![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
134 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
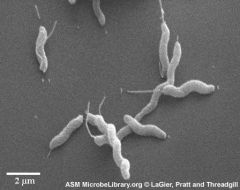
Campylobacter jejuni (Campylobacter likes the hot campfire)
Motile, curved gram negative rod (gulls wings) Microaerophilic; grows well at 42 on selective media; oxidase positive Fecal oral from poultry Common cause of diarrhea world wide |
|
|
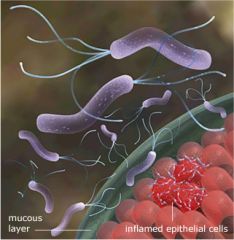
H pylori
Gram negative spiral gastric bacilli with flagella Microaerophilic 37 C growth, oxidase positive, urease positive; mucinase aids in penetration of mucous layer invasive into stomach lining where pH is neutral Inflammation prominent Causes chronic gastritis and duodenal ulcers; associated with stomach cancer |
|

|
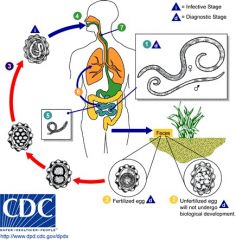
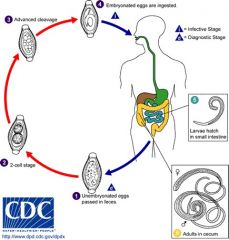
Ascaris Lumbricoides Egg; most common helminth worldwide; largest roundworm
egg ingested -> migrates to lungs where it's coughed up and reswallowed -> mature in small intestine May obstruct intestine or bilt duct |
|
|
Toxacara Canis
|
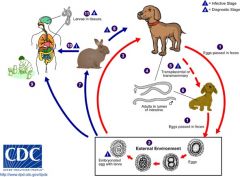
Visceral Larva Migrans (if in retina = blindness)
Eggs ingested from handling puppies or eating dirt in yard -> larvae wander aimlessly until they die; can cause inflammation |
|
|
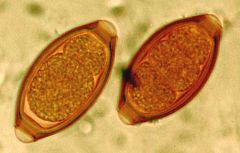
Trichurias Trichuria; whipworm in cecum, can cause appendicitis and rectal prolapse
Eggs are ingested (barrel shaped with bipolar plug detected in stool) |
|
|
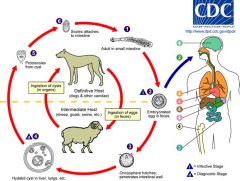
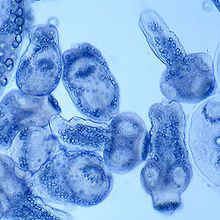
Ecchinocus Granulosus
Carnivore sheep herders; cause hytaid cysts in liver which can cause anaphylaxis if ruptured |
|
|
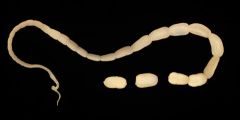
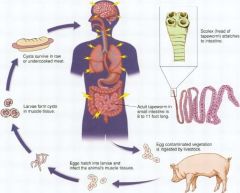
Taenia Soliumm; pork tapeworm
Rare/raw pork ingested; causing intestinal tapeworm; proglottids (segment of worm) or eggs in feces |
|
Blood Fluke
|
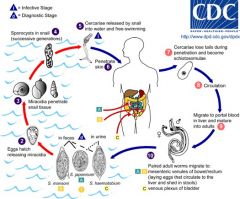
Schistosoma
Snails are host; cercariae penetrate skin of humans; cause granulomas, fibrosis and inflammation of the spleen and liver; |
|
|
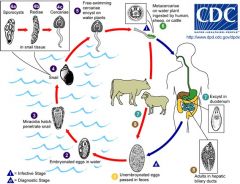
Fasciola hepaticae; Sheep liver fluke; ingestion of acquatic plants (water cress); operculated eggs
|
|
|
Cercaria of fasciola hepatica
|
|

|
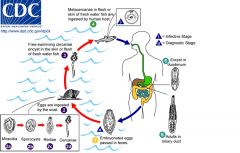
opisthorchis sinensis;
Human liver fluke; prevalent in east asia; third most prevalent worm parasite in the worm |
|
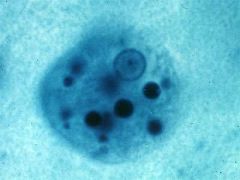
|
Enamoeba histolytica trophozoite
Protozoan which causes DYSENTERY; |
|
|
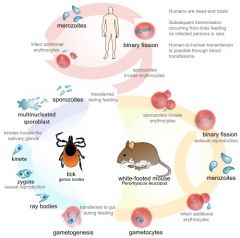
Characteristics of Malaria
|
Cyclic fever, headache, anemia, splenomegaly
|
|
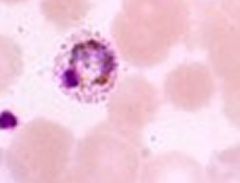
|
Shuffner Dots characteristic of P. Vivax and P. Ovale
|
|
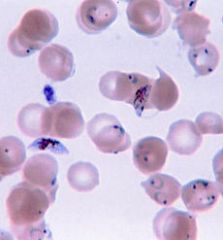
|
Ring forms of plasmodium falciparum
|
|
|
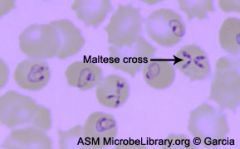
