![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
264 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which bugs do not Gram stain well?
|
These Rascals May Microscopically Lack Colour
Treponema (too thin), Rickettsia (intracellular), Mycobacteria, Mycoplasma (no cell wall), Legionella (intracellular), Chlamydia (intracellular) |
|
|
Which bugs require the Giemsa stain?
|
Borrelia, Plasmodium, trypanosomes, Chlamydia
|
|
|
Which stain is used to diagnose Whipple's disease?
|
PAS (periodic acid-Schiff) - stains glycogen, mucopolysaccharides
|
|
|
What is the Ziehl-Neelsen stain?
|
Acid-fast stain. Used to identify acid-fast organisms, mainly Mycobacteria. Nocardia is also weakly acid fast
|
|
|
Which stain is used to detect the presence of Cryptococcus neoformans?
|
India ink - The background is stained while the organisms remain clear (negative stain).
|
|
|
Which stain is used to detect the presence of Legionella and fungi (eg. pneumocystitis)?
|
Silver stain
|
|
|
Which stain is used to detect amyloidosis?
|
Congo Red
|
|
|
What are some examples of obligate aerobes?
|
Nagging Pests Must Breathe
Nocardia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Bacillus |
|
|
What are some examples of obligate anaerobes?
|
Can't Breathe Air
Clostridium, Bacteroides, Actinomyces They lack catalse and/or superoxide dismutase and thus susceptible to oxidative damage. Note: Aminoglycosides are ineffective because it requires O2 to enter bacterial cell. |
|
|
What are some examples of obligate intracellular bugs?
|
Rickettsia, Chlamydia (can't make own ATP)
|
|
|
What are some examples of facultative intracellular bugs?
|
Salmonella, Neisseria, Brucella, Mycobacterium, Listeria, Francisella, Legionella
|
|
|
What are some examples of encapsulated bacteria?
|
Some Killers Have Nice Shiny Bodies
Strep pneumonia, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenza B, Neisseria meningitidis, Salmonella, group B strep. |
|
|
What bugs have a positive quellung reaction?
|
If encapsulated bug is present, capsule swells when specific anticapsular antisera are added.
Some Killers Have Nice Shiny Bodies Strep pneumonia, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenza B, Neisseria meningitidis, Salmonella, group B strep. |
|
|
What are some examples of urease-positive bugs?
|
Particular Kinds Have Urease
Proteus, Klebsiella, H. pylori, Ureaplasma |
|
|
What are superantigens?
|
Bind directly to MHC II and T-cell receptor simultaneously, activating large numbers of T cells to stimulate release of IFN-gamma and IL-2, thus generating a massive immune response which is not specific to any particular epitope.
Ex. S. aureus (toxic shock syndrome); S. pyogenes (Scarlet fever) |
|
|
Which bug?
Floppy baby |
Clostridium botulinum
|
|
|
Which bug?
Causes pharyngitis and 'pseudomembrane' in throat. Potent exotoxin inhibits protein synthesis via ADP ribosylation of EF-2. |
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
|
|
Which bug?
ADP ribosylation of G protein stimulates adenylyl cyclase. Increased pumping of Cl into gut, and decreased Na absorption -> voluminous rice-water diarrhea |
Vibrio cholerae
|
|
|
Which bug?
Heat-labile toxin stimulates adenylate cyclase. Heat-stable toxin stimulates guanylate cyclase. Both cause watery diarrhea |
E. coli
|
|
|
Which bug?
alpha toxin, a lecithinase that acts as a phospholipase to cleave cell membranes and causes gas gangrene; get double zone of hemolysis on blood agar. |
Clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
Which bug?
Blocks the release of GABA and glycine; causes 'lockjaw' |
Clostridium tetani
|
|
|
Which bug?
Blocks the relase of ACh (causes anticholinergic symptoms), CNS paralysis, especially cranial nerves |
Clostridium botulinum
|
|
|
Which bug?
Spores found in canned food, honey |
Clostridium botulinum
|
|
|
Which bug?
Toxin cleaves host cell rRNA and also enhances cytokine release, causing HUS (hemolytic uremic syndrome) |
Shigella
|
|
|
Which bacteria display alpha-hemolysis?
|
Partial hemolysis - Strep pneumoniae, Strep viridans.
Forms green ring around colonies on blood agar. |
|
|
What are the Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (GAS)?
|
Strep pyogenes
|
|
|
What are the beta-hemolytic bacteria?
|
Complete hemolysis - forms a clear area of hemolysis on blood agar.
Ex. Staph aureus, Strep pyogenes (Group A), Strep agalactiae (Group B), Listeria monocytogenes |
|
|
Which bug?
Protein A virulence factor; Can cause inflammatory disease (skin infections, organ abscesses), and toxin-mediates disease (scalded skin syndrome, rapid-onset food poisoning), etc. |
Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
Which bug?
Infects prosthetic devices and intravenous catheters by producing adherent biofilms. Component of normal skin flora. |
Staphylococcus epidermidis. Can be associated with endocarditis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Most common cause of: meningitis, otitis media (in children), pneumonia, sinusistis |
Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which bug?
Lancet shaped; encapsulated; contains IgA protease |
Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which bug?
Normal flora of the oropharynx and cause dental caries and subacute bacterial endocarditis. |
Viridans group streptococci
|
|
|
Which bug?
Can cause pharyngitis, cellulitis, impetigo, scarlet fever, rheumatic fever, acute glomerulonephritis |
Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococci)
|
|
|
Which bug?
ASO (Anti-streptolysin O) titer detects recent infection. |
Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococci)
One of the first bacterial markers used for diagnosis and follow up of rheumatic fever or scarlet fever. |
|
|
Which bug?
