![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atom
|
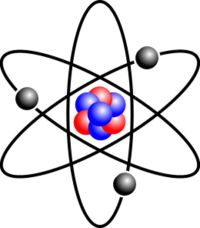
the smallest particle of a substance that can exist by itself or be combined with other atoms to form a molecule
|
The atom is the smallest unit that defines the chemical elements and their isotopes
|
|
|
Atomic Mass
|
the mass of an atom usually expressed in atomic mass units
|
Atomic mass is the average weight of atoms of an element.
|
|
|
Atomic Mass Unit
|

a unit of mass for expressing masses of atoms, molecules, or nuclear particles equal to 1⁄12 the mass of a single atom of the most abundant carbon isotope 12C
|
The standard unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale.
|
|
|
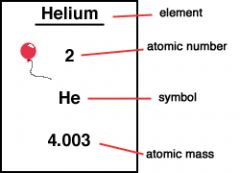
Atomic Number
|
an experimentally determined number characteristic of a chemical element that represents the number of protons in the nucleus which in a neutral atom equals the number of electrons outside the nucleus and that determines the place of the element in the periodic table
|
The number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom of an element.
|
|
|
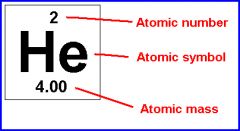
Atomic Symbol
|
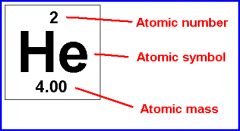
The atom of each element is made up of electrons, protons and neutrons.
|
Atomic symbol is code for the name of a chemical element.
|
|
|
Chemical Symbol
|

Chemical symbol is code for a chemical element.
|
An abbreviation of a chemical element on the periodic table
|
|
|
Electron
|
a very small particle of matter that has a negative charge of electricity and that
travels around the nucleus of an atom |
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative charge
|
|
|
Group
|
A column of elements on the periodic table. There are 18 numbered groups
|
One group on the periodic table would be N, P, As, Sb, Bi
|
|
|
Isotopes
|
any one of various forms in which the atoms of a chemical element can occur
|
Isotopes are atoms of elements with different number of neutrons
|
|
|
Mass Number
|
an integer that approximates the mass of an isotope and designates the number of nucleons in the nucleus
|
The totally number of protons and neutrons in an element
|
|
|
Metal
|
A substance (such as gold, tin, or copper) that usually has a shiny appearance, is a good conductor of electricity and heat, can be melted, and is usually capable of being shaped
|
Metal is good at forming bonds with non-metals
|
|
|
Metalloid
|
a chemical element that has properties in between, or is a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals
|
They have both metal and non-metal properties
|
|
|
Neutron
|
A very small particle of matter that has no electrical charge and is part of the nucleus of all atoms except hydrogen atoms
|
These have no charge
|
|
|
Nonmetal
|
In chemistry, a nonmetal (or non-metal) is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes.
|
Substance that does not exhibit any metal characteristics. Example, oxygen
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
the central part of an atom that is made up of protons and neutrons
|
The center and core of the atom is the nucleus
|
|
|
Period
|
A horizontal row of elements on the periodic table.
|
Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells
|
|
|
Proton
|
a very small particle of matter that is part of the nucleus of an atom and that has a positive electrical charge
|
In the nucleus of the atom, has a positive charge.
|
|
|
Subatomic Particle
|
A subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom: it may be elementary or composite
|
Particle physics and nuclear physics concern themselves with the study of subatomic particles, their interactions, and matter made up of them which do not aggregate into atoms.
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
the central part of an atom that is made up of protons and neutrons
|
The center and core of the atom is the nucleus
|
|
|
Period
|
A horizontal row of elements on the periodic table.
|
Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells
|
|
|
Proton
|
a very small particle of matter that is part of the nucleus of an atom and that has a positive electrical charge
|
In the nucleus of the atom, has a positive charge.
|
|
|
Subatomic Particle
|
A subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom: it may be elementary or composite
|
Particle physics and nuclear physics concern themselves with the study of subatomic particles, their interactions, and matter made up of them which do not aggregate into atoms.
|

