![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
152 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adapter
|
A connector that converts from one type of connector to another (e.g., from phone to RCA).
|
|
|
Air Monitor
|
In audio, the speaker that allows an operator to hear the transmitted broadcast signal.
|
|
|
Alter
|
To change an audio signal so that it is different from the original signal that was transduced.
|
|
|
Amplify
|
To magnify an audio or video electrical signal for mixing, distribution, and transducing purposes.
|
|
|
Amplitude
|
The height of a sound wave. Amplitude determines the volume of the sound. The higher the amplitude, the louder the sound.
|
|
|
Analog
|
A method of representing video or audio signals using a “wave” of continuously varying value.
|
|
|
Analog Cartridge
|
A loop with pre-recorded sound and inaudible cue signals used for playback during production.
|
|
|
Audio Console
|
The piece of equipment that is used to gather, mix, select, and amplify sounds and send them on to their next destination.
|
|
|
Audition
|
A separate audio speaker that is not tied to what is being mixed by the audio console or sent over the air.
|
|
|
Auxiliary Send
|
A routing bus on the audio console used to feed external processing gear, multitrack recording equipment, or other audio equipment.
|
|
|
Backplate
|
The part of a condenser mic that is electrically charged.
|
|
|
Balance
|
In audio, the achievement of the correct ratio among several sound sources.
|
|
|
Balanced Cables
|
Audio cables that have three wires, one for positive, one for negative, and one for ground.
|
|
|
Bass
|
Low sounds produced at fewer cycles per second (hertz) than higher treble sounds.
|
|
|
Bidirectional
|
A microphone that picks up sound from two directions.
|
|
|
BNC Connector
|
A bayonet-type connector used for video and sometimes for digital audio.
|
|
|
BNC Connector
|