Colonizes vagina; Causes pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis, mainly in babies |
Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococci)
|
|
|
Which bug?
Screened in pregnant women at 35-37 weeks. Patients with positive culture receive intrapartum penicillin prophylaxis. |
Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococci)
|
|
|
Which bug?
Normal colonic flora that are penicillin G resistant and cause UTI and subacute endocarditis. |
Enterococci (group D streptococci)
|
|
|
What are some examples of spore-forming gram-positive bacteria?
|
Found in soil: Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium tetani.
Other: Bacillus cereus, Clostridium botulinum, Coxiella burnetii |
|
|
Which bug?
Produces 2 toxins. Toxin A, enterotoxin, binds to the brush border of the gut. Toxin B, cytotoxin, destroys the cytoskeletal structure of enterocytes, causing pseudomembranous colitis. |
Clostridium difficile.
Diagnosed by detection of one or both toxins in stool. |
|
|
Which bug?
Associated with black eschar (painless ulcer/necrosis) if contact. Or flulike symptoms that rapidly progresses to fever, pulmonary hemorrhage, mediastinitis, and shock if inhaled. |
Bacillus anthracis.
|
|
|
Which bug?
Acquired by ingestion of unpasteurized milk/cheese and deli meats or by vaginal transmission during birth. Can cause amnionitis, septicemia, and spontaneous abortion in pregnant women; neonatal meningitis; meningitis in immunocompromised patients; mild gastroenteritis |
Listeria monocytogenes
|
|
|
Which bug?
Forms yellow 'sulfur granules' in sinus tracts. Causes oral/facial abscesses that may drain through sinus tracts in skin. Normal oral flora. |
Actinomyces israelii
|
|
|
What is a Ghon focus?
|
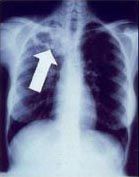
Subpleural caseous granuloma caused by Mycobacterum tuberculosis. Classical location for primary TB infection is surrounding the lobar fissures, either in the upper part of the lower lobe or lower part of the upper lobe. Only detectable by chest X-ray if it calcifies or grows substantially
|
|
|
What is a Ghon complex?
|
If the Ghon focus also involves infection of adjacent lymphatics and hilar lymph nodes, it is known as the Ghon's complex or primary complex.
|
|
|
What are the most common sites of extrapulmonary disease in tuberculosis?
|
Mediastinal, retroperitoneal, and cervical (scrofula) lymph nodes - The most common site of tuberculous lymphadenitis (scrofula) is in the neck, along the sternocleidomastoid muscle; it is usually unilateral and causes little or no pain; advanced cases of tuberculous lymphadenitis may suppurate and form a draining sinus; Vertebral bodies (Pott's disease); Adrenals; Meninges; GI tract
|
|
|
Which organism?
Lowenstein-Jensen agar |
Mycobacteria tuberculosis
|
|
|
Which organism?
Chocolate agar with factors V (NAD+) and X (hemantin) |
Haemophilus influenza
|
|
|
Which organism?
Thayer-Martin (or VPN) media |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
Which bug?
Acid-fast bacillus that likes cool temperatures (infects skin and superficial nerves) and cannot be grown in vitro. The reservoir in USA: armadillos |
Mycobacterium leprae - leprosy (Hanesen's disease).
Has 2 forms - lepromatous (presents diffusely over skin and is communicable); tuberculoid (limited to a few hypoesthetic skin nodules) |
|
|
Give some examples of bugs that grow pink colonies on MacConkey agar.
|
Lactose-fermenting enteric bacteria.
Fast fermenter - Klebsiella, E. coli, Enterobacter Slow fermenter - Citrobacter, Serratia |
|
|
Which bug?
Found naturally in the environment, usually in water. Grow best in warm water, like the kind found in hot tubs, cooling towers, hot water tanks, large plumbing systems, decorative fountains. Can lead to severe pneumonia and fever |
Legionella pneumophila
Legionnaire's disease = severe pneumonia and fever Pontiac fever = mild flulike syndrome (patient does not have pneumonia). |
|
|
Which bug?
Wound and burn infections, pneumonia (especially in cystic fibrosis), sepsis, external otitis, UTI, diabetic osteomyelitis. |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
Which bug?
Produces pyocyanin (blue-green pigment) |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
Which bug?
Produces Shiga-like toxin. Microbe invades intestinal mucosa and toxin causes necrosis and inflammation. Can present as dysentry. |
E. coli (EIEC - Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli)
|
|
|
Which bug?
Labile toxin/stable toxin. No inflammation or invasion. Presents as traveler's diarrhea (watery) |
E.coli (ETEC - Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli)
|
|
|
Which bug?
No toxin produced. Adheres to apical surface, flattens villi, prevents absorption. Presents as diarrhea usually in children. |
E. coli - EPEC (Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli)
|
|
|
Which bug?
Produces Shiga-like toxin and hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Presents as dysentry and does not ferment sorbitol |
E. coli - EHEC (enterohemorrhagic E. coli)
O157:H7 is the most common serotype |
|
|
Which bug?
Intestinal flora that causes lobar pneumonia in alcoholics and diabetics when aspirated. Also cause of nosocomial UTIs. |
Klebsiella
|
|
Which bug?
Can cause fever, diarrhea, headache, and rose spots on abdomen. Can remain in gallbladder chronically. Transmission via 'food, fingers, fecese, and flies' |
Salmonella typhi - typhoid fever.
|
|
|
Which bug?
Major cause of bloody diarrhea, especially in children. Fecal-oral tranmission through foods such as poultry, meat, unpasteurized milk. Comma, or S-shaped, oxidase-positive, grows at 42C. Common antecedent to Guillain-Barre syndrome |
Campylobacter jejuni
|
|
|
Which bug?
