![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dynein vs Kinesin:
Role |
Both are microtubular motor proteins
Dynein: retrograde transport--moving organelles toward nucleus (as in axons); also functions in ciliary/flagellar movement! Kinesin--anterograde transport--moving intracellular vesicles and organelles toward plus (rapidly growing) ends of MTs. |
|
|
Cleft lip vs Cleft palate:
Pathophys |
Both form during 6th week of embryonic development
2 medial nasal prominences fuse to form midline intermaxillary segment (becomes philtrum, medial maxillary (UPPER JAW) teeth, primary palate) Left and right maxillary prominences fuse with midline maxillary prominence to form upper lip. If one of maxillary prominences fails to fuse with maxillary prominance-->unilateral cleft lip If both maxillary prominences fail to fuse-->bilateral cleft lip Palate formed by intermaxillary segment and maxillary prominences. Palatine shelves grow from maxillary prominences medillay toward one another and toward intermaxillary segment. If palatine shelves fail to fuse with one another or with primary palate (intermax seg)-->cleft palate |
|
|
COX-1 vs COX-2:
Roles |
COX-1: platelets, GI fn (mucous production?)
COX-2: inflammn |
|
|
Turner's Syndrome:
Congenital abnormalities |
Webbed neck (duh)
Streak ovaries (ovaries infiltrated with fibrous tissue) Coarctation of the aorta Bicuspid aortic valve Horseshoe kidney |
|
|
Prominent occiput
Micrognathia Low-set ears Rocker-bottom feet |
Trisomy 18--Edwards Syndrome
|
|
|
Holoprosencephaly
Microcephaly Polydactyly Rocker-bottom feet |
Trisomy 13--Patau Syndrome
|
|
|
Describe triglyceride metabolism.
|
TG-->Glycerol + FA's via LIPASE
FA's-->beta-oxidation/ketogenesis Glycerol-->Glycerol-3-phosphate via GLYCEROL KINASE G3P-->DHAP-->Glycolysis (energy) or Gluconeogenesis (Glucose) GLYCEROL KINASE ONLY FOUND IN LIVER! |
|
|
Which component of the rotator cuff is most frequently damaged?
Effects? |
Supraspinatus tendon most likely to be damaged; presents with pain during ABDuction of the humerus.
|
|
|
Adductor of humerus
|
Lattisimus dorsi
|
|
|
Medial rotation of humerus
|
Subscapularis
|
|
|
What is factitious disorder?
|
Munchausen's--purposeful faking of syx to receive medical attn
|
|
|
What is malingering?
|
Purposeful faking of syx for secondary gain, typically financial (disability benefits)
|
|
|
What is matching and what bias does it control?
|
Matching involves selecting variables that could be confounders (e.g., age, race). Cases and controls are then selected based on matching variables, such that both groups have similar distribution in accordance with the variables.
|
|
|
Child with recurrent pulmonary infections
Distended capillaries on sun-exposed areas Loss of balance |
Distended capillaries on sun-exposed areas = telangectasias
Loss of balance = ataxia This is Ataxia telangectasia |
|
|
Ataxia telangectasia:
Presentation Pathophys |
Recurrent pulmonary infections
Ataxia (loss of motor coordination) Telangectasias Due to mutation of ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) gene responsible for DNA break repair. DNA in pts w/A-T is hypersensitive to x-ray radiation that causes multiple chromosomal breaks. |
|
|
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
Defective purine catabolism
X-linked recessive; defect in HGPRT gene Leads to hyperuricemia, gout, self-mutilating bhvr, mental retardation, chorea, spasticity. Also results in IgA deficiency which explains the resp infections |
|
|
Niemann-Pick disease
Pathophys Presentation |
AR defect in sphingomyelinase, results in accumuln of sphingomyelin within monocytes-->death by age 3
Presents with HSM, anemia, motor neuropathy leading to hypotonia and areflexia, cherry red spot on macula |
|
|
ST segment elevation
HR 42 BP 90/60 |
Inferior MI, usually due to blockage of RCA (responsible for SA node perfusion); presents with bradycardia
|
|
|
Treatment of inferior MI with bradycardia?
Contraindication? Why? |
Atropine to block vagal influence on SA node and to increase HR.
Blocks muscarinic receptors in other organs. In eye, causes mydriasis-->narrowing of anterior chamber-->diminished outflow of aqueous humor. Results in ACUTE CLOSED ANGLE GLAUCOMA (presents with unilateral severe eye pain). |
|
|
Hydatidiform mole:
Pathophys Complete vs Partial |
Complete mole: no fetal structures; composed of large, edematous, disordered chorionic villi ("bunch of grapes" appearance). Occurs when sperm fertilizes egg and replicates its own chromosomes while eliminating maternal chromosomes. Mole has 46 XX karyotype (dad's DNA ONLY).
