![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define 'Sound'. |
Any pressure variation inair, water or other elastic medium that the human earcan detect. |
|
|
What's the difference between 'sound' and 'noise'? |
Sound is considered as wanted whereas noise is unwanted. |
|
|
Can sound travel in a vacuum? Explain why. |
Sound cannot travel in a vacuum since there is no medium for it to travel. |
|
|
Define 'infrasound' and 'ultrasound'. |
Infrasound: Below 20Hz Ultrasound: Above 20kHz The upper and lower most limits of what is considered as human hearing range. |
|
|
What are the names for the points of maximum and minimum points of pressure in a sound wave called? |
High pressure: Compressions Low Pressure: Rarefactions |
|
|
What are transverse and longitudinal waves and which one is sound? |
Transverse waves are when the medium vibrates at right angles to the direction of travel. Longitudinal waves are when the medium vibrates parallel to the direction of travel. Sound is longitudinal. |
|
|
Do the air molecules travel with the sound wave? |
No, the air molecules vibrate in the same plane the the wave is travelling. |
|
|
Name 3 objective and 3 subjective properties of sound. |
Objective: Frequency, Amplitude & Wavelength Subjective: Pitch, Loudness & Timbre |
|
|
Define 'frequency'. |
Frequency is the number of cycles per second. The number of wave crests passing a certain point in a specific amount of time. |
|
|
Define 'Amplitude'. |
Maximum displacement of a particle of the medium from it's undisturbed position. |
|
|
Define 'Wavelength'. |
The distance along the wavebetween two successive equivalent points,such as two crests or two troughs. |
|
|
Define 'Period'. |
The time required for the wave totravel a distance of one wavelength. |
|
|
What's the equation to relate frequency (f) and period (T)? |
f=1/T T=1/f |
|
|
How would you calculate the speed of a wave (c) from it's: a) wavelength (λ) and period (T)? b) wavelength (λ) and frequency (f)? |
a) c = λ/T (m/s) b) c = λf |
|
|
How would you calculate wavelength (λ) from the speed of sound (c) and the frequency (f)? |
λ = c/f (m) |
|
|
What is the speed of sound (roughly)? |
340m/s |
|
|
How is pitch different from frequency? |
Pitch depends on the harmonic contents of the sound in addition to the frequency. |
|
|
Describe how loudness is different from amplitude. |
Loudness of the sound is determined by itsintensity (amplitude) but is also verysubjective and depends on sound frequency. |
|
|
Describe 'Timbre'. |
Timbre represents the tonal quality of thesound and depends on the amplitudes ofharmonics present in the sound. |
|
|
What is the frequency of a wave that has aperiod of 0.0005s? |
f = 1/0.0005 = 2000Hz |
|
|
What is the wavelength of sound offrequency 2kHz? |
λ = 340/2000 = 0.17m (17cm) |
|
|
What is the speed of a wave whosewavelength is 17m and frequency is 20Hz? |
c = 17 x 20 = 340 m/s |
|
|
What does the 'power' of a sound describe? |
Sound Power describes total sound poweremitted by the sound source in all directions. |
|
|
What is sound intensity (I)? |
Intensity (I) is the measure of the sound powerflowing through a given area. It is the power P that passes perpendicularlythrough a surface divided by the area of thesurface, i.eI = P/A |
|
|
What is sound pressure? What are it's units? |
Sound Pressure is the measure of the acousticpressure at a given point. N/m^2 or Nm^-2 or Pa (Pascals) |
|
|
What is the SPL threshold of pain? |
20 N/m^2 or 20Pa |
|
|
What are the 3 main parts of the human ear? |
Outer ear: detector Middle ear: acoustic transformer Inner ear: converter |
|
|
Describe briefly how the human ear works. |
The human ear detects the sound waves andconverts them into electrical impulses fortransmission to the brain. |
|
|
List the 4 primary methods for reducing noise exposure. |
Reduce level of noise at source (i.e. turn it down!) Reduce exposure time (i.e. shorter listening times) Use mechanical means to reduce noise levels (screens etc.) Use personal protective equipment (PPE) |
|
|
List the parts to a SPL meter and their functions. |
Microphone - converts the sound signal into anequivalent electrical signal Preamplifier - follows the microphone, as thesignal is at a low level, and it needs gain andconditioning before being passed on to the rest ofthe circuit weighting network - Supposed to give a readingthat corresponds more closely to the way we ashumans hear sound filter block - typically allows (optional) octaveband or one-third octave band filters to be placedin circuit amplifier - buffers the preceding stage from thenext and supplies current to drive the followingstages RMS (root mean square) detector - provides anaverage value of the electrical signal, which isproportional to the amount of energy in the sound Hold Circuit - incorporated to store either thepeak value or the maximum RMS value. |
|
|
State the 3 things that can happen to sound at a boundary. |
It can be: -Scattered -Absorbed -Reflected |
|
|
What is the formula for Sound Intensity at adistance r1 from the centre of the soundsource? |
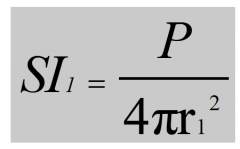
|
|
|
State what the Inverse Square Law means in terms of sound. |
Sound Intensity isinversely proportional to the square of thedistance r between the source andmeasurement point. |
|
|
SIL is reduced by roughly how many dB when the distance from the source is doubled? |
6dB |
|
|
When the distance from the source is doubled, SI is reduced by how many times? |
4 times. with each doubling of the distance SI is reduced four times. |
|
|
How does Sound Pressure decrease as distance from the source increase? |
Sound pressure decreases with 1/r at a distancefrom the sound source |
|
|
How many dB does the sound intensity decrease when the distance is doubled from a LINE source? |
3dB |
|
|
What is the total SIL increase if a second source identical to the first is added? |
+3dB (assuming no destructive interference) |
|
|
How do you use a nomograph? |
1. find the difference D in dBs betweentwo sound levels 2. find the corresponding value N 3. add this value to the higher individualsound level 4. result is the overall sound level in dBs |
|
Name the labels |
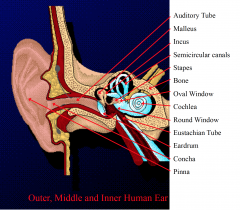
|
|
|
What are the slopes of the following crossover networks? a) First Order b) Second Order c) Third Order d) Fourth Order |
a) 6dB/octave b) 12dB/octave c) 18dB/octave d) 24dB/octave |
|
|
An octave change is to: |
Double or halve the frequency. |

