![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plain Film
|
X-ray film is exposed to ionizing radiation.
Contrast based on the density of material through which the x-ray radiation must pass. Overpenetration - darker Underpenetration - lighter Thus, gas (black), fat (gray-black), soft tissue (gray), and bone (white) on film. All structures squashed on one plane and superimposed. Depth/3D positioning = difficult to see. Unable to see organs that don't have that much contrast → indication of contrast study (barium, water-sol contrasts) |
|
|
CT
|
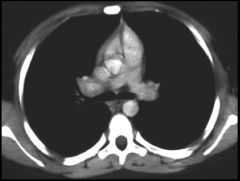
Computed Tomography, same as a plain film but, cuts the body up into slices.
Provides lateral and anteposterior view. Displayed as viewer at feet of supine (laying face up) pt. Better for emergency situations. |
|
|
MRI
|
Cuts body up into slices, but uses magnetic resonance (momentary dipoles).
Higher resolution. Slower, but good for looking at neuroanatomy and joints. |
|
|
AP vs. PA
|
Direction beam travel.
AP - Beam hits anterior, travels posterior, thus pt. lays on back. Heart looks bigger due to beam scatter (shadow) PA - Beam hits posterior and anterior, thus pt. lays on stomach. Heart looks truer to size due to less beam scatter (shadow). Distance (6ft. std) of light source and film from body will change the size. PA is standard |
|
|
Radiation Exposure Levels
|
10,000 mSv - immediate radiation sickness and death within a few weeks.
50 mSv - lowest dose at which cancer may occur in adults. 15 mSv - CT Scan of abdomen and pelvis. 2 mSV - natural radiation exposed to, head CT. 0.1 mSV chest X-ray, 0.01 mSv dental x-ray |
|
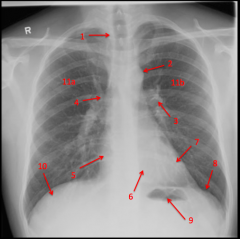
Plain Chest Film
|
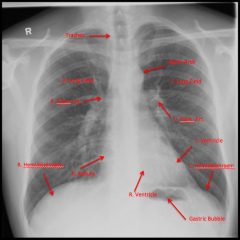
Pulmonary arteries come out under aortic arch.
Clavicles are good landmarks for oreintation/rotation. Anterior ribs - lucent since mostly made of cartilage |
|
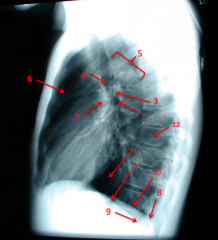
Lateral Chest Film
|
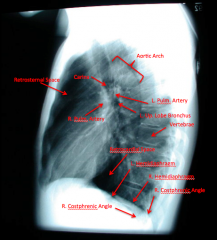
Left lateral is standard.
Would want to take Right side if you suspect pneumothorax, inhaled object, or trauma on that side. |
|
|
Air Lines
|
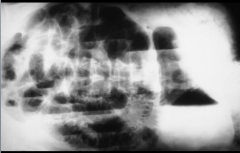
Lateral decubitis. Straight lines
|
|
|
Calcifcations
|
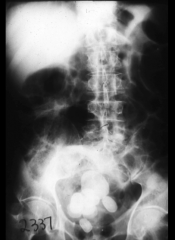
White masses in lower pelvis.
Films not good for viewing galstones (spongy) |
|
|
Abnormal Mass
|
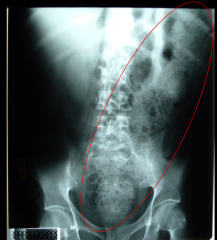
Severe constipation
|
|
|
Double Wall Sign
|
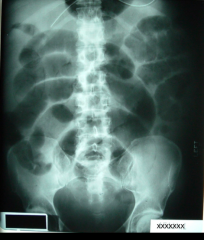
Air inside and outside of intestines causes tubular lines
|
|
|
Calcified Abdominal Aortic Aneurism
|
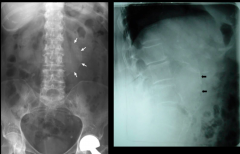
|
|
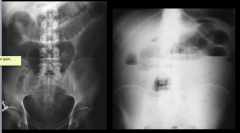
|
Dilated loops in Small bowel - air/fluid. String of pearls sign.
|
|
|
Abdominal Film
|
Good for calcifications (kidney stones), free air in the peritoneal cavity, obstructions in the GI tract, masses in the cavity, tumors, aneurysms, foreign objects.
|

