![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is foot and mouth disease |
a severe, highly contagious viral disease of clove hoofed livestock with significant economic impact. Causes lesions on hoofs and in and around the mouth. Also characterized by fever. In 2001 an epidemic resulted in 6.24 million animals slaughtered. Cost the taxpayer £20 billion. |
|
|
What is the virus life cycle? |
1. recognition 2. attachment to host cell 3. penetration into host cell 4. uncoating of viral DNA 5. transciption of viral DNA 6. Synthesis of viral proteins 7. Replication of viral dNA 8. envelopment 9. Budding and release or lysis and release |
|
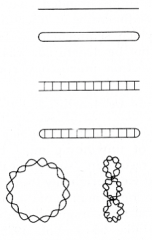
What types are these virus DNA molecules? |
1. Linear single stranded 2. circular single stranded 3. linear duplex 4. duplex with closed ends 5. closed circular duplexes (with and without supercoils) |
|

What typed are these virus RNA molecules? |
1. Linear, single strand infectous "positive" strand 2. Linear, single strand, non-infectous "negative" strand 3. Segmented positive strands 4. segmented negative strands 5. double strand segmented 6. diploid single strands |
|
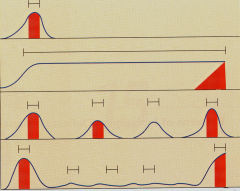
What are these patterns of infection? |
1. Acute infection 2. Persistent infection 3. Latent, reactivating infection 4. Slow virus infection |
|
|
What is the mechanism of latent herpes simplex and variella-zoster virus infection in man? |
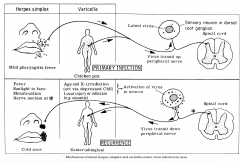
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) causes chickenpox and herpes zoster (shingles). Chickenpox follows initial exposure to the virus, virus transits up the peripheral nerve. Reactivation of the dormant virus via depressed CMI (from local injury of infection). Virus transits down the peripheral nerve. results in the characteristic painful dermatomal rash of herpes zoster, which is often followed by pain in the distribution of the rash. |
|
|
What are the mechanisms of viral transmission? |
-Respiratory or salivary spread -formites (eg tissue, clothes) -Sexual contact -Zoonoses -Blood transfusions, organ transplant, needle sharing |
|
|
How can viral diseases be controlled? |
-Public health care -Vaccination -Chemotherapy |
|
|
give some examples of viral infections that cannot be prevented by vaccine |
HIV, RSV, rotavirus |
|
|
Give some difficulties associated with the design and use of ant-viral drugs |
1. few biochemical pathways are unique to viruses 2. therapeutic index is often when low 3. there will always be a selection of drug resistant mutants 4. Many viruses which cause similar diseases have very different models of replication and may not be sensitive to some drugs 5. By the time symptoms appear often chemotherapy is too late to make much of a difference to clincal course of disease. |
|
|
give some examples of anti viral drugs |

|
|
|
Give a brief overview of HIV/AIDS |
the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) was first recognized in 1981 and has since become a major worldwide epidemic. AIDS is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). |
|
|
How does HIV work |
By leading the destruction and/or impairment of cells of the immune system (eg CD4 + T cells) HIV progressively destroys the bodies ability to fight infection and certain cancers. |
|
|
How does HIV work |
By leading the destruction and/or impairment of cells of the immune system (eg CD4 + T cells) HIV progressively destroys the bodies ability to fight infection and certain cancers. |