Usually transmitted from pet feces (eg. puppies), contaminated milk, or pork. Outbreaks of diarrhea are common in day care centers. Causes mesenteric adenitis that can mimic Crohn's disease or appendicitis |
Yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
Which bug?
Causes gastritis and up to 90% of duodenal ulcers. Risk factor for peptic ulcer, gastric adenocarcinoma, and lymphoma. |
Helicobacter pylori
|
|
|
List the spirochetes.
|
Borrelia (big size), Leptospira, Treponema
|
|
|
Which bug?
Question mark-shaped bacteria found in water contaminated with animal urine. Can produce flulike symptoms, fever, headache, abdominal pain, jaundice, and photophobia with conjunctivitis. Most prevalent among surfers and in the tropics. |
Leptospira interrogans - leptospirosis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Jaundice and azotemia from liver and kidney dysfunction; fever, hemorrhage, and anemia |
Leptospira interrogans.
Weil's disease (icterohemorrhagic leptospirosis) |
|
|
Which bug?
Presents with erythema chronicum migrans and flulike symptoms. Can progress to neurologic (Bell's palsy) and cardiac manifestations (AV nodal block), as well as chronic monoarthritis, and migratory polyarthritis. |
Borrelia burgdorferi - Lyme disease (3 stages)
|
|
|
Which bug?
Transmitted by the tick Ixodes. Mice are important reservoirs. Deer required for tick life cycle. |
Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease)
|
|
|
Which bug?
Presents with painless chancre |
Treponema pallidum - primary syphilis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Disseminated disease with constitutional symptoms, maculopapular rash (palms and soles), condylomata lata, and patchy alopecia |
Treponema pallidum - secondary syphilis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Gummas (chronic granulomas - soft, non-cancerous growth), aortitis (vasa vasorum destruction), neurosyphilis (tabes dorsalis), Argyll Robertson pupil |
Treponema pallidum - tertiary syphilis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Saber shins (sharp anterior bowing of the tibia), saddle nose (loss of height of the nose, because of the collapse of the bridge), CN VIII deafness, Hutchinson's teeth (smaller and more widely spaced teeth with notches on their biting surfaces), mulberry molars (multiple rounded rudimentary enamel cusps on the permanent first molars) |
Treponema pallidum - congenital syphilis
|
|
|
What is the VDRL test? What can produce a false positive?
|
VDRL detects nonspecific antibody that reacts with beef cardiolipin, and used for the diagnosis of syphilis.
False positive: Viruses (EBV, hepatitis) Drugs Rheumatic fever Lupus and Leprosy |
|
|
Which bug?
Life cycle contains 2 forms - infectious elementary body, and a replicating, non-infectious reticulate body. |
Chlamydiae
|
|
|
Which bug?
Causes reactive arthritis, conjunctivitis, nongonococcal urethritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease |
chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Chronic infection that can cause blindness due to follicular conjunctivitis in Africa |
Chlamydia trachomatis - serotypes A, B, C
|
|
|
Which bug?
Most common bacterial STD in USA; Can cause urethritis/PID, ectopic pregnancy, neonatal pneumonia (staccato cough), or neonatal conjunctivitis |
Chlamydia trachomatis - serotypes D - K
|
|
|
Which bug?
Lymphogranuloma venereum - Swollen lymph nodes in the genital area (lymph edema) |
Chlamydia trachomatis - serotypes L1, L2, L3
Note: Not to be confused with granuloma inguinale (donovanosis), which is caused by Klebsiella granulomatis |
|
|
Which bug?
Only bacterial membrane containing cholesterol |
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which bug?
Classic cause of atypical 'walking' pneumonia (insidious onset, headache, nonproductive cough, diffuse interstitial infiltrate). Frequent outbreaks in military recruits and prisons. |
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Mississippi and Ohio river valleys. Causes pneumonia |
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Associated with bird or bat droppings; Causes pneumonia; Found within macrophages |
Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
States east of Mississippi River and Central America; Causes inflammatory lung disease and can disseminate to skin and bone. |
Blastomycosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Broad-based budding (same size as RBC); Forms granulomatous nodules; Can cause pneumonia |
Blastomycosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Southwestern Unites States, California; Causes pneumonia and meningitis; Can disseminate to skin and bone. |
Coccioidomycosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
San Joaquin Valley or desert 'valley fever" |
Coccioidomycosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Spherule filled with endospores (larger than RBCs); Case rates increase after earthquakes (spherules in dust are thrown up in the air). Can cause pneumonia |
Coccioidomycosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Latin America. Can cause pneumonia |
Paracoccioidomycosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Budding yeast with 'captain's wheel' formation (much larger than RBCs); Can cause pneumonia |
Paracoccioidomycosis
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Responsible for Tinea versicolor - degradation of lipids produces acids that damage melanocytes and cause hypopigmented and/or hyperpigmented patches |
Malassezia furfur (cutaneous mycoses)
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Responsible for Tinea pedis (athlete's foot), Tinea cruris (jock itch), Tinea corporis (ringworm of the body), Tinea capitis (ringworm of the scalp) |
Dermatophytes - Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Oral and esophageal thrush in immunocompromised (neonates, steroids, diabetes, AIDS), vulvovaginitis (diabetes, use of antibiotics), diaper rash, endocarditis in IV drug users, disseminated candidiasis, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis |
Candida albicans
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Mold with septate hyphae that branch at acute angles |
Aspergillus fumigatus
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Dimorphic - yeast with pseudohyphae in culture at 20C; germ tube formation (an outgrowth produced by spores of spore-releasing fungi during germination) at 37C (diagnostic). |
Candida albicans
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
"Soap bubble" lesions in brain |
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Heavily encapsulated yeast. Not dimorphic. Found in soil, pigeon droppings. Culture on Sabouraud's agar. Latex agglutination test detects polysaccharide capsular antigen and is more specific. |
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Mold with irregular nonseptate hyphae at wide angles. |
Mucor and rhizopus spp.