Partial mole: Some formation of fetal structures grossly. Typically results from fertilization of an oxum by two or more sperm (two sets of haploid paternal chromosomes) results in 69XXY or 69XXX karyotypes. |
|
|
Which amino acids are dibasic?
How would a disorder in their absorption present? |
Lyine
Arginine Ornithine Cystine If can't absorb very well, will be excreted in urine/feces. However, cystine isn't very soluble at physiologic pH, so will present with recurrent cysteine stones in urine. |
|
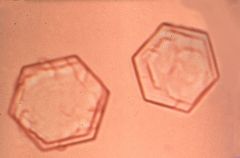
|
cystine crystals
|
|
|
What are PTH and calcium levels like in osteroporosis?
|
Normal
|
|
|
This virus binds CD21 cells.
|
EBV
|
|
|
Which bacteria produce beta-lactamase?
|
Staph aureus
H flu Bacteroides Other gram negs |
|
|
Which vessels will experience increased pressure in liver cirrhosis?
|
Porstal system: portal vein and splenic vein
|
|
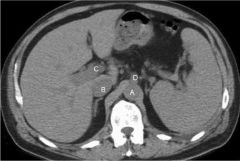
|
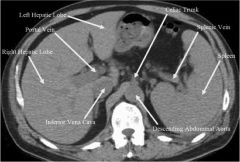
|
|
|
What is filtration fraction?
|
Portion of renal plasma flow that is filtered from glomerular capillaries into Bowman's space.
FF = GFR/RPF |
|
|
Effect of urethral diameter on GFR and filtration fraction.
|
Smaller diameter-->dec'd GFR
FF=GFR/RPF Thus dec'd FF as well |
|
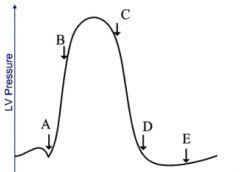
Label cardiac events.
|
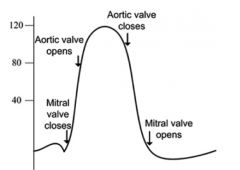
|
|
|
What determines the onset of anesthesia?
Discuss gradient and solubility. |
When sufficient concentration of anesthetic transferred to brain
Arteriovenous concentration gradient reflects the solubility of the anesthetic in tissues. The greater the gradient, the more soluble the drug is (in tissue), and the slower the onset of action. Onset is slower because a higher solubility requires a larger amount of anesthetic to saturate the blood. |
|
|
What are extrapyramidal symptoms?
What causes them? Be specific. |
Side effect of typical antipsychotics and of some atypical antipsychotics.
Syx include tardive dyskinesia and involuntary choeroathetoid movements of the limbs, trunk, and head. Of the atypicals: Risperidone is most likely to cause EPS while clozapine is least likely to cause EPS--clozapine is a last resort bc can results in agranulocytosis. |
|
|
Masked facies
Cogwheel rigidity Pill-rolling finger |
Parkinson's
Can be caused by benztropine |
|
|
Dystonia:
What is it? Drugs that cause it? Treatment? |
Dystonia = muscle spasms/stiffness, tongue protrusions or twistings, opisthotonus (arching of the back), and oculogyric crisis (forced, sustained elevation of the eyes)
Tx: antihistamines (diphenhydramine), or antichol (benztropine) |
|
|
This drug can result in Parkinsonian symptoms.
|
Benztropine
|
|
|
Describe the metabolism of glucose under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
|
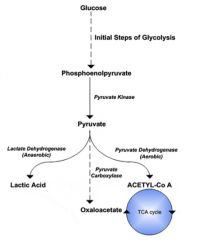
|
|
|
How is NAD+ regenerated in anaerobic conditions?