|
|
|
BNC Connector - Male |

|
|
|
BNC Connector - Female
|

|
|
|
Boom
|
Any device consisting of a movable base, an adjustable stand, and a long arm for suspending a microphone above and in front of a performer.
|
|
|
Boom Operator
|
The person who is responsible for following performers with a directional mic attached to a boom during a production. |
|
|
Boundary Mic |
A flat microphone that consists of a thin pickup plate that, when mounted on a table or ceiling, uses the surface it is mounted on to collect sound waves.
|
|
|
Cables
|
Wires that transport the signals needed for audio and video production.
|
|
|
Capacitor
|
The part of a condenser mic that stores electrical energy and permits the flow of alternating current.
|
|
|
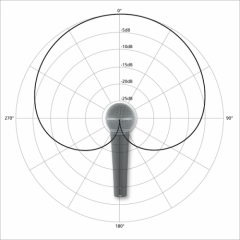
Cardioid
|
A microphone that picks up sound in a heartshaped pattern and is more sensitive to sounds coming directly from the front.
|
|
|
Cardioid
|
|
|
|
CD Player
|
Equipment that plays back discs on which sound has been recorded digitally.
|
|
|
Channeling
|
Moving signals from one place to another.
|
|
|
Clip
|
A digital audio phenomenon where sound that is overmodulated disappears or is intermittent.
|
|
|
Compressor
|
An electronic device used to lessen the distance between the highest and lowest audio volume levels.
|
|
|
Condenser
|
A high-quality mic whose transducer consists of a diaphragm, backplate, and capacitor.
|
|
|
Connectors
|
Metal housings that allow audio, video, or other signals to travel from one cable to another.
|
|
|
Crossfade
|
To bring in one sound slowly while taking another out slowly.
|
|
|
Cross-pair Miking
|
A stereo mic setup that uses two cardioid mics placed like crossed swords.
|
|
|
Cue Button
|
A control on an audio board that allows an operator to hear a sound without transmitting or taping it. It is used to prepare sound before it is to be aired or recorded.
|
|
|
Cycles per second
|
A basic unit of frequency measurement for electromagnetic and acoustic waves; now usually referred to as hertz.
|
|
|
Decibel
|
A unit of measurement of sound that compares the relative intensity of different sound sources.
|
|
|
Diaphragm
|
The vibrating element in a microphone that responds to the compressed air molecules of sound waves.
|
|
|
Digital
|
A method of representing video or audio signals that uses discrete “on” and “off” pulses. The value of a digital signal at any point can be either “off” (0) or “on” (1).
|
|
|
Digital Audio Recorder
|
An outboard audio unit that records sound onto solid state media for playback.
|
|
|
Digital Audiotape
|
Recording medium that gives high-quality sound because it records information in digital form.
|
|
|
Digital Audio Workstation
|
A stand-alone computer that can be used to record, store, edit, sweeten, and mix sounds.
|
|
|
Digital Cart
|
A piece of equipment that replaced the analog cartridge player. It stores audio selections in files on a hard drive and can be programmed to bring up any files in any order.
|
|
|
Digital Delay |
A unit that holds a signal temporarily and then allows the signal to leave. It is often used for talk shows so that something a participant says can be halted before it goes on the air. |
|
|
Distortion
|
A muddy sound caused by playing a sound at a higher volume than the equipment can handle.
|
|
|
Dynamic Mic
|
A rugged microphone whose transducer consists of a diaphragm connected to a movable coil; also called a moving coil mic.
|
|
|
Dynamic Range
|
The difference between the softest and loudest sounds a piece of equipment can handle.
|
|
|
Equalization
|
Emphasizing, lessening, or eliminating certain audio frequencies.
|
|
|
Fade-in
|
For audio, the gradual bringing in of a sound.
|
|
|
Fade-out
|
For audio, taking a sound from full up to silence.
|
|
|
Faders
|
Control the amount of volume for each of the inputs.
|
|
|
Fiber Optic
|
A transmission cable that uses transparent strands of glass or plastic instead of copper or other metallic wire.
|
|
|
Filter
|
Equipment or code within a computer program that cuts out a particular frequency or frequency range of an audio signal.
|
|
|
Fishpole
|
A small lightweight arm to which a microphone is attached, to be handheld by an audio assistant outside of the picture frame.
|
|
|
Flat
|
When all audio frequencies are recorded equally well.
|
|
|
Floor Stand
|
A microphone holder that rests on the floor and has a pole that can be adjusted to various heights so that someone standing can talk into the mic.
|
|
|
Frequency
|
he number of oscillations per second (hertz) of an electromagnetic wave, which, in the audio range, determines the pitch of the tone and, in the light range, determines color.
|
|
|
Frequency Response
|
The range of pitches (frequencies) that any particular piece of audio equipment can pick up or reproduce.
|
|
|
Fundamental
|
The main frequency of a particular sound.
|
|
|
Gain
|
Volume of an audio signal.
|
|
|
Giraffe
|
A small boom that consists of a counterweighted arm supported by a tripod on casters.
|
|
|
Group Assign Switch
|
A control on each input channel of an audio board that allows the operator to group some audio inputs together so they can be controlled separately from other audio inputs.
|
|
|
Guide Pin
|
The part of an XLR connector that is used to line up the male and female conductors accurately.
|
|
|
Hand Mic
|
A microphone that a person holds to speak or sing into.
|
|
|
Harmonics
|
Acoustical or electrical frequencies that are higher than the fundamental tone.
|
|
|
Hertz (Hz)
|
A basic unit of frequency measurement for electromagnetic and acoustical waves, named after Heinrich Hertz.
|
|
|
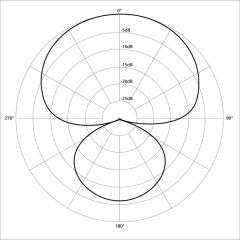
Hypercardioid
|
A narrow pickup pattern in an elongated heart shape.
|
|
|
Hypercardioid
|
|
|
|
Inverse Square Law
|
A principle of physics that states that when the distance between an audio source and its point of perception is reduced by half, its intensity will be increased fourfold.
|
|
|
Jack
|
A female connector.
|
|
|
Lavaliere
|
A small mic that can be worn near the neck.
|
|
|
Lavaliere
|

|
|
|
Limiter
|
An electronic device used to cut off audio levels when the volume is too strong.
|
|
|
Line Feed
|
An audio input for equipment, such as a video recorder or an audio recorder, that has already been amplified.
|
|
|
Loudness
|
The level of sound as it comes through a speaker or headphone; not the same as gain, which is the level of audio as it is being recorded.
|
|
|
Master Fader
|
The volume control on an audio board that is located after all the input channel controls and after any submaster controls.
|
|
|
Mic Feed
|
The relatively low strength of the electronic signal produced by a microphone prior to several stages of amplification.
|
|
|
Miniphone Connector
|
A small audio connector with a sleeve and tip.
|
|
|
Miniplug |
A small audio connector with a sleeve and tip.
|
|
|
Miniplug |

