![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
evolution |
change in a population or species over generations |
|
|
natural selection |
guiding force for evolution; alleles survive or die out based on relative fitness |
|
|
fitness |
ability to survive and reproduce |
|
|
3 principles of natural selection |
genetic variation, competition, and differential survival |
|
|
genetic drift |
an alternative driving force for evolution, other than natural selection; alleles undergo random shifts in frequency
|
|
|
homologous structure |
similar structure, shared by descendants of common ancestor |
|
|
biogeography |
where organisms live |
|
|
sexual selection |
natural selection that drives the evolution of one sex but not the other |
|
|
directional selection |
natural selection in which one allele is favored; evolution goes in one direction |
|
|
stabilizing selection |
natural selection in which intermediate phenotypes are favored; extremes (homozygotes) are less fit |
|
|
selective pressure |
something that causes differential survival; food scarcity, climate change, predation, mate scarcity, etc.
|
|
|
taxonomy |
grouping or classifying organisms |
|
|
dichotomous key |
repeated choice between two descriptions eventually leads to identification of an organism |
|
|
cladogram |
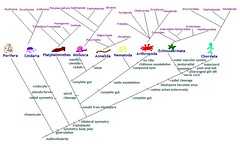
"family tree" that shows relationships among organisms |
|
|
node |
common ancestor; point on cladogram where branches meet |
|
|
adaptation |
a trait that increases fitness |

