![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe insulin manufacture. Begin with proinsulin.
|
Within beta-cell, newly synthesized proinsulin despoited in rER.
Transported to Golgi apparatus, cleaved into insulin, C peptide, and 2 pairs of aa's (via convertases). C peptide and insulin are together packaged into secretory granules and are released in equimolar concentrations. |
|
|
Escalating fever
Diarrhea Hepatosplenomegaly Rose colored spots on abdomen |
Typhoid fever (Salmonella typhyi)
Can also present with constipation |
|
|
Typhoid fever:
Locations Pathophys Presentation |
Third world nations (travelers to Asia, Africa, and Latin America)
Caued by Salmonella typhi or Salmonella paratyphi Fecal-oral dz; organism penetrates gut mucosa and is phag'd my macs. Macs carry organism to liver, spleen, BM. Results in HSM from organism growth. Leads to bacteremia. Within gut lumen, cause inflammn within Peyer's patches-->intestinal hemorrhage and potential gut perforation-->sepsis |
|
|
Trimethoprim:
MOA What other drugs share this MOA? |
Trimethoprim prevents reduction of folic acid to THF by inhibiting DHF reductase.
Other drugs that do this: Methotrexate (cell cycle specific for S phase--good for halting DNA synthesis in rapidly proliferating cells) Pyrimethamine |
|
|
This property describes the ability of a test to provide reproducible results.
|
Reliability
|
|
|
This property describe the ability of a test to measure what it's supposed to measure.
|
Validity/Accuracy
|
|
|
In a normal distribution curve, ____ of observations lie within one standard deviation of the mean, and _____ of observations lie within 2 standard deviations of the mean.
|
68% within 1SD
95% within 2SD |
|
|
Posterior cruciate ligament:
Attachments Function |
PCL attaches posterior part of intercondylar area and anterior lateral part of the medial epicondyle of the femur.
Fn: Prevents anterior displacement of femur relative to tibia while knee is flexed |
|
|
Anterior cruciate ligament:
Attachments Function |
More commonly injured than PCL!
Spans from anterior intercondylar tibia to posterior medial side of lateral femoral condyle. PRevents posterior displacement of femur relative to tibia when knee is extended |
|
|
Tibial collateral ligament:
Attachments Function |
Tibial collateral ligament = medial collateral ligament
Attaches medial femoral epicondyle to medial condyle of tibia |
|
|
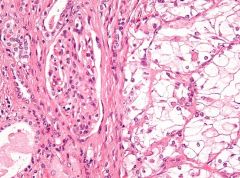
Renal cell carcinoma:
Cell origin Histologic appearance |
CLEAR CELL CARCINOMA = RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
cuboidal/polygonal cells w/clear abundant cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei High glycogen and lipid content Originate from PROXIMAL RENAL TUBULES |
|
|
Clear cell carcinoma (renal)
|
|
|
Which cytokines are anti-inflammatory?
|
TGF-beta; IL-10
|
|
|
What are the components of the neurovascular triad to the thyroid and parathyroid?
|
Superior thyroid artery
Superior thyroid vein External branch of superior laryngeal nerve |
|
|
Laryngeal nerve:
What CN does it originate form? Branches and innervations |
Vagus-->Laryngeal
-->Superior laryngeal: -External branch-->Cricothyroid Internal branch-->sensation above vocal cords -->Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve-->All laryngeal mm except cricothyroid; sensation below vocal cords |
|
|
What patients are at risk of reactivation of latent EBV infection?