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Disease mostly in ketoacidotic diabetic and leukemic patients. Proliferates in blood vessel walls when there is excess ketone and glucose, penetrate cribiform plate, and enter brain. Headache, facial pain, black necrotic eschar on face cranial nerve involvement |
Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis - Mucor and rhizopus spp.
|
|
|
What's the fungus?
Saucer-shaped yeast forms. Causes diffuse interstitial pneumonia. Immunosuppression (AIDS) predisposes to disease. Identified by methenamine silver stain of lung tissue |
Pneumocystic jiroveci (formerly carnii).
Start prophylaxis when CD4 drops <200 cells/mL in HIV patients. |
|
|
What's the fungus?
Dimorphic fungus that lives on vegetation. When traumatically introduced into skin, typically by a thorn ("rose gardener's disease"), causes local pustule or ulcer with nodules along draining lymphatics (ascending lymphangitis) |
Sporothrix schenckii - Sporotrichosis.
Cigar-shaped yeast forms, unequal budding. |
|
|
Which bug?
Cat scratch fever |
Bartonella spp.
|
|
|
Which bug?
Louse - recurrent fever from variable surface antigens |
Borrelia recurrentis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Undulant fever (fever rises and falls in waves); transmission via diary products, or contact with animals |
Brucella spp
|
|
|
Which bug?
Tularemia - Transmission from tick bite; rabbits; deer |
Francisella tularensis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Plague - transmission from flea bite; rodents, especially prairie dogs |
Yersinia pestis
|
|
|
Which bug?
Cellulitis and osteomyelitis - transmission from animal bite (cats, dogs) |
Pasteurella mutlocida
|
|
|
What is the classic triad of Rickettsia?
|
Headache, fever, rash (vasculitis)
Exception: Coxiella causes Q fever - no rash, not transmitted by an arthropod vector (tick feces and cattle placenta release spores that are inhaled), has negative Weil-Felix reaction |
|
|
What is the Weil-Felix reaction?
|
Patient serum mixed with Proteus antigens, antirickettsial antibodies cross-react to Proteos O antigens and agglutinate (Weil-Felix is negative in Coxiella infection)
|
|
|
What's the bug?
Rash on palms and soles (migrating to wrists, ankles, then trunk), headache, fever. Endemic to East coast. |
Rickettsia rickettsii - Rocky Mountain spotted fever
|
|
|
What diseases are associated with palm and sole rash?
|
Coxsackie A infection (hand, foot, and mouth disease), Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Syphylis
|
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Causes bloating, flatulence, foul-smelling, fatty diarrhea. Transmitted as cysts in water, and often seen in campers/hikers. |
Giardia lamblia (giardiasis). Diagnosis: trophozoites or cysts in stool
|
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Bloody diarrhea (dysentery), liver abscesses (reddish brown), RUQ pain. Transmitted via cysts in water. |
Entamoeba histolytica (amebiasis).
Diagnosis: serology and/or trophozoites or cysts in stool; RBCs in cytoplasm of entamoeba |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Severe diarrhea in AIDS patients. Mild disease (watery diarrhea) in non-immunocompromised patients. Transmitted via cysts in water. |
Cryptosporidium.
Diagnosis: cysts on acid-fast stain. |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Brain abscess in HIV (ring-enhancing brain lesions on CT/MRI). Classic triad: chorioretinitis (uveitis), hydrocephalus, and intracranial calcifications. Transmission via cysts in meat or cat feces. Note: Crosses placenta (pregnant women should avoid cats) |
Toxoplasma gondii.
Diagnosis: Serology, biopsy |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Rapidly fatal meningoencephalitis. Transmission via swimming in freshwater lakes; enter via the cribiform plate. |
Naegleria fowleri.
Diagnosis: Amoebas in spinal fluid |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
African sleeping sickness (enlarged lymph nodes, recurring fever, somnolence, coma). Transmission via Tsetse fly (painful bite). |
Trypanosoma brucei (T. gambiense, T. rhodesiense).
Diagnosis: Blood smear |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Painful bite from Tsetse fly |
Trypanosoma brucei (T. gambiense, T. rhodesiense).
African sleeping sickness |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Chagas' disease (dilated cardiomyopathy, megacolon, megaesophagus); predominantly in South America. Transmission via Reduviid bug ("kissing bug"), painless bite |
Trypanosomsa cruzi.
Diagnosis: Blood smear |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Painless bite from Reduviid bug ("kissing bug") |
Trypanosoma cruzi
Chagas disease |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Spiking fevers, hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia. Transmission via the sandfly. |
Leishmania donovani (Visceral leishmaniasis).
Diagnosis: Macrophages containing "amastigotes" (form that lacks flagella) |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
48hr (tertian) cyclic fever, headache, anemia, splenomegaly. Transmission via the mosquito (anopheles) |
Plasmodium (P. vivax/ovale, P. falciparum, P. malariae)
Diagnosis: Blood smear |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Cerebral malaria |
P. falciparum.
parasitized RBCs occlude capillaries in brain |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Fever, hemolytic anemia; predominantly in northeastern US. Transmission via Ixodes tick. |
Babesia (babesiosis).
Diagnosis: blood smear, no RBC pigment, appears as "Maltese cross" Note: Ixodes tick is the same as Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) and may often coinfect humans. |
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Appears as "Maltese cross" on blood smear |
Babesia
|
|
|
What's the protozoa?
