![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sense that you could Lose if you got a fracture in the cribriform plates of the ethmoid bone? |
Olfactory sense |
|
|
Non-bone structure that would be damaged if a bullet penetrated the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone? |
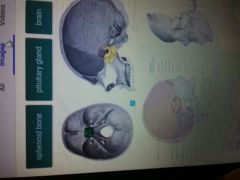
Pituitary Gland |
|
|
Fracture on dens is what especially broken bone |
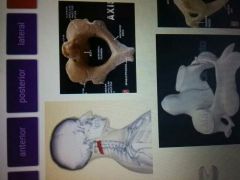
Axis |
|
|
On which body region is the axis bone located |
cervical |
|
|
____are soft spotsin the fetal & infant skull thathave yet to be converted to bone |
Fontanels |
|
|
Advantages of soft spots is |
1. allow brain growth 2. compresses skull to make birth easier |
|
|
Three bony projections that make delivery difficult |
sacral promontory, coccyx, ischial spines |
|
|
first three regions of vertebral column superior to inferior w/ number of vertebrae |
Cervical 7 Thoracic 12 Lumbar 5 |
|
|
Movable bone in skull |
mandible |
|
|
Movable joint in the whole skull |
Temporomandibular joint |
|
|
The _______ _____of the mandible articulates with the _______ _____ of the temporal bone to form the temporomandibular joint |
Mandibular condyle, mandibular fossa |
|
|
someone has a paranasal sinus infection, what four particular bones do you know may be involved with her problem _____ |
Frontal, Sphenoid, Ethmoid,and Maxillary bones |
|
|
What’s the specific source of the hormone named PTH (Parathyroid hormone) |
From parathyroid gland, triggered by too high calcium levels |
|
|
What specific kind of cell does PTH stimulate |
osteoclasts(Bone Calcium Breakers) |
|
|
The stimulation PTH provides has what effect relative toblood calcium levels? |
Since it breaks down the calcium in bones it will INCREASE the BLOOD calcium levels |
|
|
What is the epiphyseal plate of long bones made of |
Cartilage |
|
|
What phenomenon does the epiphyseal plate provide for |
Length Wise growth of long bones that occur in children and adolescence |
|
|
Scoliosis |
Abnormal lateral curvature of the back of the thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
Kyphosis/hunchback |
Exaggerated posterior curvature of thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
Lordosis/swayback |
Exaggerated anterior curvature of the lumbar vertebrae |
|
|
What are laminae and what's their relation to spina bifida |
They are the posterior portions of the vertebral arch. Spina bifida is the failure or fusion of laminae during development |
|
|
What's the name for the material located outside of the cells of connective tissues, including bone. |
Extracellular matrix |
|
|
Organic and inorganic properties of bone and what do they provide to bones |
Calcium phosphate that provides cartilage |
|
|
Cleft palate results when the palatine bones(palatine process) of the _____ fail to fuse medially during fetal development |
The maxilla fails to fuse correctly |
|
|
Red Bone Marrow Function |
Hematopoesis: Make red blood cells |
|
|
In what portion of a long bone is red bone marrow located |
Epiphysis |
|
|
Red Bone marrow is housed |
In the spongy bone |
|
|
4 types of bone markings that serve is attachment sites for ligaments and muscles(via tendons) |
Tuberosity, Trochanter, Tubercle, Epicondyle |
|
|
What is a fossa |
A shallow, basin like depression in a bone; often serves as an articular surface |
|
|
What is a meatus |
A canal-like passageway through a bone |
|
|
What is a foramen |
An opening in a bone |
|
|
What is a magnum |
Big opening of skeleton in an occipital bone |