What risks does this pose and why? |
Immunosuppressed (AIDS pts) at risk of latent EBV reactivation
EBV is tropic for B lymphocytes, can lead to non-Hodgkin's diffuse B-cell lymphoma |
|
|
Interstitial vs Lobar Pneumonia:
General |
Interstitial: inflammatory infiltrate confined to alveolar walls
Lobar: inflammatory process involves entire lung lobe |
|
|
Describe the four stages, in order of progression, of lobar pneumonia.
|
Congestion--first 24 hours of pneumonia: lobe is red, heavy and boggy; vascular dil,tion, alveolar exudate = bacteria
Red hepatization: days 2-3; lobe is red and firm; alveolar exudate contains RBCs, nphils, fibrin Gray hepatization: days 4-6; lobe is gray-brown, firm; RBCs disintegrate, alveolar exudate contains nphils and fibrin Resolution: restoration of normal architecture; enzymatic digestion of exudate |
|
|
IFN-alpha vs -beta vs -gamma:
Functions |
IFN-alpha and -beta-->inhibit viral replication and synthesize antiviral proteins that impair translation of viral mRNA without impacting cellular mRNA
IFN-gamma: increase activation and efficacy of virus-specific T killer cells (ex: stimulates macs to produce more IL-12, which promotes differentiation of more naive T helper cells into TH1 helper cells, which then secrete more IFN-gamma, etc) |
|
|
CREST syndrome:
Presentation Associated antibody |
Calcinosis (subcutaneous calcium deposits)
Raynaud's phenomenon (painful episodes of pallor, cyanosis, and erythema of hands) Esophageal dysmotility Sclerodactyly (thickening of skin of hands and feet--begins as tight and shiny) Telangiectasias (dilated blood vessels on skin) Anti-centromere Ab |
|
|
How do aortic stenosis and atrial fibrillation specifically affect cardiac output?
|
Aortic stenosis decreases cardiac output (harder to pump blood out) and thus reduced arterial pressure.
Atrial fibrillation results in loss of atrial kick, thus, less LV preload, and a dec'd cardiac output. May also increase pulmonary venous pressure enough to cause acute pulmonary edema, hypotn. |
|
|
Heart muscle is perfused during [diastole/systole].
|
Diastole--contraction during systole-->compression of coronary aa and disruption of flow.
|
|
|
How does myocardial oxygen requirement and consumption differ from other tissues?
|
Myocardial oxygen extraction and requirements exceed any other tissue or organ in the body.
|
|
|
When in the breathing cycle is resistance the lowest?
|
At functional residual capacity.
|
|
|
What is the effect of constricting the efferent arteriole of the kidney?
|
Constriction of the efferent arteriole will impede blood flow through the kidney
This will decrease renal plasma flow, incresase glomerular hydrostatic pressure, and cause an increase in the filtration fraction. |
|
|
Elevated ALT and AST
HBsAg positive Hepatitis B infection: Proliferative vs Integrative Phases -General -When does hepatocellular damage occur? |
Proliferative: virion and ag's of HBV DNA present; viral HBsAg and HBcAG expressed with MHC1, which activates CD8+ cells; CD8+ cells destroy infected hepatocytes (virion doesn't have cytopathic effect)
Integrative phase: HBV DNA incorporated into host genome cells that survived immune response; infectivity ceases and liver damage tapers off when when antiviral Ab's appear and viral replication stops. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma remains elevated. |
|
|
Enzyme deficiencies in porphyrin synthesis:
Early steps vs Late steps -Examples -Effects |
Deficiencies in early steps:
-Results in neuropsychiatric manifestations without photosensitivity -Ex: ALA dehydrase, HMB synthase Deficiency in late steps: -Photosensitivity resulting in vesicle and blister formation on sun-exposed areas as well as edema, pruritis, pain and erythema -Ex: Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, Coproporhyrinogen oxidase |
|
|
Recent travel to Mexico
Nausea Vomiting Watery diarrhea Resolves without antibiotics |
Cholera-like toxin from Enterotoxigenic E. coli
|
|
|
Function of capsules in bacteria.
