the aeration tank - dark brown scummy foam appears on the aeration tank surface - all of the above |
dark brown scummy foam appears on the aeration tank surface
|
|
|
|
What are the four reagents used to prepare a sample before performing a Winkler?
- alkali iodide, manganese sulfate, starch, & sulfuric acid - mercuric chloride, manganese sulfate, starch, & sulfuric acid - borage buffer, phosphoric acid, alkali iodide, & starch - alkali iodide, manganese sulfate, starch, & phosphoric acid |
alkali iodide, maganese sulfate, starch, & sulfuric acid
|
|
|
|
At what temperature does the muffle furnace have to remain at, in the determination of the volatile solids?
- 103 degree C - 500 degree C - 550 degree C - 600 degree C |
550 degree C
|
|
|
|
How much oxygen is required to oxidize one pound of ammonia to nitrate?
- 1.0 lb - 3.0 lbs - 4.6 lbs - 6.4 lbs |
4.6 lbs (DO) |
|
|
|
The population equivalent factor for BOD is...
- 0.15 lbs/day BOD/person - 0.17 lbs/day BOD/person - 0.20 lbs/day BOD/person - 0.22 lbs/day BOD/person |
0.17 lbs/day BOD/person
|
|
|
|
For a conventional activated sludge process the food / microorganisms f:m ratio should be in the range of ____________ .
- 2.0 to 5.0 - 0.01 to 0.07 - 0.2 to 0.5 - 0.07 to 0.15 |
0.2 to 0.5
|
|
|
|
What is the normal detention time in the following activated sludge aeration tanks?
- contact stabilization - conventional - extended |
- contact stabilization 4 hours or less
- conventional 4 to 8 hours - extended 24 hours |
|

