![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who was Democritus?
|
He was the first to discuss the atom.
|
|
|
Who was John Dalton?
|
He devised the first modern atomic theory.
|
|
|
What did John Dalton go by?
|
1) All matter is made of atoms (100%)
2) Atoms of different elements have different masses (100%) 3) Compounds form when atoms join together (100%) 4) Atoms cannot be created or destroyed (50%) |
|
|
What did Democritus go by?
|
"Everything is atoms and the void"
-invisible (100%) -indestructible (50%) -indivisible (50%) |
|
|
Who was Sir J.J. Thomson and what did he do?
|
![He discovered the electron, and devised a model of the atom. [Plum Pudding Model/Rasin Bun Model]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/38/44/28/4384428_m.jpg)
He discovered the electron, and devised a model of the atom. [Plum Pudding Model/Rasin Bun Model]
|
|
|
What did Sir Ernest Rutherford discover, and how?
|
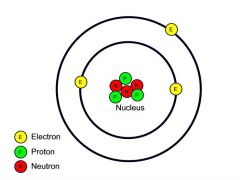
He discovered the nucleus through the gold foil experiment.
|
|
|
What else did Sir Ernest Rutherford discover?
|
The nucleus contains protons, so technically he discovered that too.
|
|
|
What did Sir Ernest Rutherford devise, and who helped complete it?
|
He devised the Nuclear Atom, it was completed when Sir James Chadwick discover the neutron.
|
|
|
What is the mass of a proton?
|
1 amu.
|
|
|
Where is a proton located?
|
In the nucleus.
|
|
|
What is the mass of a neutron?
|
1 amu.
|
|
|
Where is a neutron located?
|
In the nucleus.
|
|
|
What is the mass of an electron?
|
1/2000 amu.
|
|
|
Where is the electron located?
|
In the 'cloud' of the atom. (orbital)
|
|
|
What does the number of protons equal?
|
The atomic number.
|
|
|
What does 'atomos' mean in Greek?
|
'Not knife'.
"A" meaning 'not' and "tomos" meaning 'knife'. An atom cannot be cut. |
|
|
Who was Niels Bohr?
|
He proposed the Orbital Theory.
|
|
|
What are some points of the Orbital Theory?
|
1) Electrons occupy "orbits" like planets around a sun or star
2)They are usually found close the nucleus "ground state" 3) When electrons absorb energy (heat or electricity) they jump to a higher orbit "excited state" - they lose this energy by giving off a photon of light, the energy of which matches the energy difference between the 2 orbits - the colour depends on the energy |
|
|
What is the maximum electron population in the first orbit?
|
2 electrons.
|
|
|
What is the maximum electron population in the second orbit?
|
8 electrons.
|
|
|
What is the maximum electron population in the third orbit?
|
8 electrons (--->18e-)
|
|
|
What is the maximum electron population in the fourth orbit?
|
8 electrons (--->32e-)
|
|
|
Who studied and helped develop The Quantum Mechanical Model?
|
Warner Heisenberg
Erwin Schrodinger Wolfgang Pauli (among others) |
|
|
The Aufbau Diagram!
|
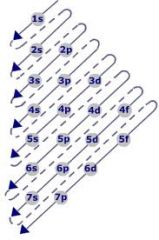
2 electrons (maximum) in the first column.
6 electrons in the second column. 10 electrons in the third column. 14 electrons in the fourth column. |
|
|
The atomic number is equal to what?
|
The number of protons.
|
|
|
How do you find the mass number?
|
It's the number of neutrons + the number of protons.
|
|
|
Give three points on the QMM (that was developed by those three guys).
|

1) Bohr's orbits weren't circles around the nucleus- they were volumes
2) Each orbit has overlapping sublevels. We call them orbitals. 3) Each orbital can hold 2 electrons. This led to the need for more elaborate description of the arrangement/location of the electrons. |
|
|
What are the main points on Quantum Weirdness?
|
1) Electrons can jump from one orbital to another without crossing the space in between.
2) Electrons behave as both particles and energy waves. "Wave particle duality" |
|
|
What two elements are found in lightbulbs?
|
Tungsten and argon.
|
|
|
What is another element used in household lighting?
|
Neon!!
|
|
|
What liquid element is electrically conductive?
|
Mercury.
|
|
|
What colour is mercury?
|
Silver.
|
|
|
What element is used for the shiny metallic coating on car parts?
|
Chromium.
|
|
|
Name 2 gases that are lighter than air.
|
Helium and hydrogen.
|
|
|
Which element that is lighter than air flammable?
|
Hydrogen.
|
|
|
What are "tin" cans made of?
|
Iron.
|
|
|
What is "tin" foil made of?
|
Aluminum.
|
|
|
What are 3 magnetic metals?
|
Iron, nickel, and cobalt.
|
|
|
Provide a symbol that would BE ACCEPTABLE for chemists all over the world.
|
- must be unique
- 1st letter capitalized, printed - 2nd letter lower-case, printed |
|
|
What is the simplest form of matter?
|
Elements.
|
|
|
Elements _______ be decomposed. (Can/Cannot)
|
Cannot :)
|
|
|
What are elements made out of?
|
Atoms.
|
|
|
What are elements identified by?
|
Symbols.
|
|
|
What do elements have to be approved by?
|
IUPAC (The governing body of chemisty)
|
|
|
What was the only element named after the person who found it?
|
31 Galium.
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 1 (based on the atomic number)?
|
Un.
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 2?
|
Bi!
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 3?
|
Tri :)
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 4?
|
Quad.