Which specific bacteria have a capsule? |
Protects against phagocytosis
Some Killers Have Nice Shiny Bodies Step pneumo Klebsiella Haemophilus influenzae (B) Neisseria meningitdis Salmonella Group B Strep |
|
|
Enterotoxigenic E. coli:
Presentation Pathophys |
Watery diarrhea with abdominal cramps, n/v, that resolves
Pathophys: heat labile (cholera-like) and heat stabile enterotoxins. Heat labile-->inc'd adenylate cyclase, inc'd cAMP; heat stabile-->inc'd intracell cGMP. Both result in water and electrolyte loss through diarrhea. |
|
|
Cholera-like toxin
|
Heat labile toxin; ETEC
|
|
|
ACE inhibitors:
MOA |
Block ACE, decreasing AgII and aldosterone
Results in inc'd renin and Ag I Without ACE, bradykinin metabolism decreases, resulting in an increase in bradykinin |
|
|
This enzyme is essential to the metabolism of bradykinin.
|
ACE
|
|
|
Carbamazepine:
AE |
Exaggerated response to ADH (vasopressin)--Causes SIADH...weird
|
|
|
ADH:
Location Role |
Released by posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis); produced in supraoptic nuclei of hypothalamus.
Neurophysins play role in posttranslational processing of ADH. |
|
|
Neurophysins:
Role |
Posttranslational processing of oxytocin and vasopressin. They're released into circulation from the posterior pituitary along with ADH and oxytocin.
|
|
|
This hormone is produced in the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus.
|
ADH
|
|
|
This hormone is produced in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus.
|
Oxytocin
|
|
|
Galactosemia:
Pathophys Presentation |
Impaired galactose-1-phosphate metabolism (deficiency of galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase)
Results in increased levels of Galactitol, which irreversibly damages eyes and liver Presentation: Vomiting Lethargy Failure to thrive after breastfeeding is begun Resolves if placed on galactose-free diet |
|
|
Hypertensive crisis:
Clinical definition Histological findings Pathophys of findings |
Diastolic BP (second number) >130, ex: BP of 240/150
Hyperplastic arteriosclerosis-->onion-like concentric thickening of renal arteriolar walls Renal arteriolar stenosis-->dec'd glomerular perfusion and GFR-->stimulates renin-aldosterone system -->further increase in BP-->malignant nephrosclerosis Arises in retinal hemorrhages, exudates, papilledema |
|
|
MacConkey agar:
Utility |
Isolates gram-negative organisms (like E Coli)
Pink-->lactose fermenter (E. coli) |
|
|
How does E. coli result in meningitis?
Include virulence factors. |
K-1 capsular antigen
E. coli can invade blood stream of infants from nasopharynx or GI tract and travel hematogenously to meninges. K-1 antigen inhibits complement, phagocytosis, and other host responses. Capsule is immunogenic and anticapsular Ab's are protective. |
|
|
Hyponatremia
Hyperkalemia Acidosis |
Aldosterone and cortisol deficiency
|
|
|
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia:
Pathophys Presentation |
Deficiency of 21-OHase-->cortisol and aldosterone deficiency
Adrenal gland can't synthesize coritsol efficiently-->inc'd production of adrenal androgens (accumulating cortisol precursors diverted to androgen synthesis PW). Low cortisol triggers pituitary to produce ACTH which increases adrenal androgen production even more. Presents with hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, acidosis, hypoglycemia and CLITEROMEGALY (in girls). Male infants normal in appearance (probably go into salt-wasting crisis?). |
|
|
Retroviral reverse transcriptase inhibitors vs Non-nucleoside retroviral reverse transcriptase inhibitors :
General Examples |
RT inhibitors prevent synthesis of viral DNA from RNA template and require activation via intracellulary phosphorylation
Ex: of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor = Zidovudine (AZT) NNRTIs do not require activation and are structurally unrelated to nucleosides Ex: Nevirapine, efavirenz, delavirdine |
|
|
Gram positive algorithm
|
Gram (+): Purple/blue
Cocci and Rods (bacilli): If cocci: Catalase (+)--Clusters or Catalase (-)--Chains Catalase (+): Staph If Staph: Coag (+): Staph aureus Coag (-): Staph epidermidis; Staph saphrophyticus If Catalase (-): Strep ---- If rods (bacilli): Clostridium Listeria Bacillus |
|
|
Draw gram negative algorithm.
|
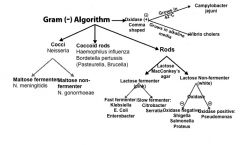
|
|
|
Define ectopy.