Plasmodium falciparum
|
Irregular fever spikes; causes cerebral malaria
Multiple ring forms and crescent shaped gametes |
|
|
Babesia
Transmission by Ioxides tick Babesiosis: fever and hemolytic anemia; predominantly in the Northeastern US |
|
|
Pt w/ jaundice, anorexia, nausea, RUQP, pn on palpation, cigarettes taste foul, elevated liver enzymes
Food borne (possibly contamined raw oysters or clms); 14-45 days without chronicity; study naked RNA virus |
Hepatitis A
|
|
|
Pt w/ jaundice, anorexia, nausea, RUQP, pn on palpation, cigarettes taste foul, elevated liver enzymes
IV drug abuse, needle stick; chronic carrier state; cirrhosis; primary hepatocellular carcinoma; DNA virus easily inactivated by alcohol |
Hepatitis B
|
|
|
Pt w/ jaundice, anorexia, nausea, RUQP, pn on palpation, cigarettes taste foul, elevated liver enzymes
Enterically trannsmitted with high fatality in pregnant women, no chronic form |
Hepatitis E
|
|
|
Acute abdominal pain; intestinal blockage suspected
|
Ascaris lumbricoides or potentially diphyllobothrium latum
|
|
|
Bile duct blockage flowing surgery
|
AScaris lumbricoides
|
|
|
Cirrhosis w/ travel history (Puerto Rico, Peace Corps); egg granulomas block triads -> fibrosis
|
Schistosoma mansoni
|
|
|
Pancreatitis with swelling of salivary glands
|
Mumps virus
|
|
|
Megaloblastic anemia; likely organism?
|
Diphyllobothrium latum; sucks up B12
|
|
|
Microcytic and hypochromic anemia; likely organism?
|
Ancyclostoma, Necator, Trichuris; suck blood from intestinal walls
|
|
|
Patient with cylic or irregular fever, decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit; often foreign travel to tropics. Schiontz in RBCs
|
Plasomdium
|
|
|
Reduced CD4 cell count; organism?
|
HIV
|
|
|
Increased PMN (isolated?
|
Extracellular bacterial infections
|
|
|
Isolated esosinophilia
|
Allergy or helminths during migratoin
|
|
|
Increases in mononuclear leukocytes (monocytes or lymphocytes)
|
Viral intracellular organisms
Listeria, Leishmania, Toxoplasma, Pneumocystis |
|
|
Increases in lymphocytes with fever, fatigue, lymphadenopath, myalgia and headache
Pt is hterophile positive w/ Downey cells |
Epsteinn-Barr Virus EBV
|
|
|
Increases in lymphocytes with fever, fatigue, lymphadenopath, myalgia and headache
Pt is hterophile negative |
CMV; txoplasma listeria
|
|
|
Ham, potato salad, cream pastries; pt w/ abd cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, NO fever for <24 hrs
|
Staphylococcus aureus
Heat stable enterotoxin produced in food contaminated by food handler with skin lesion; food sits at room temp |
|
|
An infant presents with diarrhea after coming home from day care. Noninflammatory water diarrhea, vomiting, fever and dehydration
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
An older kid or adult presents with diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. This is due to water, food or fecal oral routes.
