![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what happens in osmosis?
|
osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a higher concentrated solution to a lower concentration in a solution through a partially permeable membrane
|
|
|
What is a partially permeable membrane? |
A partially permeable membrane has very small holes that only allow tiny molecules like water to diffuse through. this causes the higher concentration side to fall and the lower concentration to rise. |
|
|
where do you find tissue fluid in the body? What is tissue fluid?
|
tissue fluid is found surrounding the cells in our bodies. it is released in the blood capillaries and it is made up of water oxygen and glucose and it is used to supply the cells with everything they need. the tissue fluid has a different concentration to the fluid inside the cell.So water can move in or out of the cell by osmosis. |
|
|
what are the three main gas and solute exchanges?
|
the three main exchanges are: *diffusion *Osmosis *active transport these exchanges allows life processes to happen such as photosynthesis respiration where gasses are exchanged for these actions to happen. |
|
|
how are exchange surfaces adapted to make these processes more efficient?
|
exchange surfaces are adapted by : *being thin so that substances only have short distances to diffuse from. *they have a large surface area that allows more diffusion to happen at once. |
|
|
how does the structure of the leaf allow gasses to diffuse in and out of the cell?
|
within the leaf it has air spaces that allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into for photosynthesis. the leaf also has stomata's that allow oxygen and water vapour(evaporation) to diffuse out of. the stomata's has guard cells that open and close. the flattened shape, air spaces and cell walls creates a larger surface for gasses to diffuse. |
|
|
what is the job of the guard cell in a stomata?
|
guard cells control water loss when there is not enough water the guard cell will become flaccid-causing guard cells to close to much water-stomata will become turgid-therefor causing the guard cells to open. they are also sensitive to light therefore closing at night. |
|
|
what is ventilation? what happens during the process in terms of muscles?
|
ventilation is when we breath in and out. when we breath in our intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract. This creates a larger volume in the lungs and it decreases the pressure. when we breath out it does the opposite! *muscles diaphragm relax *lung volume decrease and a increase in pressure to release the air out. |
|
|
what are the two types of artificial ventilators? ventilators are machines that pump air into and out of the lungs. |
iron lung- they seal the body until it got to there shoulders. Were air is pumped out of the case, which will cause the pressure to drop and the ribcage to expand to let air in positive pressure ventilators-works by pumping in air into the lungs, which will expand the ribcage ,wen it stops pumping the ribcage relaxes it releases the air out. |
|
|
lungs transfer oxygen to the blood and remove CO2. what do lungs contain and how are they specialised to maximise diffusion? |
the lungs contain millions of air sacks called Alveoli that helps with gas exchange Alveoli has: *large surface area *moist lining *thin walls *good blood supply |
|
|
where are villi found? what are their functions? how are they adapted for these functions? |
in the small intestine it is covered with millions of villi. villi has a large surface area to allow more digested foods to be absorbed into the blood villi has: *big surface area *good blood supply for quick absorption *one cell thick allows short distance for absorption. |
|
|
What is active transport? how is active transport used in root hair cells?
(note active transport also occurs in our gut!) |
Active transport is the movement of molecules from a low concentration to a higher concentration against a concentration gradient using energy. root hairs uses the process of active transport to take in minerals from a dilute solution. minerals are essential for growth. However this process requires energy which is provided through respiration. |
|
|
how are food/minerals transported through the plant? (phloem)
|
food molecules made in the leaves such as sugar are transported through phloem tubes.they are made up of columns of living cells that has a hole in the end to allow substances to flow through. these food substances are transported to mainly the growing regions and storage organs of the plant. |
|
|
how is water and minerals transported in the plant?
|
water and minerals are transported through the Xylem tubes which is made up of dead cells stacked on top of each other. Between where they join there are no walls to allow the water and minerals to pass through. They go from the Root to the Stem and Leaf by the Transpiration stream. |
|
|
what is transpiration? what causes it? what is a transpiration stream? |
transpiration is the lose of water in a plant it is caused by evaporation and diffusion were it creates a low supply of water in the leaves. therefor more water is needed to be taken from the roots through the xylem creating a constant transpiration stream. the water molecules are bonded by cohesion therefor when the water evaporates it creates a pull motion. |
|
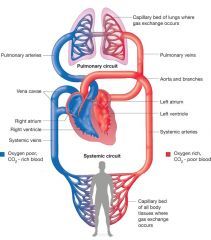
Describe double circulatory system? (what are there functions?) |
the double circulatory system has two circuits joined together. • One pumps Deoxygenated blood into the lungs to take in Oxygen and goes back to the heart. *the second pumps Oxygenated blood to various organs to provide the body cells with oxygen. This causes the blood to become deoxygenated. Were it will return to the heart to be supplied with more oxygen in the lungs. |
|
|
what does the heart do? it contains valves, why? |
the heart is a organ that keeps blood flowing throughout the body. The heart is mostly made out of muscle cells. the heart has valves to make sure that the blood is flowing in the right direction .the valves prevent the blood from flowing in the other direction. |
|
|
the heart consist of 4 chambers that help pump blood, name them and explain what they do?