Foul-smelling, greenish discharge from vagina; itching and burning. Transmission is via sexual contact (cannot exist outside human because it cannot form cysts) |
Trichomonas vaginalis (vaginitis)
Diagnosis: Trophozoites (motile) on wet mount. Note: Do not confuse with Gardnerella vaginalis (gram negative bacteria) that causes vaginosis. |
|
|
What's the helminth?
Food contaminated with eggs; intestinal infection; causes pruritus; can use "Scotch tape test" to help with diagnosis |
Nematode: Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm)
|
|
|
What's the helminth?
Pinworm |
Nematode: Enterobius vermicularis
|
|
|
What's the helminth?
Eggs are visible in feces; intestinal infection. "Giant roundworm" |
Nematode: Ascaris lumbricoides
|
|
|
What's the helminth?
Undercooked meat, usually pork; inflammation of muscle (larvae encyst in muscle); periorbital edema |
Nematode: Trichinella spiralis
|
|
|
What's the helminth?
Larvae in soil penetrate the skin; intestinal infection; causes vomiting, diarrhea, anemia. |
Nematode: Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
|
What's the helminth?
Larvae penetrate skin of feet; intestinal infection can cause anemia. "Hookworms" |
Nematode: Ancylostoma duodenale, Nectar americanus (hookworms)
|
|
|
What's the helminth?
Female mosquito; causes blockage of lymphatic vessels (elephantiasis) |
Nematode: Wuchereria bancrofti
Note: Takes 9 months to 1 year after bite to get elephantiasis symptoms. |
|
|
What's the helminth?
Ingestion of larvae encysted in undercooked pork leads to intestinal tapeworms. Ingestion of eggs causes cysticercosis and neurocysticercosis, mass lesions in brain ("swiss cheese" appearance) |
Cestodes (tapeworms): Taenia solium
|
|
|
What's the helminth?
Snails are host. Cercariae penetrate skin of humans; causes granulomas, fibrosis, and inflammation of spleen and liver. Can lead to squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder. |
Trematodes (flukes): Schistosoma
|
|
|
What are some examples of live attenuated viral vaccines?
|
Smallpox, yellow fever, chickenpox (VZV), Sabin's polio virus, MMR (measles, mumps, rubella), intranasal influenza
|
|
|
What is the only live attenuated vaccine that can be given to HIV-positive patients?
|
MMR (measles, mumps, rubella)
|
|
|
What are some examples of killed/inactivated viral vaccines?
|
Rabies, influenza (IM), Salk polio, and HAV
|
|
|
What test is used to identify the herpesvirus family?
|
Tzanck test - a smear of an opened skin vesicle to detect multinucleated giant cells. Used to assay HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV. Infected cells also have intranuclear Cowdry A inclusions
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Gingivostomatitis, keratoconjunctivitis, temoral lobe encephalitis (most common cause of sporadic encephalitis in US), herpes labialis. Route of transmission is via respiratory secretions, saliva. |
Herpesvirus: HSV-1
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Herpes genitalis, neonatal herpes. Transmission via sexual contact, perinatal. |
Herpesvirus: HSV-2
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Shingles, encephalitis, pneumonia. Transmission via respiratory secretions. |
Herpesvirus: VZV
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Infectious mononucleiosis, Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Transmission via respiratory secretions, saliva |
Herpesvirus: EBV
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Congenital infection, mononucleosis (negative Monospot), pneumonia. Infected cell's have characteristic "owl's eye" inclusions. Transmission is congenital, via transfusion, sexual contact, saliva, urine, transplant |
Herpesvirus: CMV
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Roseola: high fevers for several days that can cause seizures, followed by a diffuse malar rash. Undetermined mode of transmission |
Herpesvirus: HHV-6 "sixth disease"
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Associated with HIV patients. Transmission via sexual contact |
Herpesvirus: HHV-8 (Kaposi sarcoma)
|
|
|
Where does HSV-1 classically remain during the latent period? HSV-2?
|
HSV-1: trigeminal ganglia
HSV-2: sacral ganglia |
|
|
Where does VZV classically remain during the latent phase? EBV? CMV?
|
VZV: trigeminal and dorsal root ganglia
EBV: B cells CMV: mononuclear cells |
|
|
What's the virus?
Characterized by fever, hepatosplenomegaly, pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy (especially posterior cervical nodes). |
Herpesvirus: EBV.
Peak incidence 15-20yrs "kissing disease" |
|
|
What is the Monospot test?
|
Heterophil antibodies detected by agglutination of sheep RBCs.
Positive with mononucleoisis due to EBV; negative when due to CMV |
|
|
What's the virus?
Aplastic crises in sickle cell disease, "slapped cheeks" rash in children (erythema infectiousum/fifth disease), RBC destruction in fetus leads to hydrops fetalis and death, pure RBC aplasia and rheumatoid arthritis-like symptoms in adults. |
Parvovirus: B19 virus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Genital warts, CIN, cervical cancer. |
Pappilomavirus: HPV
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Acute or chronic hepatitis; vaccine available. |
Hepadnavirus: HBV
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Febrile pharyngitis (sore throat); acute hemorrhagic cystitis; Pneumonia; Conjunctivitis (pink eye) |
Adenovirus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in HIV |
Polyomavirus: JC virus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Flesh-coloured dome lesions with central dimple. |
Poxvirus: Molluscum contagiosum.
Note: Smallpox also falls into the Poxvirus family |
|
|
What's the virus?
Cause of common cold |
Picornavirus: Rhinovirus OR
Coronavirus: Coronavirus (common cold and SARS) |
|
|
What's the virus?
