![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
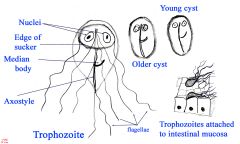
A 25 year old woman had recently returned from a trip to the Rocky Mountains. She had been traveling with a group of campers, who had obtained their drinking water from a lake. A few days after returning home, she presented to her internist suffering from profuse watery diarrhea, crampy epigastric pain and foul smelling flatulence.
A permanent trichrome stain revealed some oval protozoan trophozoites. The broad anterior end contained a concave area covering half the ventral surface. The structure of the parasite gave the appearance of a “smiling face”. Rare cysts, having four nuclei, and characteristic median bodies and longitudinal fibers were also seen. Organism? |
Giardia lamblia (flagellate); transmissted through cysts in water
Fat rich ghirardelli chocolates for fatty stools of Giardia! |
|
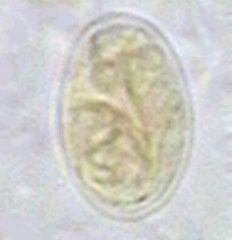
You note oval cysts under the microscope from a patient stool sample. You also see the presence of trophozoites Organism?
|
Giardia lamblia; causes giardiasis (bloating, flatulence, foul smelling fatty diarrhea - often seen in campers/hikers)
|
|
|
A 3- year old girl was brought to her pediatrician by her mother who was concerned about the child’s diarrhea of 1 week’s duration. She had also vomited several times. The girl attended a day care center while her mother was at work. The pediatrician ordered stool specimens for culture for enteric pathogens and a routine O & P examination. No enteric pathogens were isolated in culture. Microscopic exam was negative for O & P. No parasites were detected in the smears stained with trichrome. What kind of stain should be performed now?
|
Acid fast to detect for cysts
|
|
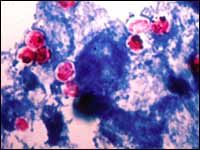
Acid fast stain reveals pinkish red 4-6 um oval structures. What protozoan is responsible for the patient's illness?
|
Cryptosporidium
*ACID FAST CYSTS |
|
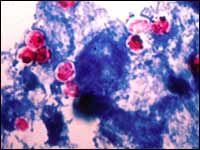
A patient presents with severe diarrhea. The patient is notable for a history of AIDS. Acid fast stains reveal cysts in the stool. Organism?
|
Cryptosporidium
|
|
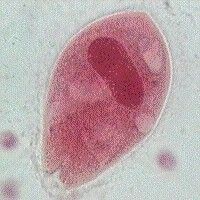
a patient presents with intermittent watery diarrhea with blood and pus. A stool sample reveals LARGE ciliated trophozoites. You note that there is a bean shaped macronucleus. Organism?
|
Balantidium Coli
|
|
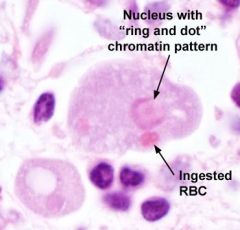
A patient presents with numerous bloody stools per day and right upper quadrant pain and fever. Direct wet mounts reveals motile trophozoites with ingested RBCs. Also noted is the presence of cysts with 4 nuclei. Organism?
|
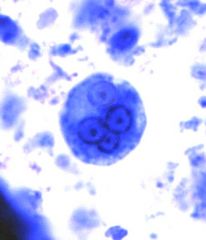
Entamoeba histolyica; RBC in cytoplasm of entamoeba; transmitted via cysts in water
RING AND DOT PATTERN |
|
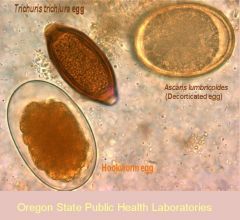
A 19-year-old woman who had recently returned from a semester of schooling in costa Rica had been suffering from crampy abdominal pain and diarrhea for just over a week. Stool cultures where ordered and standard O & P examination was performed. Microscopic examination revealed several types of nematode eggs. These eggs had thick shells and were oval, with some being more broadly oval than others . Several eggs had a nubby out covering (a) while others lacked the outer covering (b). Golden brown eggs on wet preparation!
|
Ascaris lumbricoides
Larvae emerge in small intestine; travel to lungs (pneumonitis); swallowed a second time to mature in intestine; larvae mature to adults and produce eggs which pass into feces |
|
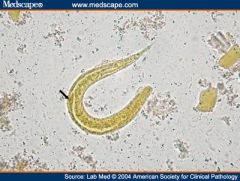
A patient has a bout of unexplained diarrhea and abdominal pain. There is also pneumonitis and abdominal pain. Stool reveals filariform larvae.