|
|
|
Mix-minus
|
An output from an audio board that is missing at least one of its elements so that the missing element can be recorded.
|
|
|
Monaural
|
Sound coming from only one direction.
|
|
|
Monitoring
|
Listening to sound as it is being manipulated.
|
|
|
Mute
|
A control that turns off an assigned channel of an audio console.
|
|
|
MOS |
Mute Out Sound, or a video sequence that is recorded without sound. |
|
|
Normalled
|
Having inputs and outputs of an audio patch bay permanently wired so that sound goes from one to the other if it is not sent somewhere else by a patch cord.
|
|
|
Off-mic
|
Distorted sound that occurs when noise from outside a mic’s pickup area is transduced and amplified.
|
|
|
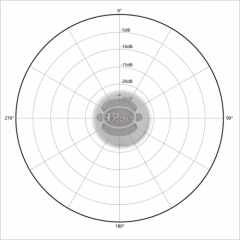
Omnidirectional
|
A microphone that picks up sound from all directions.
|
|
|
Omnidirectional
|
|
|
|
Outboard Equipment
|
Pieces of equipment that are used in conjunction with the audio board, such as CD players, DAT recorders, and digital carts.
|
|
|
Overtones
|
Acoustical or electrical frequencies that are higher than the fundamental tone.
|
|
|
Pan Knob
|
A control that shifts an audio signal from the left speaker to the right speaker for stereo mixing. For a mono mix it is usually placed at the 12:00 position.
|
|
|
Patch Bay
|
A board with numerous terminals (inputs and outputs) through which various audio, video, or lighting signals can be connected by patch cords to other channels or circuits.
|
|
|
Patch Cord
|
A cable with connectors on both ends that is used to go from one connector on a patch bay to another.
|
|
|
Peak
|
In audio, to reach the high point of volume level for a particular sound sequence; the ideal place to peak is at the 0 position on the VU meter.
|
|
|
Peak Program Meter (PPM)
|
Feature of an audio board that measures loudness peaks; a PPM reacts more quickly to overmodulation than a VU meter and can help keep sound from distorting (analog) or clipping (digital).
|
|
|
Perambulator
|
A large three-wheeled movable platform that holds a mic operator and a mic in such a way that the mic can follow action throughout a studio.
|
|
|
Perspective
|
In audio, the matching of visual and sound distance.
|
|
|
Phantom Power
|
Current sent to a condenser mic from the audio console.
|
|
|
Phase
|
The relationship of the positive and negative portions of the sine waves of two different electrical signals, determining to what extent their oscillations are synchronized. Sounds that are out of phase tend to cancel each other out, resulting in silence or on-and-off sound.
|
|
|
Phase Cancellation
|
A problem encountered when mics placed too close to each other cancel out each other’s audio.
|
|
|
Phone Connector
|
A connector with a sleeve and tip that is used for patch bays, among other things.
|
|
|
Pitch
|
The highness or lowness of a sound, determined by the frequency of the sound wave.
|
|
|
Playback
|
The process of retrieving electronic signals from a storage device and turning them into sound and/ or images.
|
|
|
Plosives
|
In speech, a popping “p” sound that is augmented by some mics.
|
|
|
Plug
|
A male connector.
|
|
|
Pop Filter
|
A metal or foam ball placed over the top of a mic to minimize plosive sounds.
|
|
|
Ports
|
The holes in a directional mic that allow reflected sound to be filtered out.
|
|
|
Pots
|
Knobs on an audio board that control the volume.
|
|
|
Pressure Zone Mic
|
A flat microphone that consists of a thin pickup plate that, when mounted on a table or ceiling, uses the surface it is mounted on to collect sound waves.
|
|
|
Program Monitor
|
An audio speaker on which you can hear the output of the audio board.
|
|
|
Proximity Effect
|
The boosting of bass frequencies as a sound source (particularly a male voice) gets closer to a cardioid mic.
|
|
|
RCA Connector
|
A connector with an outer sleeve and a center shaft.
|
|
|
RCA Connector
|