|
Norwalk Virus
|
|
|
Pt presents with ab cramps, watery diarrhea and blood after eating a hamburger
|
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli
|
|
|
Profuse water diarrhea with vomiting (rice water stools)
|
Vibirio Cholera
|
|
|
Pt presents with loose, pale greasy diarrhea; mild to severe malabsorption syndrome after camping and swimming
|
Giardia lamblia
|
|
|
Pt presents with diarhea and enteritis after eating poultry and unpastuerized milk.
|
Campylobacter jejuni
|
|
|
Intracytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies (Owl's eye)
|
Cytomegalovirus
|
|
|
Activity of Vibrio Cholerae Toxin
|
Choleragen stimualtes adenylate cyclase
|
|
|
Activity of E. coli (ETEC) toxin (Traveler's diarrhea)
|
LT stimulates adenylate cyclase
|
|
|
Activity of Clostridium Difficile Toxin (causes diarrhea)
|
Toxin A and B inhibit protein synthesis and cause loss of intracellular K+
Lecithinase (alpha toxin) damage sthe membrane |
|
|
Which blood protozoa can be detected by gimesa stain?
|
Plasmodium, Babesia Trypanosoma, Leishmania
|
|
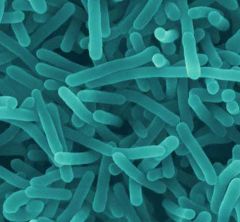
Pt with diarrhea who ate coleslaw
|
Listeria
Gram positive, nonspore forming rods; facultative intracellular; tumbling motility ACTIN JET MOTILITY IN CELLS Cold growth: Soft cheeses, deli meats, cabbages (coleslaw) |
|
|
Invasive amebae causing dystensery, which is noted for causing extraintestinal abscesses
|
entamoeba histolytica; causes diarrhea but known for leaving GI gtract
|
|
|
Vector for Borrelia burgorfei
|
Ixodes tick
|
|
|
Poorly treatable causative agent of chronic diarrhea in AIDS patients, which is diagnosed by finding acid fast cysts in the stool
|
Cryptosporidium tx is stil experimental and not highly effectve
|
|
|
Critically careful surgery is a major component of therapy
|
Hydatid cyst disease requires delicate surgery to remove them without breaking and releasing the larvae
|
|
|
Ciliate causative agent of diarrhea
|
Balantidium is the only ciliate on the list
|
|
|
Filarial worm maturing in the lymphatics and causing elephantiasis
|
Wuchereria is the causative agent of elephantiasis; brugia is another
|
|
|
Adult females live inside the adult male groove
|
Schitosomes are not hermaphroditic like other flukes (trematodes); they have separate sexes but live permanently together with the female in a groove of the male
|
|
|
Carrier of epidemic typhus and Trench Fever
|
Human body louse (Pediculus); carries epidemic typhus and Trench Fever
|
|
|
Fatty diarrhea associated with malabsorption syndrome
|
Giardia is most noted among the parasites for causing diarrhea with fat malabsorption
|
|
|
Chronic infections associated with bladder carcinoma
|
Schistosoma are notedly associated with bladder carcinoma
|
|
|
Infection results in enteritis and eosinophilia with flu like symptoms, periorbital swelling, petechial hemorrhages, and ultimately muscle pain; later in life X-ray may show fine calcification in the muscle
|
Classical description of trichinosis, caused by Trichinella spiralis
|
|
|
Sporozoites
|
Infectious forms injected by mosquitos in plasmodium falciparum
|
|
|
Schiznots/Merozoites
|
Erythrocytic forms of plasmodium falciparum
|
|
|
44 w/ paroxysmal fever; just returned from Arica though she was taking chloroquine the whole time; stopped taking pills when she returned; blood smear reveals ring trophozoites; The stage of the parasite life cycle responsible for the appearance of the parasites 2 weeks after departure from the malarious state is?
|
Exoerythrocytic Schiznot
|
|
|
9 yo girl who is listless and inattentive; thin w/ potbelly of malnutrition. Fecal exam and CBC; CBC reveals microcytic, hypochromic anemia and fecal exam detects brown, oval nematode eggs. What was the likely mechanism of infection?
