![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
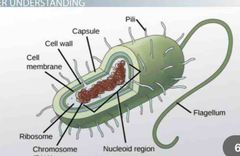
Prokaryotes |
lack a nucleus |
|
|
|
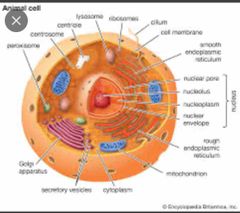
Eukaryotes |
Has a nucleus |
|
|
|
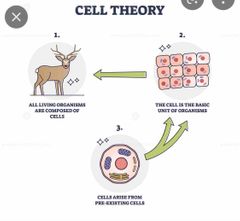
Cell theory |
they are the basic structural organizational unit of all organisms |
|
|
|
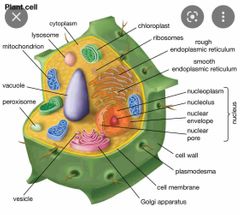
Cell wall |
the cell that Rigids nonliving permeable wall that surrounds the plasma membrane |
|
|
|
Cell membrane/plasma membrane |
separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. |
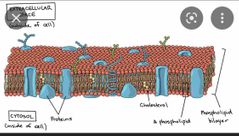
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
the material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus. |
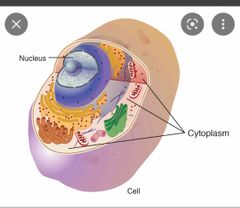
|
|
|
Plasmid |
small circular DNA molecule found in bacteria and some other microscopic organisms. |
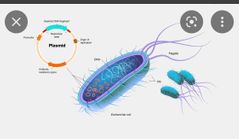
|
|
|
Ribosomes |
an intercellular structure made of both RNA and protein, and it is the site of protein synthesis in the cell |
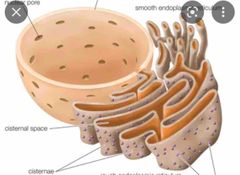
|
|
|
Nucleus |
controls and regulates the activities of the cell (e.g., growth and metabolism) and carries the genes, structures that contain the hereditary information |
|
|
|
Nucleus envelopes |
separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm and provides the structural framework of the nucleus. |
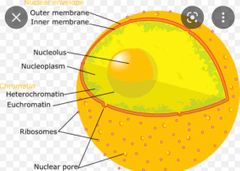
|
|
|
Nucleolus |
composed of RNA and proteins, which form around specific chromosomal regions. |
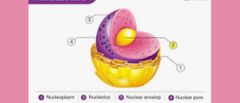
|
|
|
Chromosomes |
structures found in the center (nucleus) of cells that carry long pieces of DNA. |
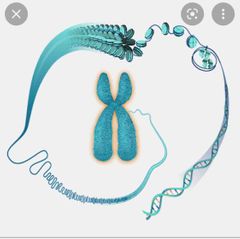
|
|
|
Chromatin |
a complex of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells |
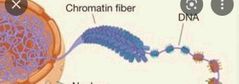
|
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
to produce proteins for the rest of the cell to function. |
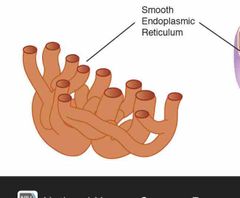
|
|
|
Microtubutes |
they provide the rigid, organized components of the cytoskeleton that give shape to many cells. |
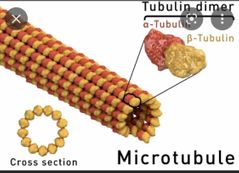
|
|
|
Microfilaments |
generate the forces used in cellular contraction and basic cell movements |
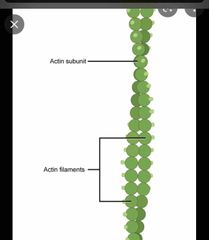
|
|
|
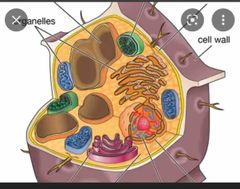
Vacuoles |
help sequester waste products |
|
|
|
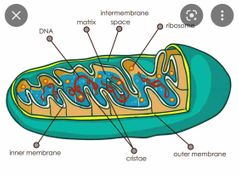
Mitochondria |
which generates ATP by utilizing the energy released during the oxidation of the food we eat. |
|
|
|
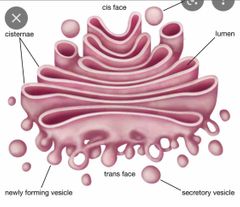
Golgi apparatus |
central intracellular membrane-bound organelle with key functions in trafficking, processing, and sorting of newly synthesized membrane and secretory proteins and lipids. |
|
|
|
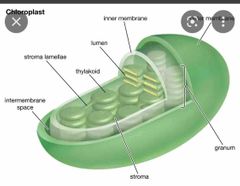
Chloroplasts |
plant cell organelles that convert light energy into relatively stable chemical energy via the photosynthetic process |
|
|
|
Lysosomes |
membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. |
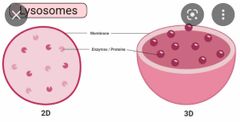
|
|
|
Cilia |
movement of the cell itself, or of other substances and objects past the cell |
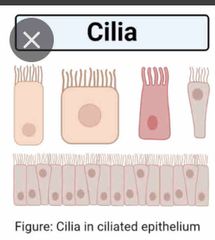
|
|
|
Flagella |
a motility organelle that enables movement and chemotaxis. |
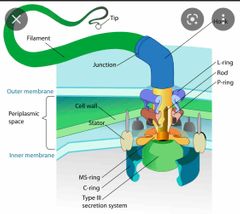
|
|
|
Hypotonic |
has a lower concentration |
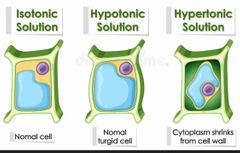
|
|
|
Hypertonic |
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration than most solitons |
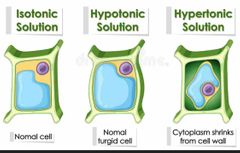
|
|
|
Isotonic solution |
Has an equal concentration |
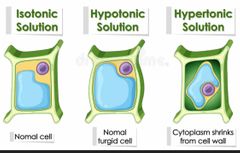
|
|
|
Osmosis |
movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane. |
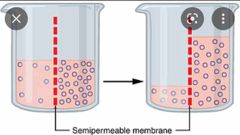
|
|
|
Diffusion |
the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. |
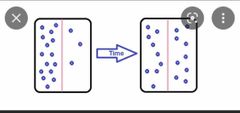
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient. |
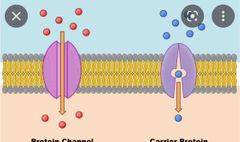
|
|
|
Semi-permeable |
thin biological sheets of material that allow certain molecules to pass through them more easily than others |
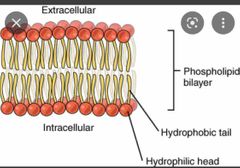
|
|
|
Active transport |
the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy |
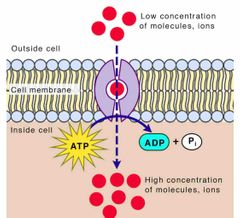
|
|
|
Passive transport |
does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes. |
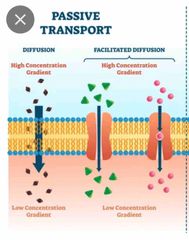
|