|
Right Atrium-Deoxygenated blood is flown through the vena cava. The R atrium then contracts to push the blood into the right ventricle. Right ventricle-contacts to force the blood into the pulmonary artery and out of the heart Left atrium- the blood then flows through the pulmonary vein and into the Left atrium were it will contract to force Oxygenated blood into the L ventricle. Left ventricle-contract to force Oxygenated blood into the aorta. |
|
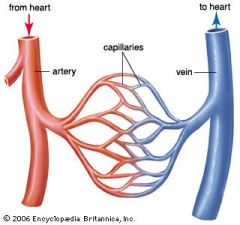
what are the three types of blood vessels and what are their functions? how are they formed? |
*arteries-carry blood away from the heart. *veins-carry blood to the heart *capillaries-to allow food and oxygen to diffuse into the cell arteries branch of into capillaries and when the capillaries join up they form veins |
|
|
what is the function of the arteries? how are they adapted to this? |
arteries-carry blood away from the heart adapted *the walls are strong and elastic to cope with high pressure of the blood. *thick layers of muscle allows the pressure to be maintained. |
|
|
what is the function of the veins? how are they adapted to this? |
veins-carry blood to the heart adapted *the blood pressure is low therefor the walls are one cell thick. *they have a larger lumen to help blood flow *they contain valves to keep the blood flowing in one direction. |
|
|
what is the function of the capillaries? how are they adapted to this? |
*capillaries-allow food and oxygen to diffuse into the cell. They also carry blood to every cell when exchanging the substances (ex.oxygen). adapted *they have permeable walls that allow substances to diffuse from. *the walls are one cell thick therefore allowing diffusion to happen quicker because of the decrease in distance it has to travel. |
|
|
what are the four main things in our blood? (what does the blood contain) |
our blood contains: • Red blood cells • White blood cells • Platelets • Plasma |
|
|
what does the Red blood cells do? how are they adapted fro their job?
|
the red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells in our body. Red blood cells contain haemoglobin which combines with oxygen to form Oxyhaemoglobin were oxygen is stored. adapted *they have a doughnut shape that give it a large surface area for absorption of oxygen. *does not contain a nucleus, meaning there is extra room for haemoglobin. |
|
|
what are platelets? what do they do/stop from happening?
|
platelets are small fragments of cells that do not contain a nucleus. platelets help blood clot, by stopping the blood from pouring out and to also stop microorganisms from entering the wound. |
|
|
what does the plasma do? what does it carry? |
the plasma carries everything in the blood including red and white blood cells. The substances that plasma carries are: *carbon dioxide *anti body and toxins *hormones *urea. these substances are carried through the body to perform important functions. the plasma maintains blood pressure and regulates body temperature. |
|
|
why do we use Artificial blood? what is the solution used? |
artificial blood is used when someone loses a lot of blood. Low supply of blood means that less oxygen is being supplied to the body cells. therefore a blood substitute known as saline is used temporarily to replace the lost blood to allow the body to reproduce more blood cells to become more stable. |
|
|
what are artificial hearts and how are artificial hearts used? what is a advantage and disadvantage of |
artificial hearts are mechanical devices that are used to replace hearts to pump blood temporarily until a heart donor is found. advantage *artificial hearts are less likely rejected by the body because it is made of metal/plastic. disadvantage *during surgery of implanting a artificial heart it can lead to bleeding and infections. *parts can wear out *the flow of blood is less smooth causing blood clots to occur |
|
|
what are the functions of stents?
