![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Section 1.1: what are the three parts of a seed which comes from a seed plant? |
the outer layer (seed coat), the embryo, or baby plant which is on the inside, and the cotyledon. |
|
|
Section 1.1: what are the 6 parts of a plant? |
flower, stems, seeds, leaves, cones, roots. |
|
|
Section 1.2: what are 3 processes for moving water up the stems from the roots? define them. |
transpiration (plants sweating) capillary action (water traveliong up the roots through tiny stems and when water particles are attracted to each other or stick together) and osmosis (in cells, the movement of water against the cell membrane). |
|
|
Section 1.2: what is a process that plants use to make food and what is the equation for it? |
photosynthesis, and chloroplasts (the structure in the plant that carries out photosynthesis), and the equation is solar energy + carbon dioxide + water = food and oxygen. |
|
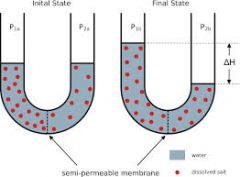
Section 1.2: what does this represent? |
osmosis |
|
|
Section 1.2: what is a process that plants use to use food? what is its equation? define it. |
Cellular respiration- the process in which cells break down sugar particles into carbon dioxide, water and energy. equation: food + oxygen + water = energy and carbon dioxide and water. |
|
|
Section 1.3: what are the two ways for plant reproduction? |
sexual reproduction (seeds to make new plants) and vegetative reproduction (no seeds) |
|
|
section 1.3 what are the reproductive parts of a flower? |
stigma, ovary and anther, filament |
|
|
section 1.3: what are the steps that occur in pollination? |
1. pollen lands on pistil 2. pollen grains travel down the style to the ovary 3. each ovule in the ovary contains an egg. sperm fertilizes it. 4. the fertilized seed becomes an embryo and forms a seed. |
|
|
Section 1.3: what is the plant cycle? |
seeds-stage 1is the embryo, stage 2 is stored food, stage 3 is the seed coat. seedling stage- produces leaves and can produce its own food. adult stage- produces reproductive structures. |
|
|
1.5 plants need the right amount of: |
light, water, nutrients, space |
|
|
1.5 what are the 5 key nutrients a plant needs? what happens if there is a lack of nitrogen? |
nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium. lack of nitrogen leads to yellow leaves. |
|
|
section 2 what do plants do in the environment? |
they provide oxygen, provide shelter, provide food, polants build and protect soil, plants are crucial for the food chain. |
|
|
section 2.3 l what are living, non living and non sustainable resources? |
living resources are those living things that humans need to meet their basic needs. non sustainable resources are those things that we are using more quickly then they are being replaced. |
|
|
section 4; what is a yield? |
the amount of useful plant material produced per crop or per sectioned crop. ex. California has a higher yield or oranges then Canada. |
|
|
section4; what are 3 ways for yields? |
shelter and green house, hydroponic systems and fertilizer. |
|

what is this? |
artificial environment
|
|
|
what is a species, variety and traits? |
a species is living things of the same kind that are able to reproduce, a variety is a group of organisms of the same specifies that have specific characteristics that can distinguish it from other variety's of species. a trait is a characteristic for those organisms. |
|
|
what is selective breeding/ |
a technology for producing new variety's of an organism that involves choosing parents with desired traits in order to produce an offspring with these traits. |
|
|
what is genetic engineering? |
a process in which single genes are added to a plants genetic material. |
|
|
what are herbicides and pesticides? |
they are things that kill harmful insects and plants. |
|
|
what is biological control? |
a process which natural predators of the pests are introduced to an area where the pest thrives. |
|
|
what is mono culture and biodiversity? |
mono culture is when each planted field is used to produce plant growth. biodiversity is when ther4e is a number of different species in an environment. |

