![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Urinary System
|
Maintains water balance and removes nitrogenous wastes from the body
|
|
|
Nitrogenous Waste
|
Metabolic processes produce waste in the form of nitrogen. This waste is removed from the blood by filtration of the kidneys (specifically the glomerulus) and makes up part of urea
|
|
|
Waste Removal Process
|
- Products left over from chemical reactions within cells leaves the cell via diffusion
- This metabolic waste travels in the blood - Filtered from the blood and transferred to the bladder (via the ureter tubes) by the kidneys - Gathered in the bladder - Leaves the body via the urinary tract (urethra) |
|
|
Kidney
|
A pair of organs which filter waste from the blood. They also play a part in maintaining pH of the blood by excreting those ions which are in excess
|
|
|
Medulla
|
The innermost section of the kidney which contains the collecting duct and Loop of Henle of the nephrons and is made up of sections known as "renal pyramids"
|
|
|
Renal Pyramids
|
Consist mainly of tubules which transport and collect urine produced in the cortex before the urine passes to the ureter
|
|
|
Cortex
|
The outermost section of the kidney which holds the glomerulus and convoluted tubules of the nephron
|
|
|
Nephron
|
Long tubules which are the functional unit of the kidney. The nephron is the structure that actually produces urine in the process of filtering the blood
|
|
|
Glomerulus
|
A cluster of capillaries within the nephron which filters blood at high pressure
|
|
|
Bowman's Capsule
|
A capsule-shaped membranous structure surrounding the glomerulus of each nephron, serving as a filter
|
|
|
Collecting Ducts
|
A series of tubules and ducts that connect the nephrons to the ureter and plays a part in electrolyte and fluid balance
|
|
|
Loop of Henle
|
Part of the nephron structure which lays in the medulla of the kidney. Principal function: the recovery of water and salt from urine
|
|
|
Ureter
|
The duct by which urine passes from the kidney to the bladder
|
|
|
Bladder
|
A membranous sac in which urine is collected for excretion
|
|
|
Urethra
|
The tube that leads from the bladder which transports and discharges urine outside the body
|
|
|
Convoluted Tubules
|
Intricate tubing of the nephron which specialises in re-absorption
|
|
|
What Happens Where
|
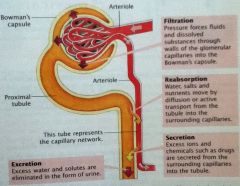
|
|
|
Kidney Diagram
|
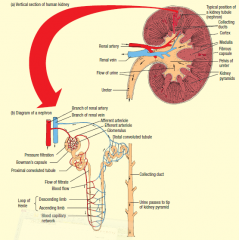
|
|
|
ADH
|
Anti-diuretic hormone: conserves and prevents excess loss of water via urine from the kidneys
|
|
|
Osmoregulation
|
The maintenance of constant osmotic pressure in the fluids of an organism by the control of water and salt concentrations
|
|
|
Homeostasis
|
The tendency of an organism/cell to regulate its internal conditions and attempt to achieve equilibrium
|