|
Pyruvate + NADH-->Lactate + NAD+ via Lactate DH
|
|
|
Thrombi in brain
Renal infarcts Elongated limbs Vision problems |
Thromboembolic episodes involving large and small vessels + syx of Marfan's-->Homocystinuria
|
|
|
Homocystinuria:
Pathophys Presentation Treatment |
Error of methionine metabolism caused by cystathionine synthetase deficiency
Results on thromboembolic events in large and small vessels--esp. brain (occurs at any age) Also see syx of Marfan's (ectopia lentis, elongated limbs, arachnodactyly, scoliosis) Tx: High dose Pyridoxine (B6) |
|
|
Thiamine deficiency:
Presentation |
AFFECTS ALCOHOLICS; also those on dialysis, or taking high doses of diuretics
Dry Beriberi (nervous system effects): difficulty walking, loss of sensation in hands/feet, mental confusion, nystagmus, tingling Wet Beriberi (CV effects): Awaking SOB, tachycardia, dyspnea on exertion, edema Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (common in alcoholics; see ataxia, leg tremor, nystagmus, inability to form new memories, confabulation, hallucinations) |
|
|
Ascorbic acid deficiency:
Effects |
Results in inhibited proline hydroxylation in collagen-->dec'd strength of collagen fibers (poor CT-strength-->scurvy)
|
|
|
Joint pain
Pruritic Rash Fibrinoid necrosis and neutrophil infiltration of arteries |
Serum sickness--type II hypersens rxn
|
|
|
Serum sickness:
Hypersensitivity type Pathophys Presentation |
Type II rxn (Ab-Ag complexes)
Presents as fever, urticaria, arthralgia, GN, LAD, VASCULITIS WITH FIBRINOID NECROSIS AND NPHIL DEPOSITION These reactions activate complement at local sites where immune complexes w/IgG and/or IgM complement-fixing Abs have been deposited. Often results in HYPOCOMPLEMENTEMIA (including dec'd C3 level) |
|
|
Blue-white spots on buccal mucosa
Cough Nasal discharge Conjunctivitis |
Measles--rubeola
|
|
|
Rubeola:
Virus type Presentation |
Rubeola = measles; enveloped, non-seg'd, negative-sense RNA virus
Koplik spots, cough, conjunctivitis, RASH |
|
|
Pneumonia in elderly
Following exposure to relatives with fever, HA, myalgias, cough |
Pneumonia in elderly following exposure to influenza A-->superinfection with pneumonia
In order of probability: Strep pneumo Staph aureus H. influenzae |
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae:
Populations affected Effects |
Nosocomial UTI
Nosocomial pneumonia Pneumonia in alcoholics and IVDU |
|
|
Vancomycin:
Bugs affected |
Gram-poz
|
|
|
Colistin:
Bugs affected |
AKA polymixin; gram-neg EXCEPT nesisseria meningitidis and neisseria gonorrhea
|
|
|
Nystatin:
Bugs affected |
Yeast, fungi
|
|
|
Trimethoprim:
Bugs affected |
Gram-neg other than Neisseria
|
|
|
Thayer-Martin mediums:
What are they? Function? |
Chocolate agar that contains vanco, colistin, nystatin, and trimethoprim.
Selectively grows Neisseria |
|
|
Asymmetric pupils
Irregular breathing pattern STEMI treated with streptokinase |
Intracranial hemorrhage secondary to streptokinase
|
|
|
Streptokinase:
MOA AE |
Thrombolytics; converts plasminogen into plasmin, which then degrades fibrin
AE: Hemorrhage, hypersens (derived from streptococci) |
|
|
Chest pain that radiates to the interscapular area
|
Aortic dissection (appears as widened mediastinum on CXR)
|
|
|
Anterior third of tongue:
Pain vs Taste Innervation |
Pain: Mandibular of Trigeminal
Taste: Chorda tympani of facial nerve |
|
|
Posterior third of tongue:
Pain vs Taste Sensation |
Pain: Glossopharyngeal
Taste: Glossopharyngeal |
|
|
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators:
Role Examples AEs |
Tissue-selective E2 agonist and antagonist properties (activity varies with tissue type)
In breasts, they're anti-estrogenic (useful in ER-positive BrCa). In endometrial tissue, has stimulatory effect. Thus AE = endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Ex: Tamoxifen, Raloxifene |
|
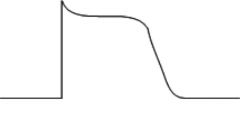
Identify cell and label phases.
|
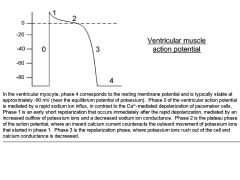
|
|
|
Identify personality disorder:
Feelings of inadequacy Timidity Fear of rejection |
Avoidant PD
|
|
|
Identify personality disorder:
Submissiveness Clinging behavior Fear of abandonment |
Dependent PD
|
|
|
Identify personality disorder:
Self-absorbed Little pleasure in intimacy Isolated No desire for acceptance |
Schizoid PD
|
|
|
Describe the metabolism of glycogen and include relevant disorders.
|
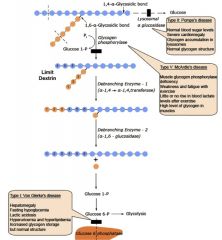
|
|
|
67 year-old male
Tibial pain and deformity Hearing loss |
Paget's disease that has affected tibia and skull (hearing loss)
|
|
|
Paget's Disease:
Pathophys Hallmark |
Overactive osteoclasts leading to excessive bone resorption
Osteoclasts with up to 100 nuclei = Paget's (shouldn't have more than 2-5 nuclei) |
|
|
What hormones play a role in osteoclast differentiation?
|
RANK-L and M-CSF (macrophage colony stimulating factor)
|
|
|
Effect of fibroblast GF on bone.
|
Stimulates osteoblasts
|
|
|
Effect of insulin GF on bone.
|
Inc'd oblast replication
|
|
|
How do cancer cells become resistant to chemotherapy?
|
Express human multidrug resistance gene (MDR1) for P-glycoprotein--an ATP-dependent efflux pump that has broad specificity for hydrophobic compounds.