Provide an example. |
Microscopically and functionally normal cells/tissues found in an abnl location due to embryonic maldevelopment
Ex: Meckel diverticulum |
|
|
What is a Meckel's diverticulum?
|
Congenital anomaly of small intestine
Results in blind pouch (diverticulum) connected to ileum. Variety of tissues found in the diverticulum, including gastric, pancreatic, colonic, jejunal, duodenal, and endometrial. |
|
|
Sildenafil:
MOA |
inhibits cGMP PDE-->activate cGMP second messenger system (bc there's a net increase in intracell cGMP)
|
|
|
How does NO result in vasodilation?
What other hormone shares this MOA? |
NO binds a receptor protein that has guanylate cyclase enzymatic ability (cGMP second messenger system)
Atrial natriuretic peptide also does this |
|
|
What second messenger does insulin employ?
|
Tyrosine kinase
|
|
|
How does diabetes type 1 arise?
What does this put patients at risk of? |
Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta-cells
Puts pts at risk of developing other autoimmune disorders, including autoimmune adrenalitis, Hashmitoto's thyroiditis, Graves' dz, Addison's dz, vitiligo, pernicious anemia |
|
|
DM1
Anorexia Weight loss Dec'd insulin requirement Hyperpigmentation ACTH fails to elicit increase in serum cortisol |
Autoimmune adrenalitis (DM1 is due to auto-ab's) resulting in primary adrenal insufficiency
|
|
|
Primary adrenal insufficiency:
What is it? Lab values? |
Defect in adrenal glans that does not permit release of its secretions
Presentation: Hyponatremia Hyperkalemia Hypochloremia Metbaolic acidosis Exogenous ACTH does not elevate cortisol levels |
|
|
How do the three subtypes of Class I antiarrhythmics differ by receptor association time?
Which drugs belong to each class? |
1A: Intermediate binding to Na, also blocks K channels
1B: rate of binding and release so rapid no change in Vmax seen. 1C: very tight binding, slow release. Police Department Questioned (IA) The Little Man (IB) For Pushing Ecstasy (IC) IA: Procainamide, disopyramide, quinidine IB: Tocainamide, lidocain, mexiletine IC: Flecainide, propafenone, encainide |
|
|
Hyperthermia
Hypertension Tachycardia Mydriasis Bilateral hyperreflexia Inducible ankle clonus Agitation, confusion |
Serotonin syndrome
|
|
|
Serotonin is a metabolite of ___________.
|
Tryptophan
|
|
|
GABA is a metabolite of __________.
|
Glutamate
|
|
|
Histamine is a metabolite of ________.
|
Histidine
|
|
|
NE is a metabolite of _______.
|
TYROSINE (not tryptophan!)
|
|
|
Phenylalanine is a precursor of ______.
|
DA, E, NE, melanin
|
|
|
Serotonin syndrome:
Symptoms Treatment |
Confusion, agitation
Hyperthermia HTN Mydriasis Clonus Hyperreflexia Tx: nonspecific serotonergic antagonist (blocks 5HT1 and 5HT2 receptors)-->Cyproheptadine (technically an anti-histamine) |
|
|
Naloxone:
Use |
Narcotic OD
|
|
|
Flumazenil:
Use |
Bendo OD
|
|
|
C. tetani:
Effects Prophylaxis Treatment |
Produces exotoxin, tetanospasmin, which blocks release of inhibitory NTs from CNS (GABA, glycine).