|
Typical hookworm disease; usually Necator americanus; infection acquired by penetration of the filariform larvae through the skin of the feet (contaminated soil w/ eggs in soil);
|
|
|
HIv positive pt w/ low CD$+ count w/ diarrhea -> acid fast oocysts found in stool -> what is the proper care and prognosis?
|
Cryptosporidium; very difficult infection in AIDS pts (normally self resolving); usually unrelenting even w/ tx
Cryptosporidium is usually acquired from water; Toxoplasma is from cats |
|
|
24 yo woman in eighth month of pregnancy; positive IgM titier to toxoplasma for first time; how should she be advised?
|
Retinochoroiditis can be prevented by drug tx of an infant with a positive IgM response
|
|
|
Army captain w/ painful, erosive lesion near ear lobe since his return from Desert Storm; punch biopsy reveals macrophages distended with oval amastigotes. How was the infection acquired?
|
Bite of sandfly; Leishmania;
|
|
|
What does the tsetse fly transmit?
|
African Sleeping sickness
|
|
|
Students go camping; collect fresh water; a week after their return they all get sick with profuse diarrhea and tenesmus. Stool samples are yellow, greasy and foul smelling. What atribute of this parasite imparts its pathogenicity?
|
Ventral sucking disc of Giardia; common in mountain streams; causes its pathology by adherence to the mucosa of the upper small intestine with sucking disc; (no toxic metabolites or lytic enzymes)
|
|
|
Serologic test results from a hepatitis pt revelas (anti-HBc + , HBsAg +, anti-Hbs -); correct interpretation?
|
Chronic Carrier State
Core antibodies are not present if the person is only vaccinated |
|
|
If a person progresses rapidly to full blown AIDS and dies in three years, what regulatory gene is highly active?
|
tat; products of tat and rev genes increase viral maturation and act to decrease the latent period
|
|
|
If you ablated expression of the HIV pol gene, what other aspect of the virus's life cycle would be directly altered?
|
Integration of proviral DNA; pol encodes for both reverse transcriptase and the integrase, which allows linear proviral DNA to be integrated;
|
|
|
Interferons inhibit viral growth primarily by affecting
|
Interferons interfere w/ virus multiplication by blocking translation of viral protein (inhibit viral RNA and hence inhibit protein synthesis); they do NOT inhibit transcription, assembly or release or inhibit host protein synthesis
|
|
|
A chronic infection of hepatitis B is defined as having demonstrated the presence of
|
Presence of HbsAg for 6 months is considered chronic
|
|
|
To design a vaccine against HIV infection, a logical goal would be to alter some native
molecule or product of the virion in order to make it highly immunogenic. If you wished to prevent the attachment of the virus to helper T lymphocytes, which molecule or family of molecules might best be targeted?? |
Gp120; surface antigen of HIV that mediates attachment of CD4 lymphocytes
|
|
|
Which other virus is hepatitis A most closely related genetically?
|
Hepatitis A is a picornavirus so that is the most likely choice. If you do not know the family but know that it is naked and positive RNA,you can eliminate hepatitis B because it is DNA.Measles, rubella, and influenza are all enveloped.
|
|
|
A baby has the greatest chance of acquiring which owl eyed virus?
|
CMV dsDNA virus
|
|
|
What is the most common lab testing method for diagnosing infectious mononucleosis?
|
Monospot test to detect EBV specific antibody;
|
|
|
Atypical lymphocytes (Downey Cell)
|
EBV or CMV; determined by heterophile test
|
|
|
Which virus has such high genetic drift that more than one antigenic variant be isolated from most infected individuals who have high viral titers?
|
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV); complicates the development of an effective vaccine
|
|
|
19 yo w/ sore throat and fatigue following normal tasks like getting up in the morning; says he has been sick ofr several months and now his girlfriend appears to have the same thing. His tonsils have white exudative, cervical lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly.
