![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Common Compound Ions |

|
|
|
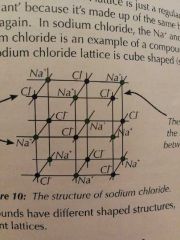
Giant ionic lattices |
|
|
|
Ionic Compound Qualities |
Conductive when molten or dissolved High melting points (strong electrostatic attraction) Soluble in polar liquids ie Water |
|
|
Covalent Bonding Types |
Single Double Triple Dative |
|
|
Dative Notation |

|
|
|
Simple Covalent Structures |
Lots of individual molecules (covalently bonded) & weak intermolecular |
|
|
Giant Colavent Structures |
Macromolecular.
Huge network of covalently bonded atoms. |
|
|
Covalent Example Carbon Structures |
Graphite (3 covalent, 1 delocalised electron) Diamond (4 covalent, tetrahedral shape - crystal lattice structure) |
|
|
Charge Cloud: Define |
An area where bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons have a high likelihood of being. |
|
|
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory |

Lone pair charge clouds repel eachother more than bonding pairs so this affects atom shape |
|
|
Molecular Shape: 2 Bonding Pairs |
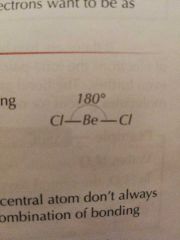
Linear |
|
|
Molecular Shape: 3 Bonding Pairs |
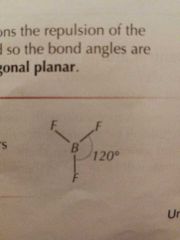
Trigonal Planar |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 4 Pairs (4 Bonding) |
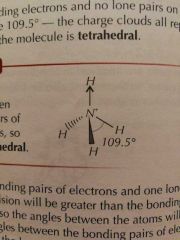
Tetrahedral |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 4 Pairs (3 Bonding) |
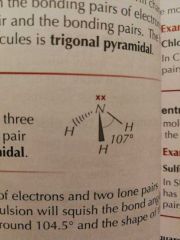
Trigonal Pyramidal |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 4 Pairs (2 Bonding) |
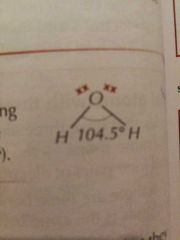
Bent / Non Linear |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 5 Pairs (5 Bonding) |
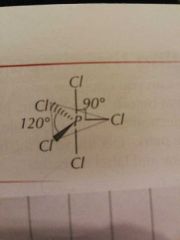
Trigonal Bipyramidal |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 5 Pairs (4 Bonding) |
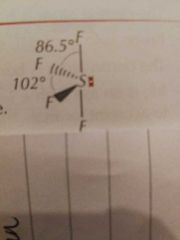
Seesaw |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 5 Pairs (3 Bonding) |
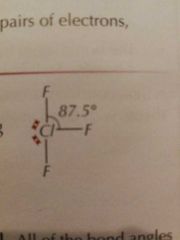
T-Shape |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 6 Pairs (6 Bonding) |
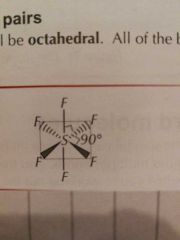
Octahedral |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 6 Pairs (5 Bonding) |
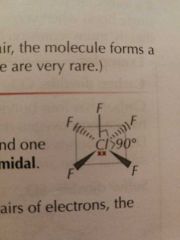
|
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 6 Pairs (4 Bonding) |
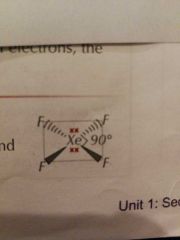
Square Planar |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 6 Pairs (Commonalities) |

90° Angles OCTAHEDRAL SQUARE PYRAMIDAL SQUARE PLANAR |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 4 Pair Commonalities |

Difference of 2.5° |
|
|
Molecular Shapes: 5 Pair Commonalities |

One straight 'spear' |
|
|
Electronegativity: What Scale is this measured on? |
Pauling Scale |
|
|
Define: Polar Molecules |
A molecule where charge is distributed unevenly across the entire molecule (due to differences in electronegativity). This causes a permanent dipole |
|
|
Define: Van Der Waals Forces |
A type of intermolecular forces caused by charge clouds causing temporary dipoles which attract and cause temporary dipoles in neighbouring molecules |
|
|
Define: Permanent Dipole Dipole |

Weak intermolecular forces between molecules which are polar |
|
|
Hydrogen Bonding: Define |
Occur between hydrogen and Fluorine, Nitrogen or Oxygen atoms of other molecules. Responsible for the unusual solid density of water. |

