![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Nikolsky sign? |
1. Absence of cohesion in the epidermis 2. Upper layers are easily made to slip laterally by slight pressure or rubbing |
|
|
What is the Asboe-Hasen sign? |
1. Direct pressure on intact bulla leading to bulla-spread phenomenon |
|
|
What bx are often taken in bullous disorders? |
1. Punch 2. H&E rom edge of intact blister 3. Perilesional DIF |
|
|
What will a bx yield in pemphigus vulgaris?1. |
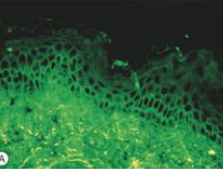
1. Anti-desmoglein IgG in lower epidermis |
|
|
What will a bx yield in pemphigus foliaceus? |
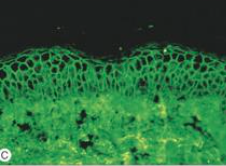
1. Anti-desmoglein IgG mostly in superficial epidermis |
|
|
What is desmoglein-3? Desmoglein-1? |
3--- mucosal antigen 1--- mucocutaneous antigen |
|
|
What are the ssx of pemphigus vulgaris? |
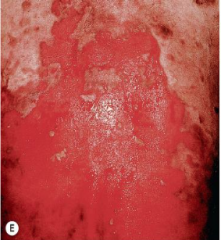
1. Flaccid bullae 2. +Nikolsky and Asboe-Hansen 3. Appear first in nose/mouth, then groin, scalp, face, neck axillae, and/or genitals |
|
|
What is the MC location of the first lesion in pemphigus vulgaris? |
1. Mouth |
|
|
What drugs can cause pemphigus vulgaris? |
1. Penicillamine 2. Captopril, other -prils 3. Piroxicam 4. Penicillin derivatives 5. Pyrazolone |
|
|
How do you tx pemphigus vulgaris? |
1. Silvadene topical 2. Maalox for mouth 3. Steroids 4. Plasmapharesis, IVIG |
|
|
What are the ssx of pemphigus vegetans? |
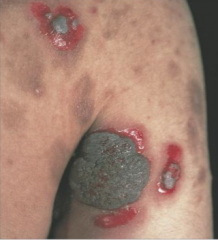
1. Flaccid bull that become eroded and form vegetative plaques 2. Often in body folds 3. Foul odor
|
|
|
What are the ssx of pemphigus foliaceus? |
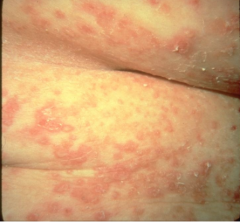
1. Flaccid bullae 2. Often only erythematous patches, crusts, or erosions--- cornflakes 3. Nikolsky sign + 4. Oral lesions rare |
|
|
What antibody is present in pemphigus foliaceus? |
1. Desmoglein 1 |
|
|
What are the ssx of pemphigus erythematosus? |
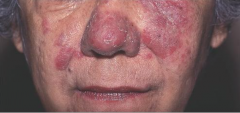
1. Localized pemphigus foliaceus with SLE overlap 2. ANA+ 3. Erythematous erosions, crusting |
|
|
How do you tx pemphigus erythematosus? |
1. Sun protection 2. Oral/topical steroids |
|
|
What is the MC associated underlying malignancy in paraneoplastic pemphigus? |
1. Non-hodgkin lymphoma |
|
|
What is the MC location of paraneoplastic pemphigus? |
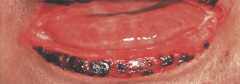
1. Severe stomatitis extending onto vermilion lip |
|
|
What are the ssx of subcorneal pustular dermatosis? |
1. Serpiginous vesicles or pustules 2. Underlying IgA gammopathy |
|
|
What are the ssx of intraepidermal neutrophilic type IgA pemphigus? |
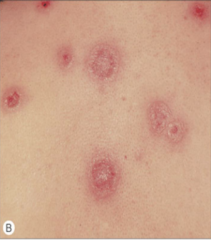
1. Flaccid pustules and bull involving intertriginous locations 2. Enlarge to form annular arrangement |
|
|
How do you tx both IgA pemphigus disorders? |
1. Dapsone 2. Oral corticosteroids |
|
|
What is the MC autoimmune blistering disease? |
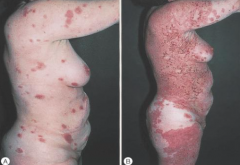
1. Bullous pemphigoid |
|
|
What antibodies are present in bullous pemphigoid? |
1. Bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 2. Bullous pemphigoid 2 |
|
|
What are the ssx of bullous pemphigoid? |
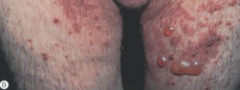
1. Urticarial wheals 2. Evolve into large, tense bull over medial thighs, groin, abdomen, and legs 3. Pruritus with subsequent tenderness |
|
|
What PMN predominates in bullous pemphigoid? |
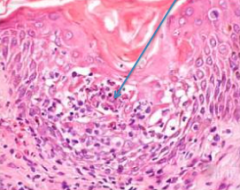
1. Eosinophils |
|
|
How do you dx bullous pemphigoid? |
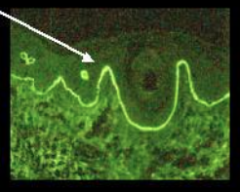
1. Linear IgG and C3 along dermal/epidermal junction |
|
|
How do you tx bullous pemphigoid? |
1. Corticosteroids 2. Tetracycline with nicotinamide TID |
|
|
What are the ssx of cicatricial pemphigoid? |
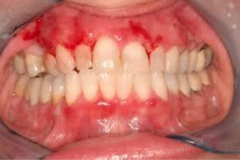
1. Scarring of mucous membrane 2. Slowly progressive shrinkage of the ocular mucous membranes and blindness |
|
|
What are the MC sites for cicatricial pemphigoid? |
1. Conjunctiva 2. Oral mucosa |
|
|
What are the antibodies associated with cicatricial pemphigoid?