|
EBV
dsDNa, enveloped icosahedral virus |
|
|
Diarrheal epidemic at Lincoln Grade School; 20% of children got ill/stayed home and three teachers and a custodian have also called in sick
|
Communal eating can lead to food contaminated by Norwalk virus;
|
|
|
16 yo dropout develops dark urine and yellow sclera; says he has not felt well for the past week and quit smoking because the cigarettes tasted funny
|
Hepatitis B
|
|
|
The baby was born at the 31st week of gestation. It was small for gestational age and
showed jaundice. Petechiae were noted and the spleen and liver were enlarged. The pathology department reported that placental examination revealed chorioamnionitis, villitis, and owl's eye intranuclear inclusion bodies. |
CMV
|
|
|
Plasmodium malariae
|
Bar and band forms; rosette schiznots
|
|
|
Trypansoma brucei
|
African sleeping sickness; transmitted by tsetse fly;
|
|
|
A 6-month-old child has had watery diarrhea for 6 days. The stools have no blood and no pus. The causative agent is a double-stranded RNA virus. Which is the most likely causative agent?
|
Rotavirus; pts age and symptoms (and the viral vlue) indicate rotavirus
|
|
|
Which of the hepatitis viruses has the highest associatio with hepatocellular carcinoma?
|
Chronic Hepatitis B; A and E are naked viruses and do not set up long term infections
|
|
|
What is the main component of the EBV?
|
Viral Capsid Antigen (VCA) protein
|
|
|
In traveler's diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli, what is responsible for the fluid and electrolyte disruption?
|
Exotoxin that causes an increase in cAMP; Traveler's diarrhea is most frequently caused by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli that produce the heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST) toxin. LT is an exotoxin that causes an increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate
|
|
|
A formerly vigorous 3-month-old child has developed upper body weakness manifested by droopy eyes and head, poor feeding, and a weak cry. Changes starting with constipation were first noticed 2 days ago. The baby is afebrile and there is no sign of rash. What is the most likely causative agent and where is the infection?
|
Clostridium botulinum; GI tract infection
The child most likely has infant botulism, which is caused by ingestion of the spores (not the toxin) of the anaerobe Clostridium botulinum. The immature intestinal flora allow germination of the spores and the subsequent vegetative growth with in vivo production of the toxin. |
|
|
African sleeping sickness is transmitted by
|
Tsetse fly bite
|
|
|
There is an outbreak of watery diarrhea in 6 members of a party of 20 who ate at a Chinese restaurant the day before. Fried rice is implicated. What is the most likely causative agent?
|
Bacillus cereus; found in rice, not killed by steaming
|
|
|
Hookworm infections can be prevented by...
|
Wearing shoes outside in endemic regions; Hookworm filariform larvae may grow in the soil in endemic regions and can penetrate skin. Wearing shoes has been shown to greatly reduce the transmission of hookworm.
|
|
|
A Peace Corp volunteer recently returned to rural Africa develops symptoms of liver damage and a blocked bile duct after general anesthesia. What is the nature of the most likely causative agent?
|
Nematode; Adult Ascaris lumbricoides is a roundworm that maintains its position in the gastrointestinal tract by continual movement upstream, not by attaching. It is noted for migration into the bile duct, gallbladder, and liver, producing severe tissue damage. This process is often exacerbated by fever, antibiotics, and anesthetics.
|
|
|
What is found in the urine of multiple myeloma patients?
|
Bence Jones proteins = dimers of free light chains
|
|
|
Plague is transmitted by
|
Flea bite or respiratory droplets from an untreated person with the pulmonary form of plague
|
|
|
Six 18-year-old women return from a recent Canadian camping trip with abdominal cramping, gas, pain, and diarrhea that is pale, greasy, and malodorous. They drank untreated stream water on the last 2 days of the trip after losing their water filter. What is the most likely causative agent?
|
Giardia lamblia; attach to intestinal mucosal so need fecal antigen test to detect them
|
|
|
One advantage of a live, attenuated vaccine is
|
it induces a wide spectrum of antibodies; disadvantages include the possible production of persistent infections
|
|
|
The virulence of Francisella tularensis is most highly associated with
|
Intracellular replication
|
|
|
Following several tick bites while hiking through a wilderness park in the southeastern United States, a 19-year-old man develops fever, sore throat, malaise, headache, nausea, and a rash on the lower parts of both his arms and legs. When he starts feeling worse and his wrists and ankles begin to swell, his companions take him to an emergency department. The man's temperature is 38.9°C. Which of the following should be at the top of the differential diagnosis list?