how does stents help with diseases such as coronary heart disease? |
stents are tubes inserted inside the arteries. there main purpose is to keep the lumen open and to lower the risk of heart attacks if it isn't. this is because during diseases such as coronary heart disease causes fatty deposits to build up in the walls of the arteries causing it to narrow. Therefore stents are used to keep them open. |
|
|
Describe all the organs and tissues in our Thorax. |
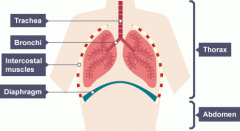
Intercostal muscles and Diaphragm expands the lungs. Air flows in through the Trachea splitting into two bronchus. (Bronchi) Each bronchus goes into one lung. The bronchi splits into more bronchioles then into alveoli which are bags where gas exchanges |
|
|
what are the three main roles of the kidney?
|
main roles (kidney cleans the blood) 1)it removes urea from the blood 2) change and balance ions in the blood 3)change and balance water content in the blood. |
|
|
how is urea produced and why is it removed? (kidneys) |
urea is produced when to much protein is being taken in therefore converting it into urea, this process happens in the liver. urea is removed as its poisonous. The liver releases it into the blood stream were it will be filtered by the kidneys and stored in the bladder to be excreted as urine. |
|
|
how is the ion content adjusted in the body? (taken in or removed) |
when we eat the ions from our food is absorbed into the blood. it is important to control ion content as it may effet the amount of water drawn out of osmosis which can damage cells if unbalanced. ion removed: *excess ion is removed by the kidneys from the blood. *ions such as sodium can be lost through sweat. |
|
|
how is water content controlled? how is water losted in our body?
|
We can consume water by food and drinks. water is lost through *urine *sweat *when we breathe |
|
|
How does your brain detect your Temperature? |
Thermoregulatory centre in the brain has receptors that sense the blood's temperature flowing by. And Thermoregulatory centre receives impulses from skin.
|
|
|
what are nephrons? what are there functions? |
Nephrons are Filtration units in the kidney. They work by building a high pressure to squeeze out the water, urea, ions and sugar in the blood into the bowman's capsule. the bowman capsule is close to the arteries to allow useful substances such as sugar sufficient water and ions to be reabsorbed. This is done through active transport. the remaining will be released as urea. |
|
|
how does sports drink help with keeping your body in balance?
|
sports drinks can help your body by replacing the water sugar and ions. water and ions are lost through sweat while sugar is used in our muscles when we exercise. calcium(good)=bones, high sodium(bad)=H blood pressure-health problems, fat(bad)= high cholesterol. claims to justify against companies *was it tested on a large amount of people to give reliable results? *was it written by a qualified person? |
|
|
what happens when waste products are not removed from the blood? how can this be fixed? |
if the waste product is not removed it will build up in the blood which can be vital as it = death. this is caused by kidneys being unable to control levels of water and ions known as kidney failure. people with kidney failure can be treated by: *having a dialysis treatment(machine) *or a kidney transplant. (donor) |
|
|
What is dialysis treatment? How does it work?
|
Dialysis treatment is when machines are used to filter out waste substances in your blood. 3 times a week for 3 hours. it can cause blood clots and infections. It would pump your blood into a selectively permeable barrier that contains dialysis fluid that is permeable to ions and waste products. The fluid is concentrated to the same as ions and glucose so that it won't be lost through the partially permeable membrane. So only waste products diffuse across barrier by diffusion. |
|
|
how can transplanted organs be rejected?
|
during a kidney transplant the kidney is receive from a donor. The kidney can be rejected by your immune system as your body releases antigens and antibodies to attack and prevent it from happening therefor precautions are put in place: *the donor tissue must match closely with the person same antigens (which=tissue type) *drugs can be used to prevent your immune system from attaking |
|
|
what are the two hormones that control blood sugar? what do they do?
|
2 hormones are : glucagon and insulin
|
|
|
what causes type 1 diabetes? |
type 1 diabetes is caused when your cells are producing a inefficient amount of insulin made in the pancreas. Meaning the sugar levels can not be controlled. treating pancreas transplant or controlling the problem through: *regular exercise and controlling the intake of sugar. * injecting insulin |
|
|
what waste are we placing into the water that is polluting the environment? w |
water pollutants *sewage and chemicals caused by industries are polluting oceans that are effecting the lives of plants and animals. *fertilisers are being washed into the rivers
Air: Smoke and gases released is causing air pollution. (Acid rain ) |
|
|
what waste are we placing into the land that is polluting the environment?
|
land pollutants *toxic chemicals used for farming are killing insects *landfill *industrial and household waste buried underground |
|
|
what are the human activities that are causing less land for animals and plants?
|
they reduce the amount of land and resources by: •Buildings • Farming • Dumping Wastes • Quarrying (metals) |
|
|
what are the natural storing ways of sequestering Co2?