THe pump reduces the influx of drugs and increases efflux from the cytosol (preventing action of chemo). |
|
|
Role of tyrosine kinase receptors:
General and specific |
General: mediates effects o hormones that promote anabolism and cell growth
Ex: insulin, IGF-1, EGF (epidermal GF), PDGF |
|
|
What is flocculation?
|
Aggregation
|
|
|
Fever
Malaise Maculopapular rash on soles and palms |
Could be syphilis (spirochete)
|
|
|
Syphilis:
Causative organism Screen, confirmatory |
Caused by treponema pallidum (spirochete)
Screen with: RPR (aka VDRL)where pt's serum is mixed w/cardiolipin, cholesterol, and lecithin. If aggregation (flocculation) is seen-->there are are cardiolipin Ab's in pt's serum (seen when T. pallidum destroys RBCs) Confirm with spirochete Ab tests such as FTA-ABS (detects Ab's against treponema) |
|
|
Retinopathy of prematurity:
Pathophys |
Neonatal distress syndrome treated with concentrated O2.
Temporary hyperoxia in the retina induces up-regulation of VEGF upon return to air ventilation, retinal vessel proliferation and possible retinal detachment with blindness may result. |
|
|
Normal pressure hydrocephalus:
Presentation Pathophys |
Presentation:
Urinary incontinence Ataxic Gait Dementia Pathophys: Decline in reasborptive capacity of arachnoid villi with accumulation of SF. Pressure remains normal because ventricular distention accommodates CSF increase. This is reversible. |
|
|
Urinary incontinence
Ataxia Dementia |
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
|
|
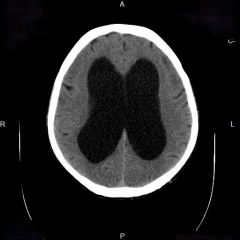
|
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
|
|
|
What is HELLP syndrome?
|
Hemolytic anemia
Elevated LFTs Low PLTs (in pregnancy, duh) |
|
|
Pre-eclampsia vs Eclampsia
|
Pre-eclampsia: HTN, proteinuria, edema
Eclampsia: pre-eclampsia + seizures |
|
|
Growth hormone:
Role Site of production/release |
Produced by hypothalamus
Released by ANTERIOR pituitary Inc'd growth of long bones through IGF-1 from liver |
|
|
Acromegaly vs Gigantism
|
Acromegaly: excess GH before epiphyseal closure
Gigantism: after epiphyseal closure |
|
|
Why do some patients with sarcoidosis present with hypercalcemia?
What other disorders does this occur in? |
In sarcoidosis, act'd T cells release IGN-gamma which increases activity of 1-alpha OHase in MACROPHAGES (not in kidneys!); this enzyme converts 25-OH D to 1,25-dihydroxy D (active).
Also occurs in other granulomatous disorders such as Hodgkin's lymphoma (extrarenal 1-alpha OHase activity) Note PTH levels are suppressed in this circumstances. |
|
|
What factors regulate vitamin D production?
What enzyme is necessary for this to occur? |
PTH
1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D (active) Phosphorus levels Requires renal 1-alpha OHase |
|
|
Thenar atrophy
Weakness of thumb abduction Pain and paresthesia over palmar surface of thumb, index, and middle fingers |
Carpal tunnel
|
|
|
Carpal tunnel syndrome:
Pathophys Causes |
Compression of median nerve associated with:
-repetitive wrist movements -Hypothyroid -DIALYSIS (renal failure) -DM -RA |
|
|
Comedocarcinoma (breast):
Histologic features |
Ductal carcinoma in situ = comedocarcinoma
Basal layer of duct preserved and uninvolved Surrounds ductal BM Appears as pleomorphic, high-grade cells with central necrosis |
|
|
Paget disease of the breast:
Presentation Pathophys |
Unilateral erythema and scale crust around nipple
Caused by malignant cells spreading from superficial DCIS into nipple skin without crossing BM |
|
|
Sclerosing adenosis of breast:
Histologic findings |
Central acinar compression and distortion by surrounding fibrotic tissue
Periphereal ductal dilation (common in fibrocystic change) |
|
|
Mammary duct ectasia:
Presentation |
Ectasia = dilation
Ductal dilation, inspissated breast secretions, chronic granulomatous inflammn in periductal and interstitial areas |
|
|
How do the effects of hypoxemia differ in the lungs?
|
In lungs, hypoxemia causes a vasoconstrictive response to divert blood away from underventilated regions of lung toward more well-ventilated regions.
In most other tissues, hypoxemia-->vasodilation |