|
The rash associated with Rickettsia rickettsii originates on the ankles or wrists and spreads to all parts of the body.
|
|
|
What is the vector for Chagas disease?
|
Reduviid bugs
|
|
|
A patient with sickle cell anemia is most likely to have repeated septicemias with what organism
|
Salmonella enteriditis; sickle cell anemia pts have problems with septicemias with encapsulated organisms (pneumococcus and Klebisella)
|
|
|
Why does Clostridium difficile cause diarrhea?
|
C difficile exotoxins damage the cells, causing a disruption in transport and attracting polymorphonuclear cells to cause the appearance of a pseudomembrane.
|
|
|
What is an appropriate and affective method for reducing the transmission of toxoplasmosis?
|
Avoid cat litter or take proper care in changing litter
|
|
|
A patient presents with explosive, watery, noninflammatory diarrhea along with headache, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Symptoms began the day after eating raw oysters in August. What is the most likely causative agent?
|
Vibri parahaemolyticus
|
|
|
How can you reduce your chances of acquiring Vibrio parahaemolyticus illness?
|
Cook fish and seafood thoroughly
|
|
|
After a trip to Peru to adopt a 6-month-old baby, a 32-year-old woman and her new baby both develop profuse, watery diarrhea with flecks of mucus. Both are hospitalized because of the severity and rapidity of the dehydration, but neither one is febrile. What is the most likely causative agent?
|
Vibrio cholerae
The mention of Peru should raise suspicion of cholera. (Rotavirus would have to be ruled out for the baby, but it is not one of the choices.) The loss of fluids and electrolytes is rapid and most severe with Vibrio cholerae. The lack of fever and lack of pus and blood in the stools suggests that the causative agent is not Campylobacter or Salmonella. The lack of blood also decreases the chance of Escherichia coli O157. If untreated, cholera may lead to dehydration, hemoconcentration, and hypovolemic shock. |
|
|
What is the nonvertebrate host for the plasmodia?
|
Malaria is spread by the Anopheles mosquito, which is also the definitive host
|
|
|
A patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome has severe, nonresolving diarrhea. Acid-fast oocysts are seen in the stools, which are not gray and greasy. What is the most likely causative agent?
|
Acid-fast oocysts are seen in infections with Cryptosporidium, a protozoan that causes severe, nonresolving diarrhea in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. In general, the bacterial causative agents are more responsive to treatment.
|
|
|
A biology graduate student who recently visited a tropical region of Africa presents with new visual impairment and the sensation that something is moving in her eye. She tells you that she is concerned because she had been warned about eye disease transmitted by black flies. When in Africa, she was in a river area, and despite her best efforts she received a lot of black fly bites. She also has some subcutaneous nodules. If her infection was acquired by black fly bite, what is the most likely causative agent?
|
Onchocerca volvulus causes river blindness and is transmitted by the bite of a black fly. The patient may be able to detect movement in the eye.
|
|
|
A surgical patient who imports food from Mexico, and so spends several months each year in rural Mexico, returns several days after her mastectomy with signs of acute appendicitis. When her appendix is removed it is found to contain a light-colored, 20.5-cm long roundworm and bile-stained, knobby eggs consistent with Ascaris. How did she acquire this infection?
|
Ingestion of food contaminated with the eggs; Fertilized Ascaris eggs released in feces may contaminate food or water, which is then consumed. Ascaris does not attach to the intestine but maintains its position by mobility. The worm may become hypermotile (e.g., during febrile periods, anesthetic use, or antibiotic use) and may migrate into the appendix or bile duct.
|
|
|
A patient whose major source of protein is smoked and cooked fish develops what appears to be pernicious anemia. What parasite is noted for causing a look-alike vitamin B12 anemia in certain genetically predisposed infected individuals?
|
Diphyllobothrium latum
|
|
|
What is the most likely reason for a chloroquine-treated case of Plasmodium vivax relapsing?
|
P vivax has a persistent exoerythrocytic stage (hypnozoite); Both Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium vivax may form liver hypnozoites, which are very slow to develop into schizonts with merozoites and proceed onto the chloroquine-sensitive erythrocytic stages. (It's not over with P ovale or P vivax unless you also treat with primaquine phosphate, which kills the liver stages.)