Transmitted by Aedes mosquitos. Virus has a monkey or human reservoir. Symptoms include high fever, black vomitus, and jaundice. Tongue can appear red on the sides, and white on the tip |
Flavivirus: Yellow fever virus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Most important global cause of infantile gastroenteritis. Major cause of acute diarrhea in USA during winter (especially in daycares and kindergartens). Villous destrution and atrophy leads to decreased absorption of Na and water. |
Reovirus: Rotavirus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Contains hemagglutinin (promotes viral entry) and neuraminidase (promotes progeny virion release) antigens. Patients at risk for fatal bacterial superinfection. Rapid genetic changes. |
Orthomyxoviruses: influenza viruses
|
|
|
What is the difference between genetic shift and genetic drift? Which change is responsible for more deadly changes in viruses?
|
Genetic shift: Reassortment of viral genome (such as when human flu A virus recombines with swine flu A virus).
Genetic drift: Minor (antigenic drift) changes based on random mutation. Sudden shift is more deadly than gradual drift. |
|
|
What's the virus?
Causes German (3-day) measles. Fever, postauricular tenderness, lymphadenopathy, arthralgias, fine truncal rash. Causes mild disease in children but serious congenital disease. |
Togavirus: Rubella
Note: a TORCH infection |
|
|
What viruses are part of the paramyxovirus family?
|
PaRaMyxovirus: Parainfluenza (croup), RSV (bronchiolitis in babies), rubeola (Measles), Mumps
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Koplik spots (red spots with blue-white center on buccal mucosa) are diagnostic. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) can develop years later; Encephalitis (1:2000); and giant cell pneumonia (rarely in immunosuppressed) |
Paroamyxovirus: Measles (rubeola)
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis |
3C's of measles (rubeola)
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Parotitis, orchitis, and aseptic meningitis. Can cause sterility (especially after puberty) |
Paramyxovirus: Mumps
|
|
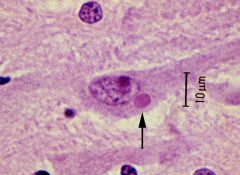
What's the virus?
Negri bodies are characteristic cytoplasmic inclusions in neurons (commonly found in Purkinje cells of cerebellum). Has bullet-shaped capsid. Travels to the CNS by migrating in a retrograde fashion up nerve axons |
Rhabodovirus: Rabies virus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Progression of disease: fever, malaise -> agitation, photophobia, hydrophobia -> paralysis, coma -> death. More commonly from bat, raccoon, and skunk bites than from dog bites in US. |
Rhabdovirus: Rabies virus
|
|
|
What viruses are part of the picornavirus family?
|
PERCH
Poliovirus, Echovirus, Rhinovirus, Coxsackievirus, HAV |
|
|
What's the virus?
Motor neurons of anterior horn |
Picornavirus: Poliovirus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Aseptic meningitis and myocarditis |
Picornavirus: Echovirus
|
|
|
What's the virus?
Aseptic meningitis, herpangina (febrile pharyngitis, hand, foot, mouth disease), myocarditis |
Picornavirus: Coxsackievirus
|
|
|
Which hepatitis virus?
DNA hepadnavirus |
HBV
|
|
|
Which hepatitis virus?
Transmitted primarily via fecal-oral route. Short incubation (3 weeks). No carriers. RNA picornavirus |
HAV
|
|
|
Which hepatitis virus?
Transmitted primarily by parenteral, sexual, and maternal-fecal routes. Long incubation (3 months) |
HBV
|
|
|
Which hepatitis virus?
Transmitted primarily via blood. Common cause of post-transfusion hepatitis and of hepatitis among IV drug users in the US. |
HCV (RNA flavivirus)
|
|
|
Which hepatitis virus?
Defective virus that requires HbsAg as its envelope. |
HDV.
Note: Can coinfect with HBV or superinfect (the latter has worse prognosis) |
|
|
Which hepatitis virus?
Transmitted enterically and causes water-borne epidemics. High mortality rate in pregnant women (20-25%). |
HEV (RNA hepevirus)
|
|
|
What's the diagnosis?
Positive: HBsAg, HBeAg, Anti-HBcAb (IgM) |
Acute HBV
|
|
|
What's the diagnosis?
Positive: Anti-HBcAb |
Window period (equivalence zone) = The time between the removal of the HBsAg and the appearance of anti-HBs is called the window period (host remains infected but is successfully clearing the virus)
|
|
|
What's the diagnosis?
Positive: HBsAg, HBeAg, Anti-HBcAb (IgG) |
Chronic HBV (high infectivity)
|
|
|
What's the diagnosis?
Positive: HBsAg, Anti-HBeAb, Anti-HBcAb (IgG) |
Chronic HBV (low infectivity)
|
|
|
What's the diagnosis?
Positive: Anti-HBsAb, Anti-HBeAb, Anti-HBcAb (IgG) |
Recovery of HBV
|
|
|
What's the diagnosis?
Positive: Anti-HBsAb |
Immunized against HBV
|
|
|
What are the 3 structural genes in HIV? What do they code for?
|
env: gp120 (attachment to host T cell), gp41 (fusion and entry)
gag: p24 (capsid protein) pol: reverse transcriptase (synthesizes dsDNA from RNA) |
|
|
What proteins do HIV particles bind to on T cells? On macrophages?
|
Virus binds CXCR4 and CD4 on T cells; binds CCR5 and CD4 on macrophages.