Mucosa and skin? Ocular? Increased cancer risk? |
1. Mucosa and skin= BPAg2 antigen 2. Ocular=B4 subunit of a6-B4 integrin 3. Increased cancer= laminin 5 antigen |
|
|
What will DIF show in cicatricial pemphigoid? |
1. C3 and IgG at lamina lucida |
|
|
How do you tx cicatricial pemphigoid? |
1. Dapsone |
|
|
What is the onset of pemphigoid gestationis? |
1. 2nd or 3rd trimester 2. Postpartum |
|
|
What are the ssx of pemphigoid gestationis? |
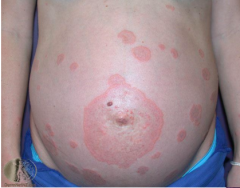
1. Urticarial plaques and papule start around umbilicus 2. Centripetal spread 3. Tense bullae 4. Spontaneous remission |
|
|
What is the antigen involved in pemphigoid gestationis? |
1. BPAg2 |
|
|
What are the risks associated with pemphigoid gestationis? |
1. Graves disease 2. Fetal prematurity 3. Small for gestational age |
|
|
What will histology show in pemphigoid gestationis? |
1. Subepidermal bulla with eosinophils 2. C3 +/- IgG at DE junction |
|
|
How do you tx pemphigoid gestationis? |
1. Oral corticosteroids |
|
|
What are the ssx of dermatitis herpetiformis? |
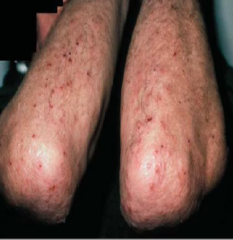
1. Polymorphous, grouped, symmetrical lesions 2. Often excoriated--- severe pruritus 3. Elbows, knees, buttocks, scalp, scapula |
|
|
What are the antibodies associated with dermatitis herpetiformis? |
1. Anti-endomysial 2. Anti-transglutaminase 3 3. Anti-gliadin
Formed in jejunum |
|
|
What are the risks associated with dermatitis herpetiformis? |
1. Thyroid disorders 2. Small bowel lymphoma 3. Non-Hodgkins lymphoma |
|
|
How do you tx dermatitis herpetiformis? |
1. Dapsone 2. Gluten-free diet |
|
|
What are the ssx of LABD adult form? |
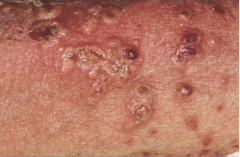
1. Annular vesicles/bullae over extensor extremities and buttock 2. Oral and conjunctival lesions can scar
"Crown of jewels" |
|
|
What antibodies are associate with LABD adult and childhood forms? |
1. LAD-1
|
|
|
What are the MC drug cause of LABD adult form? |
1. Vancomycin 2. Captopril, cephalosporin, penicillin |
|
|
How do you tx LBAD adult/childhood forms? |
1. Dapsone 2. Oral corticosteroid |
|
|
What will bx show in LBAD adult form? |
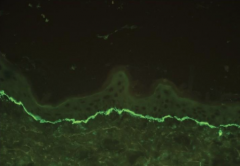
1. Tube of toothpaste--- IgA at basement membrane |
|
|
What are the ssx of LBAD childhood form? |
1. Bullae develop on erythematous or normal appearing skin 2. Crown of jewels arrangement |
|
|
What are the antibodies associated with EBA? |
1. Type VII collagen antibodies |
|
|
What are the ssx of EBA? |
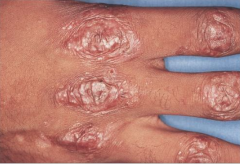
1. Noninflammatory bullae in traumatized area 2. Skin fragility 3. Atrophic scarring |
|
|
What will a bx show in EBA? |
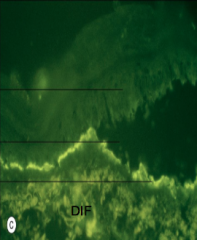
1. Linear IgG deposition at basement membrane |
|
|
How do you tx EBA? |
1. Steroids 2. Dapsone 3. Steroid-sparing agents 4. IVIG |
|
|
With what disorders is EBA associated? |
1. Myeloma 2. Granulomatous colitis 3. DM 4. Lymphoma |
|
|
What are the ssx of PCT? |
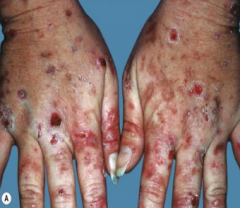
1. Hands and face MC involved 2. Tense bullae, erosions, milia, scarring on sun-exposed skin 3. Hypertrichosis on temples 4. Facial hyperpigmentation |
|
|
What is the MCC of PCT? |
1. Uroporphyringoen decarboxylase deficiency |
|
|
What are common triggers of PCT? |
1. Hepatitis C 2. Alcoholism |
|
|
How do you tx PCT? |
1. Phlebotomy every 2 weeks |