|
|
|
How is Leishmania donovani transmitted?
|
Sandfly bite; all leishmaniae are transmitted by sandflies
|
|
|
How is Schistosoma haematobium transmitted?
|
All schistosomes are transmitted by skin penetration from standing or swimming in contaminated water. Remember that snails are intermediate hosts.
|
|
|
What tapeworm is acquired from eating undercooked pork?
|
Taenia solium
|
|
|
What roundworm is most likely to be transmitted by ingestion of food or water contaminated with feces?
|
Ascaris lumbricoides is transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Enterobius is most likely transmitted via contaminated hands, clothing, or bedding. Necator enters by skin penetration. Taenia is not a roundworm. Toxocara is most commonly acquired from eating fecally contaminated dirt or soil.
|
|
|
What roundworm is transmitted by filariform larvae that are found in the soil and penetrate the skin?
|
Strongyloides stercoralis is a type of hookworm (also a roundworm). The filariform larvae of S stercoralis are picked up when walking barefoot or sitting on the ground.
|
|
|
How is Clonorchis sinensis (Chinese liver fluke) most likely transmitted to humans?
|
Raw, undercooked, smoked, or pickled fresh water fish are the most common route of transmission
|
|
|
A patient who recently returned from camping in Canada presents with malabsorption diarrhea. How does the most likely agent cause the diarrhea?
|
Suction disk attachment at duodenal-jejunal area; leads to maladsorption diarrhea and temporary lactose intolerance; Giardia
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most frequent cause of blood transfusion associated hepatitis?
|
Hepatitis C
|
|
|
Viral Capsid Antigens antibodies are found in
|
EBV; important diagnostically
|
|
|
Infantile diarrhea is usually attributable to
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
Dane particles are associated with
|
The spherical virion of hepatitis B virus is called the Dane particle
|
|
|
Which virus can lyse and kill progenitor erythroid cells causing aplastic crises in patients with hemolytic anemia?
|
Parvovirus B19
|
|
|
What is the most likely causative agent of gastroenteritis starting on day 5 of clindamycin treatment?
|
Clostridium difficile
|
|
|
Which cause a more mild gastroenteritis; Vibrio cholerae or vibrio parahaemolyticus?
|
Vibrio Parahaemolyticus
|
|
|
Yersinia pestis may be transferred by:
|
Respiratory droplets or flea bite
|
|
|
All of the following are characteristics of Salmonella typhimurium EXCEPT
(A) it has a multianimal reservoir. (B) it is one of the most common causes of enterocolitis. (C) it ferments lactose. (D) it is a common contaminant of poultry. (E) it is a gram-negative, motile, endotoxin-bearing rod. |
C. Salmonella species do not ferment lactose; though some produce acid, gas and hydrogen sulfide from glucose
|
|
|
A patient has a gastric ulcer not induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Which characteristic appears to play a central role in the ability of the organism to colonize the stomach?
(A) Phospholipase C production (B) Urease production (C) Microaerophilic lifestyle (D) O antigens (E) Motility |
Urease; major virulence factor of H. pylori
|
|
|
Francisella tularensis
|
Spread by rabbits; can cause a localized ulcerglandular form; intracellular
|
|
|
Which organism infections starts with a rash in the extremities and spreads to the trunk?
|
Rickettsia rickettsi; rocky mountain spotted fever characteristically appears on hands and feet
|
|
|
Does Shigella dysenteriae posess an endotoxin, enterotoxin or both?
|
Both an endotoxin and enterotoxin
|
|
|
Which of the following organisms invades mucosal epithelial cells?
(A) Vibrio cholerae (B) Vibrio parahaemolyticus (C) Salmonella typhi (D) Shigella sonnei |
Shigella invades the intestinal epithelium, resulting in liquid stools containing mucus, pus, and occasionally blood.
|
|
|
Does Salmonella typhimurium possess an endotoxin, enterotoxin or both?
|
Both an endotoxin and an enterotoxin
|
|
|
Does vibrio cholerae posses an enterotoxin, endotoxin, or both?
|
It posesses both an endotoxin and enterotoxin
|