|
they can be locked up by: *diffused in ocean and lakes *green plants (for photosynthesis) *peat bogs |
|
|
what does carbon dioxide and methane cause?
|
Co2 and methane trap heat from the sun by acting as a insulating layer in the atmosphere by absorbing the suns heat. causing it to radiate out towards earth. these gases are called green house gases which lead to global warming-(rise in temp) |
|
|
what are the 4 main problems caused by Deforestation?
|
*Methane- released when organisms decompose *Carbon dioxide-released when wood is burnt *Less carbon dioxide removed-less photosynthesis = less carbon dioxide removed. *less Biodiversity-decrease in different species as there habitat is destroyed. |
|
|
what are Peat Bogs? what happens when you destroy them?
|
Bogs are areas that are acidic or water logged. Plants that live in this areas cant fully decay as there is not enough oxygen therefor rotted plants build up to form Peat. peat bogs contain a lot of carbon dioxide in the dead plants. Meaning when there destroyed CO2 will be released. Peat can be used as compost and fuels. |
|
|
what are the consequences of global warming?
|
rise in sea levels when temperature increases it melts the ice. change in weather patterns -causing regions to experience extreme weather and conditions will become unpredictable. reduce in biodiversity-organisms are unable to adapt therefore becoming more distributed and even instinct. |
|
|
how is fermentation used to make biofuels? why is it good to use fermentation in bio fuels? |
fermentation uses bacteria or yeast to break down sugars by anaerobic respiration to make biofuels. it is good because natural products such as waste can be used. |
|
|
how is ethanol made? how is the substances/reactant collected?
|
Ethanol is made by anaerobic fermentation of sugar with Yeast and it is then distilled. Glucose -> Ethanol + carbon dioxide + energy Glucose can be collected from sugar cane juices or made from maize starch by carbohydras. |
|
|
how is bio gas made?
|
biogas is made by anaerobic fermentation of waste products from plants and animals that contain carbohydrates. biogas is made out of 70% methane and 30% carbon dioxide biogas can not be stored as a liquid! there fore they are used quickly. |
|
|
what are the 2 types of biogas generators? what does a biogas generator need/requirements?
|
Batch generators- make small batches of biogas and you would manually load it up with waste. AND Continuous-they make biogas all the time at a large scale and they are continuously fed with waste. requirements: *there needs to be a inlet for waste material *an outlet to allow digested material to be removed. *another outlet that allows biogas to be piped away. |
|
|
what are the 4 factors that is needed to be considered when designing a biogas generator?
|
•Cost - continuous generators are the most expensive. the cost of building one. • Convenience -cleaning and loading the generator. • Efficiency -making sure it is at 35 degrees or production will be slow. • Position-the waste will smell, meaning placement of them should be away from homes and near water sources. |
|
|
what are the economic and environmental effects caused by using biofuels? good or bad? |
*it is carbon neutral as the CO2 released from it is used for photosynthesis. *does not cause acid rain *it is cheap and always available *biogas acts like a waste disposal system. |
|
|
how can the efficiency of food production be increased?
|
*Reducing the number of stages in food chain means that less biomass is being lost. this can be achieved by growing more crops for food rather then using it for animals. *Restricting energy lost from farm animals by restricting there movement and keeping them closely compact for warmth *Making new food sources. |
|
|
what is mycoproteins?
|
mycoprotein is a meat substitute for vegetarians that are mainly made of a fungus called Fusarium.it is made by growing the fungus in a fermenters(big container) using glucose syrup as food. the fungus then respires aerobically being supplied with oxygen and other minerals (nitrogen). the fermenter is then sterilised to get rid of any other organisms. Before harvesting it. |
|
|
what measures have been placed to sustain the resource of fish?
|
(limit the days where boats can fish)- reduce the amount being caught (reduce net size)-meaning the amount of fish being caught is smaller. (no fishing zones)-prevent certain areas for fishes to be caught *Mesh size *Fishing Quotas |
|
|
name two ways fishing stocks can be conserved?
|
Fishing Quotas - limits the sizes and the number of fishes that can be caught in a certain area. Prevents overfishing. net mesh/size - allows unwanted and young fish to escape to breed. |
|
|
what is vaso dilation and vaso constriction?
|
When we are too cold the blood vessels supplying warm blood to the skin become narrow or constrict (vasoconstriction) When we are too hot, blood vessels supplying blood to the skin can swell or dilate (vasodilation). |