Prevent tetanus with toxoid immunization to trigger production of antitoxin Abs. Can give tetanus immune globulin for acute treatment. |
|
|
What are the maternity blues?
How long should it last? How does this differ from postpartum psychosis? |
Tearfulness, fatigue, depressed affect, irritability after childbirth. Usually resolves within 2 weeks of giving birth.
Postpartum psychosis presents with delusions, confusion, suicidality; requires antipsychotics, antidepressants, and possibly inpatient hospitalization |
|
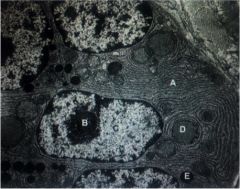
Label
|
A: rER--stippled appearance (rough) due to ribosomes bound to membranes
B: Nucleolus-synthesis and assembly of ribosomal components (NOT membrane-bound) C: Nucleus--lighter region is euchromatin (DNA that has been unpackaged and is actively being transcribed) D-Mitochondria E-Exocrine secretory granule (contains exocrine enzymes and proteins packaged for secretion) |
|
|
Fever
Rash Eosinophiluria Oliguria Post-treatment with beta-lactam |
Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis
|
|
|
Drug-induced interstitial nephritis:
Causes Pathophys Presentation |
NSAIDs
beta-lactams Suolfonamides Rifampin Diuretics Drugs cause damage to ; interstitium (glomeruli intact); likely due to hypersensitivity reaction. Present w/fever, maculopapular rash, acute renal failure. Peripheral eosinophilia and eosinophiluria**** Syx resolve after cessation of medication |
|
|
Nail pitting
Salmon-covered plaques with silvery scales Arthritis |
Psoriatic arthritis (a deforming joint dz)
|
|
|
TATA Box:
Role |
promoter region that binds transcription factors and RNA pol II during initiation of transcription; located ~25 bases upstream (towards 5') from beginning of coding region
|
|
|
DNA methylation is executed by _______.
|
DNA methyltransferases--crucial to epigenetic code
|
|
|
What is required for eukaryotic translation?
|
60S and 40S subunits
rRNA mRNA initiating factors initiator tRNA charged with methionine (met-tRNAi) GTP Ribosome then recognizes AUG start codon |
|
|
What is required for posttranslational splicing of introns from RNA?
|
snRNPs (small nuclear ribonuecleoprotein particles)
|
|
|
What is vesicoureteral reflux?
Consequences? |
Flow of urine from bladder to ureters to kidneys
Risk of pyelonephritis |
|
|
What bacteria usually cause acute pyelonephritis?
|
E coli
Klebsiella Proteus Enterococci |
|
|
What antidepressants can mimic atropine toxicity?
Presentation? |
TCAs: amitryptylines; -imipramines
Presents as fever, mucosal and axillary dyrness, cutaneous flushing, mydriasis, cycloplegia, delirium (hot as a hare!) |
|
|
Diazepam:
AEs |
Benzos!
Sedation Anterograde amnesia Respiratory depression Rarely fatal in oD |
|
|
Carbamazepine:
AEs |
Remember that this is a seizure drug, bipolar disorder too
AEs: stupor, coma, inc'd seizure risk |
|
|
What is cryptorchidism?
|
Undescended testis
|
|
|
Why would a patient with undescended testis exhibit a low sperm count but present with secondary sex characteristics?
Describe hormone levels. |
Seminiferous tubules are termperature-sensitive and prone to head-induced damage.
If not surgically moved to scrotal sac, will become atrophic and hyalinized over time. Additionally, because seminiferous tubules are responsible for secretion of inhibin, levels of inhibin decrease. FSH levels are elevated due to loss of negative inhibition by inhibin. Unlike seminiferous tubules, Leydig cells, which produce testosterone, aren't sensitive to temperature; thus testosterone and LH levels are normal. |

