![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does TBI stand for?
|
HAHA if you missed this drop out.
-Traumatic Brain Injury |
|
|
Males and females are equally likely to obtain a TBI?
|
-FALSE:
-Men are more stupider. |
|
|
T or F:
A TBI is defined as a brain injury which results in diminished or altered consciousness, and impaired cognitive and physical abilities. |
FALSE:
-it does not have to be both cognitive AND physical. It can be either OR both. |
|
|
What is the leading cause of TBI in youth/adolescents? Older population?
|
-Falls/MVA
-Older: Falls |
|
|
A diffuse axonal injury is another name for what?
|
-Concussion
|
|
|
What type of forces cause diffuse axonal injuries (concussion)?
|
-Caused by rotational forces, such as with a car accident.
-Caused by shearing forces that affect axons during ACC/DCC of brain; affects neurons of the reticular activating system; |
|
|
A _____________ is defined as an alteration of mental status due to biomechanical forces affecting the brain.
|
-Concussion
|
|
|
Concussion symptons?
|
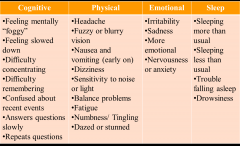
|
|
|
What are the six stages of returning from a concussion?
|
1) No activity
2) Light aerobic activity 3) Sports-specific activity 4) Non-contact drills 5) Full contact practice 6) Return to play |
|
|
What is the basic definition of a Contrecoup injury?
|
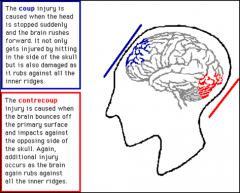
-An injury where the brain bounces off both the front and back of the skull.
|
|
|
A _________________ hematoma occurs between the skull and duramater.
-T or F: This is a medical emergency? |
-Epidural Hematoma
-TRUE: this is a medical emergency due to the rapid increase of ICP |
|
|
Executive Function and decision making are performed in which lobe?
|
-Frontal lobe
|
|
|
Balance, Coordination and Visual, are performed in which lobe?
|
-Cerebellar
|
|
|
Subdural hematomas are often associated with __________ trauma.
-With or without skull fracture?? |
-BLUNT trauma
-WITHOUT skull fracture |
|
|
Penetration Injury:
|
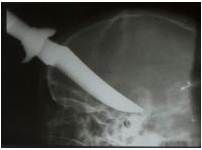
If you dont know this, again stop right now and leave. Just GO HOME.
|
|
|
KEGEL QUESTION:
-What is the normal range of intracranial pressure and what is considered increased intracranial pressure? |
0-10 mmHg
|
|
|
What is considered increased ICP?
|
>20 mmHg for >/= 5 min.
|
|
|
Cardinal S/S of increased ICP include? (4)
|
1) Headache,
2) Papilledema with retinal hemorrhages, 3) Vomiting, and eventually 4) Drowsiness, progressing to coma and death. |
|
|
_____________: metabolic defect resulting in swelling of brain cells (i.e., intracellular edema)
|
-Cytotoxic Edema
|
|
|
What type of brain herniation pushes on the midbrain medially.
|
-Uncal Herniation- herniation of uncus of temporal lobe
|
|
|
This type of herniation pushes the midbrain and pons downward?
|
-Transtentorial Herniation- herniation of midbrain and pons
|
|
|
What type of herniation pushes through the foramen magnum?
|
-cerebellar tonsillar herniation
|
|
|
Name the Herniation:
|
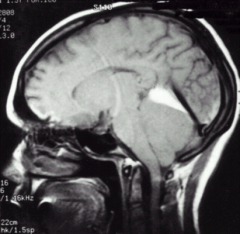
cerebellar tonsillar herniation
|
|
|
Name the Herniation:
|
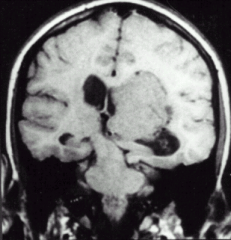
-Transtentorial
-Uncal |
|
|
Name 3-4 S/S of moderate > severe head injury.
|
-CSF coming out of the ears or nose
-Loss of consciousness -Dilated or unequal pupils -Loss of eye movement -Respiratory failure -Weakness or numbness in the extremities -Repeated nausea or vomiting -Inability to awaken from sleep -Persistent Headache -Increased confusion or agitation -Convulsions or seizures -Slurred speech |
|
|
T or F:
Patients in a coma are able to respond to some stimuli at certain times? |
FALSE: person cannot be aroused and does not respond to any type of stimulation.
|
|
|
What are the four levels of a coma?
|
1) Comatose and Unresponsive State
2) Comatose but Responsive State 3) Conscious but Unresponsive State 4) Conscious and Responsive State |
|
|
Which State?
-Patient is able to see, hear, touch, taste, and/or smell but is unable to respond. |
Conscious but unresponsive state
|
|
|
Which State?
-pt. responds to sensory stimulation with increased HR or breathing rate, facial expressions, or body movements. |
-Comatose but responsive
|
|
|
KEGEL QUESTION:
What is the difference between coma and a persistent vegetative state? |
A coma last only weeks while a vegetative state may last months >years.
|
|
|
A patient with a glasgow score of 10 has a ____________ head injury.
|
-Moderate
-Mild head injury (GCS 13-15) -Moderate head injury (GCS 9-12) -Severe head injury (GCS 8 or less) |
|
|
List 3 of the 4 guidelines to determine the need for ICP monitoring.
|
-GCS of 3-8
-Age over 40 -Posturing position (decorticate/decerebrate) -systolic BP less than 90 mmHg |
|
|
Which type of ICP monitoring is inserted directly into the ventrical?