|
|
|
Phone Connector |

|
|
|
Reverberation
|
Sound that has bounced off a surface or various surfaces more than once or sound that has been processed so it sounds like it has bounced off surfaces.
|
|
|
Sampling
|
The process used to convert an analog signal into digital form by measuring the value of the analog signal at various temporal points and converting these values into digital information.
|
|
|
Sampling
|
All else being equal, a higher rate of ____________ results in a digital signal that is a truer representation of the original analog wave.
|
|
|
Segue
|
To cut from one sound at full volume to another sound at full volume.
|
|
|
Shaping
|
Altering an audio signal by doing such things as filtering out certain frequencies or emphasizing high or low pitches.
|
|
|
Shotgun
|
A highly directional microphone used for picking up sounds from a distance.
|
|
|
Sibilance
|
In speech, a hissing “s” sound picked up by some mics. |
|
|
Signal Processing
|
Changing the elements of a sound or a picture, such as frequency response and gain, so that the resulting signal is different from the original one.
|
|
|
Signal-to-noise Ratio
|
The relationship of desired sound to undesired electronic sound. The higher the ratio, the purer the sound.
|
|
|
Sleeve
|
An outer part of a number of connectors, such as phone, miniphone, and RCA.
|
|
|
Snake
|
A connector box that contains a large number of microphone input receptacles.
|
|
|
Solo
|
The control on an audio console that silences all channels except the one that has been selected.
|
|
|
Speech Bump
|
A frequency response characteristic of a mic that enables it to pick up speech frequencies better than other frequencies.
|
|
|
Split-pair Miking
|
A method of stereo miking that mimics natural hearing by placing two mics several feet apart.
|
|
|
Stereo
|
Audio that is recorded, transmitted, and played back through two separate (left and right) channels to simulate binaural hearing.
|
|
|
Supercardioid
|
A very narrow microphone pickup pattern, often used to record sounds that are at a distance.
|
|
|
Surround Sound
|
Audio that comes from five or six speakers or more placed around a room.
|
|
|
Table Stand
|
A mic holder that sits on a table or table-like setting so that one or more people can talk into it.
|
|
|
Three-to-one Rule
|
A microphone placement principle that states that, if two mics must be side by side, there should be three times the distance between them that there is between the mics and the people using them.
|
|
|
Timbre
|
A distinctive quality each voice or musical instrument has, caused, to a large degree, by overtones.
|
|
|
Tip
|
The end of some connectors, such as phone and miniphone.
|
|
|
Tone Generator
|
An element in an audio board or other piece of equipment that produces a constant one kilohertz sound that can be used to set consistent volume levels on different pieces of equipment.
|
|
|
Transducing
|
Receiving energy in one form (such as sound waves or light energy) and converting it into another form of energy (such as electromagnetic signals).
|
|
|
Treble
|
Sounds with more cycles per second (hertz) than lower bass sounds.
|
|
|
Trim
|
To make slight adjustments in audio.
|
|
|
Turntable
|
A piece of equipment for spinning records and converting the groove vibrations into electrical energy.
|
|
|
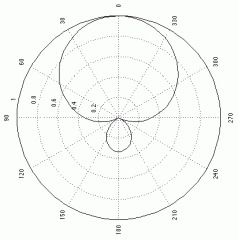
Ultracardioid
|
A very narrow microphone pickup pattern, often used to pick up sound from a distance.
|
|
|
Ultracardioid
|
|
|
|
Unbalanced Cables
|
Audio cables that have two wires, one for positive and one for both negative and ground.
|
|
|
Unidirectional
|
A microphone that picks up sound from one direction.
|
|
|
USB Connector
|

|
|
|
USB Connector
|
A digital connecting system used in computers and computer-based devices. It provides a uniform system of connecting peripherals such as cameras, hard drives or solid state media to computer components.
|
|
|
Volume Unit Meter
|
A display meter that shows the relative volume of an audio signal.
|
|
|
Wireless
|
Any system that sends audio or video signals through the airwaves as opposed to through cables.
|
|
|
XLR Connector
|
A professional-quality balanced connector with three prongs.
|
|
|
XLR Connector
|

|
|
|
Zoom Mic
|
A microphone that can change its direction pattern gradually from cardioid to super-, hyper-, or ultracardioid.
|

