![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
purulent pus filled conjunctivitis
|
bacterial
|
|
|
water exudate conjunctivitis
|
viral
|
|
|
normal ocular flora
|
gram positive organisms;
s. epidermidis (resistant to lysozymes in tears) gram negative very uncommon |
|
|
acute mucopurulent conjunctivitis
|
s. aureus (adults)
s. pneumoniae (children) unilateral hyperemia, tearing mucopurulent discharge and mattering of the eyelids |
|
|
hyperacute bacterial conjunctivitis
|
huge amounts of pus and green discharge = NEISSERIA gonorrhoae or neisseria meningitidis; sexual contraction
|
|
|
chronic bacterial conjunctivitis
|
staphylococus
|
|
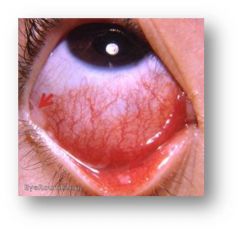
|
acute mucopurulent
|
|
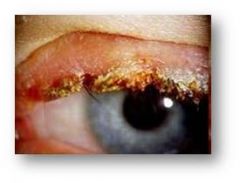
|
older pts; chronic; staph has colonized and is living in eyelids; lacrimal gland as a source or glands under hair follicles; flaking + loss of eyelashes
|
|
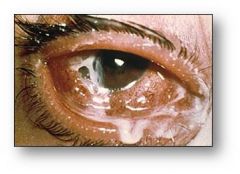
|
hyperacute purulent coinjunctivitis; usually neisseria; always consider that they have chlamydia
tx for chalmydia and neisseria |
|
|
why membranes good portals of entry
|
moist; stratified nonkeratinized (no border protection) epithelium; highly vascularized = good source of nutrients for organisms
|
|
|
lysozymes
|
hydrolyzes b1-4 linkages in peptidoglycan which destroys gram positive orgainsms (large peptidoglycan layer); however staph epidermidis is resistant to tears which is weird
|
|
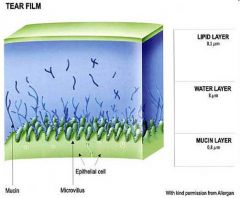
|
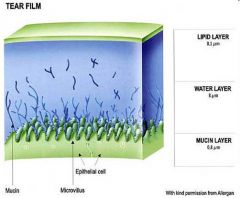
tear film
lipid layer; pseudomonas can bind to lipid layer water layer; motile, can swim mucin layer; pseudomonas has adhesion pilli that allow it to adhere to the conjunctiva |
|
|
lactoferrin
|
binds to free iron and competes w bacterial for this essential cofactor
|
|
|
follicular response
|
swelling of the lymphoid tissue in the eye; big edematous eyelid; yellowish white, discrete round elevation of conjunctiva produced by lymphocytic response; however bacteria may be able to take advantage of all the nutrients brought by the swelling
|
|
|
adenoviris mechanism of attachment to conjunctiva
|
cop-opts lactoferrin as a bridge to get into eye; uses receptor on surface of epithelium to trigger response and get into cell
|
|
|
s. epidermidis mechanism of attachment to conjunctiva
|
resistance to lysozyme and less susceptible to lactoferrin
|
|
|
neisseria, haemophilus, vibiro cholerae mechanism of attachment to conjunctiva
|
have lactoferrin receptors
|
|
|
pseudomonas mechanism of attachment to conjunctiva
|
bedridden indviduals in hospital; eyes and urinary tract; flagella for motility; fimbriae/pili which allows for adherence to host tissue
can cause ulceration by binding to injured epithlial edge via fimbriae or pili elastase promotes invasion while proteases provide protection from host defenses |
|
|
s. aureus mechanism of attachment to conjunctiva
|
produces alpha toxin to kill cells (hemolyins, proteases, lipases, superantiigens)
|
|
|
s. pheumoniae
|
encapsulated so avoids phagocytosis, produces pneumonlysin to cause corneal damage
|
|
|
Trachoma
|
chronic infection by chalmydia trachomatis A and C, causes follicular keratoconjunctivitis, mcc preventable blindenss in the world
turns eyelid in which scratches the cornea causing scarring/opacities |
|
|
chalmyudia trachomatous life cycle
|
EB bodies metabolically inactive, invade cell, produce RB bodies metabolicaly active but noninfectious, as RB bodies increase in number they become EBs which lyse the cells and are now infectious
|
|
|
artts line
|
horizontal line of conjunctival scarring; leads to scratching of cornea
|
|
|
best tx for inclusion conjunctivitis
|
system tetracycline; but dont give to young children or pregnant lactating women (can give erythromycin instead)
|
|
|
parinauds ocularglandular conjunctivitis
|
primarily caused by bartonella henselae "catch scratch fever" - rod shaped, gram negative, flagellated, flea vector infects kittens
|
|
|
acanthamoeba conjunctivitis
|
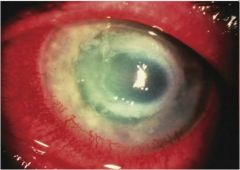
found in swimming underwater or diving; rare; blocked nose with altered sense of taste and smell
classic ring infiltrate after progression of the gray white superficial nonsuppurative infiltrate found in central or paracentral cornea |
|
|
blastomyces
|
broad based budding; sound in southeast
|
|
|
sporothrix schencki
|
conjunctivitis + arthritis affecting weight bearing joints
daisy petal formation |
|
|
viral conjunctivitis organism playing odds
|
adenovirus
|
|
|
pharyngoconjunctival fever (adenovirus 3,4,7)
|
triad of pharyngitis, fever and conjunctivitis; mild watery discharge (viral) from eye; hyperemia (edema of conjunctiva)
|
|
|
epidemic keratoconjunctivitis
|
much more serious than pharyngoconjunctival fever;
|
|
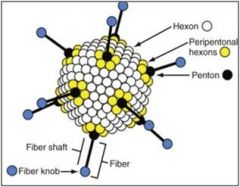
adenovirus
|
icosahderal, dsDNA, early genes (E1A/E1B - prevent apoptosis in the cell that it infects, enhances cell replication = oncogenic) and late genes (capsimer proteins)
coxsackie adenovirus receptor (CAR) |
|
|
adenovirus MHC I expression
|
buys time until cell killing by NK cells
|
|
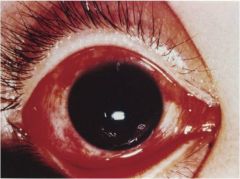
|
apollo disease (acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis)
caused by coxsackei virus and enterovirus; rapid onset of servere, painful papillary conjunctivitis; sever ehemorrhage |

