![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two types of RC oscillators |
Phase shift Wein bridge |
|
|
Two types of SSB suppression techniques |
Phase shift Filter method |
|
|
Low Level DSBFC Transmitter block diagram |
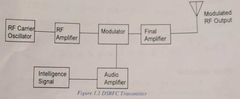
|
|
|
Low Level DSBFC Transmitter description pt 1. |
Rf Carrier Oscillator - generates the rf signal at the required frequency Rf Amplifier - boosts the rf signal to be used by the modulator Intelligence Signal - incoming audio used to modulate the trasmitter |
|
|
Low Level DSBFC Transmitter part 2. |
Audio Amp- boosts the level of audio to modulate the carrier signal Modulator - combines the audio and rf signal to produce an output Final Amp- boots the rf modulated wave to a required output level |
|
|
3 requirements that oscillators in DSBFC must have |
Spectral purity High frequency stability Accurate in frequency |
|
|
Linearity and efficiency amplifier table |
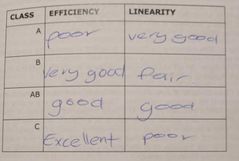
|
|
|
Two types of internal noise |
White noise Shot noise |
|
|
Sensitivity |
The ability to reproduce weak signals |
|
|
Selectivity |
The degree of distinction between the desired signal and unwanted signals |
|
|
Fidelity |
The ability to accurately reproduce the signal at the input |
|
|
Superhetrodyne receiver block diagram |
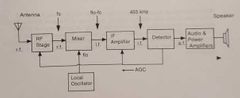
|
|
|
Superhetrodyne receiver definitions part 1. |
Antenna - picks up r.f. and passes it to r.f. amp R.f. stage - amplifies received signal (fc) LO - oscillates at the determined frequency and passes to mixer Mixer - has two inputs of fc and flo. Output is flo-fc (intermediate frequency) |
|
|
Superhetrodyne receiver part 2. |
I.f. Amp- amplifies the intermediate frequency Detector - removes the intelligence Audio and power Amp- amplifies the remaining intelligence with enough power to drive a speaker Speaker - reproduces the amplified signal |
|
|
Whats AGC and how is it derived |
A system ensuring the gain of a receiver is constant. Derives a DC signal and uses this to vary the gain of one or more rf stages. |
|
|
Advantage of dual Superhetrodyne over Superhetrodyne receiver |
Image frequency rejection is better |
|
|
Squelch and two ways it can be achieved |
Eliminates nosie Internal and external |
|
|
Requirements for oscillation |
Power supply Amplifying device Frequency determining network Postivie feeback |
|
|
Factors affecting crystal oscillators and methods |
Temp - temp oven Power supply ripple - power supply filter |
|
|
Bandwidth with respect to ceramic filters |
High degree of frequency accuracy and stability |
|
|
Pre emphasis and de emphasis |
Upper audio frequency range is amplified Reduces amplitude of higher frequency |
|
|
Piezo electrical crystal circuit |
|
|
|
Four types of pulse modulation |
Pulse Amplidute Modulation - pulse of the same duration while varying the amplitude Pulse Code Modulation - signal is converted to binary Pulse Duration Modulation - pulse of the same amplitude while varying the time Pulse Position Modulation - pulses of the same duration and amplitude while the time between pulses is varied |
|
|
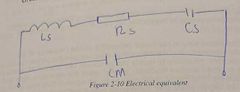
Circuit equivalent of a transmission line |
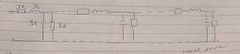
|
|
|
Why are standing waves undesirable |
Radiation loss Breakdown of insulation |
|
|
3 causes of attenuation in a fiber optic cable |
Atomic absorption Scattering of light Reflection of light |
|
|
How do antennas radiate |
Converts electrical energy represented by movement of the charge carrier in a conductor to electric and magnetic energy and travels through air as radio waves. |
|
|
4 losses of practical antennas |
Dielectric Brush discharge Copper Eddy current |
|
|
4 methods of impedance matching |
Delta Balun Stub Pi |
|
|
Isotropic radiator |

Radiates uniformly in all directions p= Pt/4 pi r2 |
|
|
Beamwidth of an antenna |
Width of largest load between 3dp points |
|
|
4 types of multiplexing |
1. SDM - physical paths are established by running new wires beside existing ones 2. FDM - each user signal modulates carrier frequency in the bandwidth 3. WDM - wavelengths of light are used for data paths through fibre 4. TDM - each signal is assigned to a time interval and gets a turn using channel links and frequncies |
|
|
FEC |
Forward error correction Helps recover data if there's loss in signal quality |
|
|
Geostationary |
Where the satellite roates with earth around the equator and looks stationary. Covers 42.4% of earth's surface |
|
|
Footprint |
Area on earth that can be received from and transmitted too. |
|
|
Balanced and unbalanced |
* Voltages on the two conductors are equal and opposite with earth * one side of the line is earthed with the other at zero |
|
|
Disadvantages of TRF |
Bandwidth increases with frequency and all r.f. stages have to track one another |
|
|
Whats required for SSB receiver |
Re-insert the carrier frequency |
|
|
3 frequency determining network circuits |
Colpitts Hartley Crystal |
|
|
Image frequency equation |
fsi = fs + 2fi |