|
-ICP ventricular monitor
-Allows withdrawal of CSF for treatment of high ICP |
|
|
_______________ is calculated as the difference between the mean arterial pressure (MAP) and the ICP
|
-Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)
-CPP value of 70mmHg considered adequate; MAP should be 90 mmHg. -CPP < 40 to 50mmHg causes ischemia. |
|
|
_________________ agonist affects memory.
|
-Acetylcholine agonist
|
|
|
T or F:
Dopamine increases arousal? |
TRUE
|
|
|
The heads up posture requires the head to be at ______ degrees while in the bed.
|
-30 degrees
|
|
|
An abnormal flexion posture is known as _____________.
|
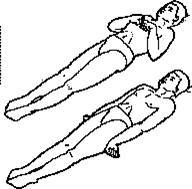
-Decorticate
-injury between cortex and red nucleus |
|
|
People with _____________ _____________damage use poor judgment and have difficulty conforming to social conventions.
|
-Orbitofrontal Cortex
|
|
|
Prognosis following a coma is determined by?
|
-Duration of coma
-Severity of coma in the first few hours after the injury -Duration of post-traumatic amnesia -Location and size of contusions and hemorrhages in the brain -Severity of injuries to other body systems sustained at the time of the TBI |
|
|
Glacow Coma Scale score of 9 or above have a ______ chance for recovery of function
|
-Good
-Lower scores are potentially fatal |
|
|
Cognitive memory changes after TBI, can include things such as?
A M I J S |
-Attention
-Memory -Initiation -Judgement -Speed |
|
|
Where would you not want to exercise with a patient who has SELECTIVE attention problems?
|
-In a crowded gym,
-They would not be able to focus |
|
|
T or F:
One of the best prognostic tools following a TBI is based on memory loss? |
TRUE.
|
|
|
PTA stands for?
|
Post Traumatic Amnersia
-Inability to lay down memories reliably from one day to the next. |
|
|
What is the inability to recall past memories?
|
-Retrograde
|
|
|
T or F:
-A Patient with anterograde amnesia is unable to learn? |
FALSE:
-They are able to motor learn but not cognitively learn new information. |
|
|
At what time frame is PTA considered severe?
|
-Severe = > 1 day and < 7 days
|
|
|
A patient following a TBI patient would be able to learn in which manner?
a) declarative b) procedural c) both |
b) procedural
-They would learn best with a classical conditioning setting. This would require excessive repetition and structure. |
|
|
What is commonly the most difficult change for a family to overcome?
|
-The personality and behavioral changes.
|
|
|
List 2 common conditions we try to prevent in the ICU setting, following a TBI?
|
-Skin breakdown
-Contractures -Other injuries |
|
|
T or F:
-Serial casting is when the extrimity is put in a stretch for an extended period of time. |
FALSE:
-You do not stretch the limb. It is placed at end range. |
|
|
What must be done between castings to improve joint lubrication?
|
-Joint Mobs in a low grade.
|
|
|
Splints with a spring are known as _____________ _______________.
|
-Dynamic Splints
|
|
|
What is one of the leading problems with Dynamic splints?
|
-The are prone to skin breakdown because they are not total contact splints
|
|
|
What Rancho level is known to be aggressive?
|
Level 4
|
|
|
The "coma level" for Rancho patients is Lever ___- ___.
|
-1-3
-Coma is defined as unresponsive to external stimuli |
|
|
A patient who is completely unresponsive to any stimuli is a level ___?
|
-Level 1
|
|
|
A patient who reacts specifically but inconsistently to stimuli is level ____?
|
-Level 3
|
|
|
A patient whos responses are limited & often the same regardless of stimulus presented is most likely a level ___?
|
-Level 2
|
|
|
Heterotopic Ossification is what?
|
-Abnormal bone growth in muscle and other areas.
|
|
|
Why is removal of heterotopic ossification's delayed initially?
|
-If it is removed too early it is very likely to return.
|
|
|
A patient who is in a heightened state of activity and demonstrating behavior that is bizarre and non-purposeful relative to immediate environment is most likely a Level ___?
|
-Level 4
-AGITATED |
|
|
What is a normal treatment time span for a Rancho level 4?
|
-Normally bouts of approx 15 min.
|
|
|
This Rancho level is described as Confused-Appropriate?
|
-Level 6
|
|
|
T or F:
Goals for levels 5-6 include motor goals, but no safety and judgement goals? |
TRUE:
They are able to motor learn, but not yet able to assess situations and use selective judgement for safety. |
|
|
What type of questions would you ask a level 5-6 patient?
|
-"do you want THIS or THAT"
-NO "yes/no questions" |
|
|
__________ is the inability to stop ones self from performing something that may not be appropriate.
|
-Disinhibition
|
|
|
___________ is when you start something and keep repeating it or inability to change off subject.
|
-Preservation
|
|
|
This Rancho level is defined as Automatic - Appropriate?
|
-Level 7
|
|
|
This Rancho level patient is able to recall and integrate past and recent events and is aware of and responsive to the environment. They show carryover for new learning and needs no supervision once activity is learned?
|
-Level 8
Purposeful - Approprite |
|
|
At what Rancho level might you consider independence a goal?
|
-Level 8
|
|
|
What is "punch drunk syndrome"?
|
-This is the cumulative effect of multiple concussions/TBIs.
-Common in boxing/MMA |
|
|
When compared to a TBI, who has a worse prognosis, TBI or axonic brain injury?
|
-Axonic Brain Injury
|
|
|
What is an Axonic Brain Injury?
|
-Secondary to incidents that alter the amount of oxygen in the blood or alters amount of cerebral perfusion for a period of time
|
|
|
These are two drugs KEGEL had listed so I may want to know:
|
-Nimbex – skeletal muscle relaxant for spasticity
-Deprovan – anaesthetic |