Note: Homozygous CCR5 mutation = immunity; heterozygous CCR5 mutation = slower course |
|
|
How is HIV diagnosed?
|
1. ELISA (sensitive, high false-positive rate and low threshold --> rule OUT test)
2. Western blot (specific, high false-negative rate and high threshold --> rule IN test) Note: Often falsely negative in first 1-2months of infection. Can be falsely positive in babies born to infected mothers (anti-gp120 crosses placenta) |
|
|
How is AIDS diagnosed?
|
<200 CD4+ (normal 500-1500). HIV positive with AIDS indicator condition (pneumocystis jiroveci) or CD4/CD8 ratio <1.5
|
|
|
What infections are HIV patients at risk for with a CD4 level <400?
|
Oral thrush, tinea pedis, reactivation VZV, reactivation TB, other bacterial infections (H. influenza, S. pneumoniae, Salmonella)
|
|
|
What infections are HIV patients at risk for with a CD4 level <200?
|
Reactivation of HSV, cryptosporidiosis, Isospora, disseminated coocidioidomycosis, Pneumocystic pneumonia (TMP-SMX for prophylaxis)
|
|
|
What infections are HIV patients at risk for with a CD4 level <100?
|
Candidal esophagitis, toxoplasmosis, histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What infections are HIV patients at risk for with a CD4 level <50?
|
CMV retinitis and esophagitis, disseminated MAC, cryptococcal meningoencephalitis
|
|
|
What bug is commonly responsible for the food poisoning?
Contaminated seafood? |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus in contaminated seafood.
V. vulnificus can cause wound infections from contact with contaminated water or shellfish |
|
|
What bug is commonly responsible for the food poisoning?
Contaminated reheated rice |
Bacillus cereus
Note: food poisoning starts quickly and ends quickly |
|
|
What bug is commonly responsible for the food poisoning?
Contaminated meats, mayonnaise, custard. Preformed toxin |
S. aureus.
Note: food poisoning starts quickly and ends quickly |
|
|
What bug is commonly responsible for the food poisoning?
Contaminated reheated meat dishes |
Clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
What bug is commonly responsible for the food poisoning?
Improperly canned foods (bulging cans) |
C. botulinum
|
|
|
What bug is commonly responsible for the food poisoning?
Undercooked meats |
E. coli )157: H7
|
|
|
What bug is commonly responsible for the food poisoning?
Contaminated poultry, meat, and eggs |
Salmonella
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in neonates (<4weeks)?
|
Group B streptocooci, E. coli
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in children (4wk - 18yr)?
|
Viruses (RSV), Mycoplasma, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in adults (18 - 4-yr)?
|
Mycoplasma, C. pneumoniae, S. pneumoniae
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in adults (40-65yr)?
|
S pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Anaerobes, Viruses, Mycoplasma
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in the elderly?
|
S. pneumoniae, Influenza virus, Anaerobes, H. influenza, Gram negative rods
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of nosocomial pneumonia?
|
Staphylococcus, enteric gram-negative rods
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in immunocompromised patients?
|
Staphylococcus, enteric-gram negative rods, fungi, viruses, Pneumocystis jiroveci (HIV)
|
|
|
What is the commonest causes of aspiration pneumonia?
|
Anaerobes
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in alcoholic/HIV drug users?
|
S. pneumoniae, Klebsiella, Staphylococcus
|
|
|
What is the commonest causes of pneumonia in CF patients?
|
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of pneumonia in postviral patients?
|
Staphylococcus, H. influenza
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of atypical pneumonia?
|
Mycoplasma, Legionella, Chlamydia
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of meningitis in newborns (0-6mo)?
|
Group B streptococci, E. coli, Listeria
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of meningitis in children (6mo - 6yrs)?
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenza type B, Enteroviruses
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of meningitis between the ages of 6-60yrs?
|
N. meningitidis, Enteroviruses, S. pneumoniae, HSV
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of meningitis after 60yrs
|
S. pneumoniae, Gram-negative rods, Listeria
|
|
|
What are some viral vauses of meningitis?
|
Enteroviruses (coxsackievirus, echovirus), HSV, HIV, West Nile virus, VZV.
|
|
|
What are the commonest causes of meningitis in HIV patients?
|
Cryptococcus, CMV, toxoplasmosis (brain abscess), JC virus (PML)
|
|
|
How do you differentiate between bacterial, fungal, and viral causes of meningitis by CSF findings?
|
Bacterial: increased pressure, PMNs, protein; decreased sugar.
Fungal/TB: Increased pressure, lymphocytes, protein; decreased sugar Viral: Normal/increased pressure and protein; increased lymphocytes; NORMAL sugar |
|
|
What is the commonest cause of osteomyelitis? In sexually active people? In diabetics and drug addicts? In sickle cell? In prosthetic replacment? In vertebrae? If cat/dog bites or scratches?
|
Common: S. aureus (assume if no other information)
Sexually active: N. gonorrhea (rare), septic arthritis Diabetics + drug addicts: Pseudomonas Sickle cell: Salmonella Prosthetic: S. aureus, S. epidermidis Vertebral: M. tuberculosis (Pott's disease) Cat/dog: Pasteurella multocida |
|
|
What are the commonest causes of UTI?
|
1. E. coli
2. Staph. saprophyticus 3. Klebsiella pneumoniae Proteus mirabilis (produces urease; causes struvite stones), Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
What are ToRCHeS infections?
|
Microbes that may pass from mother to fetus. Nonspecific signs (hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, thrombocytopenia, growth retardation).
Toxoplasma gondii, Rubella, CMV, HIV, HSV, Syphilis Others: Parvovirus B19 (hydrops fetalis) |
|
|
Which TORCH infection?
Maternal: asymptomatic; lymphadenopathy (rare) Neonatal: chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
|
|
Which TORCH infection?
Maternal: rash, lymphadenopathy, arthritis Neonatal: PDA (or pulmonary artery hypoplasia), cataracts. and deafness. May also have "blueberry muffin" rash |
Rubella
|
|
|
Which TORCH infection?
Maternal: Usually asymptomatic, mononucleosis-like illness. Neonatal: Hearing loss (unilateral), seizures, petechial rash. 90% asymptomatic |
CMV (most common)
|
|
|
Which TORCH infection?