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 5?
|
Peut :)
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 6?
|
Hex.
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 7?
|
Sept.
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 8?
|
Oct.
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 9?
|
Enn.
|
|
|
What is the assigned temporary name for 0?
|
Nil.
|
|
|
What is the temporary name of an element with the atomic number 123? What is the symbol?
|
Unbitrinium. (Ubt)
|
|
|
What is the temporary name of an element with the atomic number 285? What would the symbol be?
|
Bioctpeutium. (Bop)
|
|
|
What did Dmitri Mendeleev devise?
|
He devised the 1st periodic table, based on the Periodic Law.
|
|
|
What is the Periodic Law?
|
When elements are arranged in order of increasing mass their properties reccur on a periodic basis.
|
|
|
What did Henry Moseley conceive?
|
He conceived the atomic number (number of protons; modern periodic table is arranged by atomic mass)
|
|
|
What did Fredrick Soddy discover?
|
He discovered isotopes.
|
|
|
What are isotopes?
|
They are atoms of the same element (same # of protons/atomic number) but different masses (different numbers of neutrons).
|
|
|
What is atomic mass?
|
Weighted average of all the isotopes of an element.
|
|
|
Mass # - Atomic # = ________
|
Neutrons :)
|
|

Atomic Mass Question
|
Note: Add, not divide.
|
|
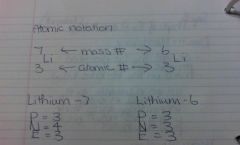
Atomic notation.
(Mass Number - Atomic Number = Neutrons) |
#YOLO
|
|
|
What is periodicity?
|
The recurrence of properties in the groups (columns) of the periodic table. This is due to each element in the column having the same number of valence electrons.
|
|
|
The variation in properties within a group (such as trends in the reactivity of elements in the Alkali Metals or Halogens) is the result of differences in...
|
Atomic radius and ionic radius.
|
|
|
What is Atomic Radius?
|
The radius of the atom.
|
|
|
What is Ionic Radius?
|
The radius of the ion.
|
|
|
What are alletropes?
|
They are different forms of an element.
|
|
|
What is an example of alletropes?
|
Carbon
- charcoal - graphite - diamond - buckeye balls - carbon fibre - buckeye tubes |
|
|
Where are metals on the periodic table?
|
Left side.
|
|
|
Where are non metals on the periodic table?
|
Right side.
|
|
|
Where are the metalloids on the periodic table?
|
In between :)
|
|
|
Are metals malleable?
|
Yes!
|
|
|
Are non metals malleable?
|
No.
|
|
|
Are metalloids malleable?
|
Maybe.
|
|
|
Are metals ductile?
|
Yes!
|
|
|
Are non metals ductile?
|
No!
|
|
|
Are metalloids ductile?
|
Maybe.
|
|
|
Are metals conductive?
|
Yes!
|
|
|
Are non metals conductive?
|
No.
|
|
|
Are metalloids conductive?
|
Maybe.
|
|
|
Do metals have lustre?
|
Yes!
|
|
|
Do non metals have lustre?
|
No.
|
|
|
Do metalloids have lustre?
|
Maybe.
|
|
|
How do metals form ions?
|
Loose electrons to form positive ions.
|
|
|
How do non metals form ions?
|
Gain electrons to from negative ions.
|
|
|
How do metalloids form ions?
|
Either gain or lose electrons.
(Maybe) |
|
|
What are some points on Halogens?
|
- they have 7 valence electrons
- if you move down the Halogens from Fluorine to Astatine, the melting point/boiling point increases - not found in nature (too reactive) - toxic - low boiling point |
|
|
How many valence electrons does Hydrogen have?
|
1 valence electron.
|
|
|
What are some points on Alkali Metals?
|
- they have one valence electron
- they are the most reactive metals - never found in their pure forms because they are so reactive - found in compounds - low melting points - solid at room temperature - conductive |
|
|
When you go down a column in the periodic table, the atomic radius gets BIGGER. Why?
|
More orbitals.
|
|
|
As you go to the right of the table, the atomic radius's get smaller. Why?
|
Because the more protons you have, the more attracted the electrons are going to be to the nucleus. So the atom is going to be smaller.
|
|
|
When a metal ion gains electrons, it's ionic radius gets _________. (bigger/smaller)
|
Bigger.
|
|
|
When a non metal loses electrons, it's ionic radius gets ________. (bigger/smaller)
|
Smaller.
|
|
|
Who is associated with periodicity?
|
Dmitri Mendeleev!
|
|
|
Who are the three men who helped develop the Quantum Mechanical Model?
|
Warner Heisenburg, Erwin Schrodinger, and Wolfgang Pauli. (Among others)
|
|
|
What are some points on Noble Gases?
|
- very non-reactive
- very low boiling points - very light density - generally non-reactive |
|
|
Who was the UBC chemist that produced the first noble gas compound?
|
Neil Bartlett.
|
|
|
What are some points on Alkaline Earth Metals?
|
- 2 valence electrons
- very reactive - good conductivity |
|
|
What are some points on the 'family of one'?
|
- having only 1 electron, it can either give or take an electron and can make either - or + ions
- it's very reactive - very rarely found in it's natural state - low density |
|
|
What did Sir William Crookes invent?
|
The gas discharge tube.
|
|
|
Who did Sir William Crookes' invention help? How?
|
Sir J.J. Thomson. (He discovered the electron and devised a rasin bun model/plum pudding model of the atom)
|
|
|
What did Sir James Chadwick discover?
|
He discovered the neutron.
|