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
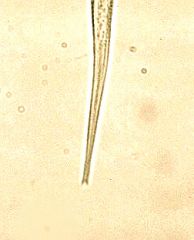
What are characteristics of the filariform larvae of Stronglyoides?
|
Notched tail; more prominent esophagus
|
|
|
49-year-old man underwent a routine outpatient colonoscopy. His medical history was unremarkable and the laboratory findings were normal. Colonoscopy showed a long, slender, white worm in the cecum against the ileocecal valve. One end of the parasite was embedded in relatively normal mucosa (Fig. 4A). The parasite was carefully retrieved by forceps. Microscopically, the parasite was consistent with a female adult worm with a prominent uterus (Fig. 4B). Numerous barrel-shaped eggs with mucoid plugs at both ends were detected in the uterus (Fig. 4C). A microscopic evaluation revealed a moderate eosinophilic infiltration in the lamina propria of the adjacent colonic mucosa (Fig. 4D). On the stool examination subsequently performed, barrel-shaped eggs with mucoid plugs eggs were detected. He was treated with albendazole for 3 days.
|
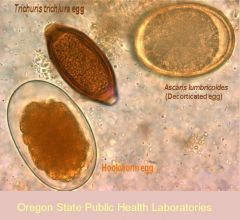
Ileal-cecal location indicates trichuris trichirua (whipworm); since worms are embedded in intestinal wall it's unusual to see them in the stool; EGGS in stool (eggs look like footballs with bumps at each end)
|
|
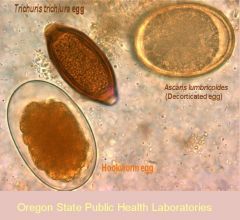
What is unique about the life cycle of trichuris trichiura?
|
Slow life cycle; don't penetrate tissue so no lung involvement or eosinophil elevation
|
|

How are schistosoma mansoni infections aquired?
|
Skin penetration by cercariae released from fresh water snails
|
|
|
A patient presents with hepatosplenomegaly with large accumulation of ascitic fluid in the peritoneal cavity. Likely organism? Organism
|
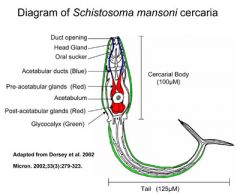
Schistosomiasis infection; skin penetration by cercariae released from freshwater snails
|
|
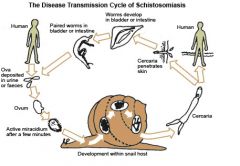
A patient presents with dermatitis, cough, hepatitis, fever, malaise, abdominal pain and liver tendernis. Dysentery (ab pain diarrhea + blood in stool) was also present. Organism?
|
Schistosomiasis infection; skin penetration by cercariae released from freshwater snails
|
|
|
At what receptors do diphenoxylate and loperamide act?
|
Mu receptors in myenteric plexus; hyperpolarize cholinergic neurons involved in motility (this allows more time for intestinal and colonic water absorption)
|
|
|
What should you note when administering diphenoxylate or loperamide with other drugs?
|
Since these drugs are opioid agonists, you have to be note that this will increase the oral bioavailability of drugs taken after administration
|
|
|
Which drug is basically dietary fiber?
|
Psyllium (metamucil); absorbs excess water, swells into a gel, and stimulates peristaltic activity
|
|
|
Which drug can be used for both diarrhea and constipation?
|
Psyllium (metamucil);
can absorb excess water (diarrhea) but also stimulate secretion (swells, stimulates motility) |
|
|
When administering psyllium (metamucil) for diarrhea what must you coadminister?
|
oral fluids, because it can cause constipation
|
|
|
What is cholestyramine used for?
|
Bile induced diarrhea due to bile acid malabsorption
also an adjunct to antimicrobials for toxin producing bacterial enteritis |
|
|
Which two organisms produce enterotoxins cholestyramine can bind to?
|
C. diff/E. coli
|
|
|
Considering cholestyramine binds bile and prevents its reabsorption, what is a predictable side effect of cholestyramine use?
|
It can cause malabsorption of fat soluble nutrients, vitamins, tetracyclines and aggravate steatorrhea induce diarrhea
|
|
|
A patient presents with diarrhea. You note he has a black tongue and black stools. Which medication might he have taken?
|
Bismuth subsalicylate (pepto-bismol)
|