Maternal: variable presentation Neonatal: recurrent infections, chronic diarrhea |
HIV
|
|
|
Which TORCH infection?
Maternal: Usually asymptomatic; vesicular lesions Neonatal: Temporal encephalitis, vesicular lesions |
HSV
|
|
|
Which TORCH infection?
Maternal: Chancre, disseminated rash, or cardiac/neurologic disease Neonatal: Often results in stillbirth, hydrops fetalis; if child survives, presents with facial abnormalities |
Syphilis
|
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
Rash begins at head and moves down; postauricular lymphadenopathy |
Rubella virus (German measles)
|
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
Rash begins at head and moves down; rash is preceded by cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and blue-white spots on buccal mucosa. |
Measles virus (rubeola, measles).
Note: blue-whit spots on buccal mucosa = Koplik spots |
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
No rash, but can [resemt with parotitis, meningitis (orchitis or oophoritis in young adults). |
Mumps virus (Mumps)
|
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
Rash begins on trunk; spread to face and extremties with lesions of different age. |
VZV (chickenpox)
|
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
A macular rash over body appears after several days of high fever; usually affects infants. |
HHV-6 (Roseola)
|
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
"Slapped cheek" rash on fact later appears over body in reticular, 'lace-like' pattern. (Can cause hyrops fetalis in pregnant women). |
Parvovirus B19 (erythema infectiosum)
|
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
Erythematous, sandpaper-like rash with fever and sore throat |
Streptococcous pyogenes (Scarlet fever)
|
|
|
What is responsible for the rash?
Vesicular rash on palms and soles; ulcers in oral mucosa |
Coxsackievirus type A (Hand-foot-mouth disease)
|
|
|
STD?
Urethritis, cervicitis, PID, prostatitis, epididymitis, arthritis, creamy purulent discharge (yellow-green) |
Gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
|
|
|
STD?
Painless chancre |
primary syphilis (Treponema pallidum)
|
|
|
STD?
Fever, lymphadenopathy, skin rashes, condylomata lata |
Secondary syphilis (Treponema pallidum)
|
|
|
STD?
Gummas, tabes dorsalis, general paresis, aortitis, Argyll Robertson pupil |
Tertiary syphilis (Treponema pallidum)
|
|
|
STD?
Painful genital ulcer, inguinal adenopathy |
Chancroid (Haemophilus ducreyi)
|
|
|
STD?
Painful penile, vulvar, or cervical vesicles and ulcers; can cause systemic symptoms such as fever, headache, myalgia |
Genital herpes (HSV-2)
|
|
|
STD?
Urethritis, cervicitis, conjunctivitis, Reiter's syndrome, PID, discharge (white/clear) |
Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis D-K)
|
|
|
STD?
Ulcers, lymphadenopathy, rectal strictures |
Lymphogranuloma venereum (Chlamydia trachomatis L1-L3)
|
|
|
STD?
Vaginitis, strawberry-coloured mucosa, corkscrew motility on wet prep |
Trichomonas vaginalis
|
|
|
STD?
Opportunistic infections, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma |
AIDS (HIV)
|
|
|
STD?
Genital warts, koilocytes |
Condylomata acuminata (HPV 6 and 11)
|
|
|
STD?
Jaundice |
Hepatitis B (HBV)
|
|
|
STD?
Noninflammatory, malodorous discharge (dishy smell); positive whiff test, clue cells |
Bacterial vaginosis (Gardnerella vaginalis)
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Low-grade fevers, cough, hepatosplenomegaly. Oval yeasts within macrophages. |
Histoplasma capsulatum (only pulmonary symptoms in immunocompetent hosts)
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Fluffy white, cottage-cheese lesions, often in mouth. Pseudohyphae |
C. albicans (thrush)
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Superficial vascular proliferation. Biopsy reveals neutrophilic inflammation |
Bartonella henselae (causes bacillary angiomatosis)
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Superficial neoplastic proliferation of vasculature. Biopsy reveals lymphocytic inflammation. |
HHV-8 (causes Kaposi's sarcoma)
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Chronic, watery diarrhea. Acid-fast cysts in stool |
Cryptosporidium spp.
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Meningitis. India ink stain reveals yeast with narrow-based budding and large capsule. |
Cryptococcus neoformans (may also cause encephalitis)
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Encephalopathy. Due to reactivation of latent virus; results in demyelination |
JC virus (cause of PML - Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy)
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Abscesses. Many ring-enhancing lesions on imaging. |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Retinitis. Cotton-wool spots on fundoscopic exam. |
CMV
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Hairy leukoplakia. Often on lateral tongue. |
EBV
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (large cell type). Often on oropharynx (Waldeyer's ring) |
EBV
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Squamous cell carcinoma. Often in anus (MSM) or cervix (females) |
HPV
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Interstitial pneumonia. Biopsy reveals cells with intranuclear (owl's eye) inclusion bodies |
CMV
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Invasive aspergillosis. Pleuritic pain, hemoptysis, infiltrates on imaging. |
Aspergillus fumigatus
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Pneumonia. Especially with CD4 <200 |
Pneumocystis jiroveci
|
|
|
Cause of infection in HIV patient?
Tuberculosis-like disease. Especially with CD4 <50. |
Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare
|
|
|
What's the bug?
Pharyngitis; grayish oropharyngeal exudate; painful throat in unimmunized child. |
Corynebacterium diphtheriae. "pseudomembranes" may obstruct airway.
Elaborates toxin that causes necrosis in pharynx, cardiac, and CNS tissue. |
|
|
What's the bug?
Epiglottitis; fever with dysphagia, drooling, and difficulty breathing due to edamtous 'cherry red' epiglottis in unimmunized child. |
H. influenza type B (also capable of causing epiglottitis in fully immunized children).
|

