![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tox causes of Bradycardia |
PACED: P ropranolol/ beta-blockers, poppies (opiates), propoxyphene, physostigmineA nticholinesterases, antiarrhythmicsC lonidine, calcium channel blockersE thanol or other alcoholsD igoxin, digitalis |
|
|
Tox Tachycardia causes |
FAST: F ree base or other cocaine forms, FreonA nticholinergics, antihistamine, antipsychotic, amphetamines, alcohol withdrawalS ympathomimentics, solvent use, strychnineT heophylline, TCAs, thyroid hormones |
|
|
Hypothermia causes tox |
COOLS: C arbon monoxideO pioidsO ral hypoglycemics and insulinL iquor (alcohol)S edative-hypnotics |
|
|
Hyperthermia causes tox |
NASA:
N euroleptic malignant syndrome, nicotineA ntihistamine, alcohol withdrawalS alicylates, sympathomimetics, serotonin syndromeA nticholinergics, antidepressants, antipsychotics |
|
|
Hypertension causes tox |
(CT SCAN)C ocaineT hyroid supplementsS ympathomimeticsC affeineA nticholinergics, amphetamines N icotine |
|
|
Hypotension tox causes |
(CRASH)C lonidine, calcium channel blockersR odenticides (has arsenic, cyanide)A ntidepressants, aminophylline, antihypertensivesS edative-hypnoticsH eroin or other opiate |
|
|
Tachypnea tox causes |
(PANT)P CP, paraquat, pneumonitis (chemical), phosgeneA SA and other salicylatesN oncardiogenic pulmonary edema, nerve agentsT oxin-mediated metabolic acidosis |
|
|
Bradypnea tox causes |
(SLOW)S edative-hypnoticsL iquor (alcohols)O pioidsW eed (marijuana) |
|
|
Whole bowel irrigation uses |
Iron lithium sustained-release medications enteric-coated tablets body Packers. Go lytely 1-2L/h |
|
|
Methanol toxicity |
Metabolized to formic acid causes blindness period increases lactate |
|
|
Ethylene glycol toxicity |
Metabolized to oxalic acid binds calcium precipitates and kidneys renal failure. Can see hypocalcemia. Anti-freeze |
|
|
Isopropyl alcohol toxicity |
Hand sanitizers mouthwash rubbing alcohol makes you clinically intoxicated metabolize to acetone. Breathe out. Cerebellar signs |
|
|
Treatment of acute toxic alcohol ingestion |
FOmeprazole. alcohol dehydrogenase inhibition. remember to redose. 20 mg / kg then 10 mg / kg q12h x 4 doses |
|
|
Serum osmolal gap equation |
= osm calculated - osm measured Normal -14 - 14. Osm calculated =2Na + glucose/18 + BUN/2.8 + alcohol/4.6 If large gap consider toxic alcohol |
|
|
Phenothiazine toxicity |
TCA like, seizure, VT, hypotension, pinpoint pupil. Compazine Reglan Thorazine ( Prochlorperazine promethazine chlorpromazine) |
|
|
Zofran toxicity |
QT prolongation torsades |
|
|
Torsades treatment |
Magnesium 2G IV over 60 Seconds. Overdrive pacing |
|
|
Medications with risk of torsades |
Phenothiazines antidysrhythmics Haldol macrolides fluoroquinolones methadone Zofran |
|
|
Cocaine toxicity and treatment |
Hypertension hyperthermia rhabdo seizure VT Tx : benzos cooling nitrates CCB (nicardipine). Avoid bb |
|
|
GHB toxicity |
Date rape drug. Bradycardia Bradypnea, rapid Awakening. loss of coordination |
|
|
Indications for crofab in snake bites |
Progression of swelling low platelets or low fibrin. |
|
|
Black widow spider symptoms |
Painful bite. Bullseye lesion |
|
|
Brown recluse spider bite |
Painless bite. Local reaction: erythema. induration. Central ulcer. necrosis. poor wound healing. Prayer hemolysis, DIC, shock |
|
|
Ciguatera |
Toxin from dinoflagellates. Grouper Barracuda snapper. Effects of sodium channels and cholinergic receptors. Onset 6 hours gastroenteritis, hot cold reversal myalgia, loose teeth, bradycardia, respiratory arrest. Tx : mannitol
|
|
|
Scombroid |
Poor refrigeration of fish histamine tuna mahi-mahi mackerel peppery flavor Rapid onset skin Flushing, gastroenteritis |
|
|
Difference in beta blocker and calcium channel blocker toxicity |
Hypoglycemia with beta blocker hyperglycemia with calcium channel blocker. |
|
|
Digoxin toxicity |
Bradycardia, PVC, bi-directional VT. CNS: agitation lethargy psychosis Yellow green vision. Nausea vomiting abdominal pain. hyperK |
|
|
Medications that cause bradycardia and hypotension |
CCB, BB, clonidine, digoxin |
|
|
Toxic salicylate ingestion level acute |
100mg/kg |
|
|
VX nerve agent presentation |
Patient drops quick, seizure, n/v, diaphoresis, diarrhea, salivation (sludge) paralysis, pinpoint pupil, Bradycardia. |
|
|
VX nerve agent tx |
Basically is organophosphate. Stops breakdown of acetylcholine. Decontaminate Intubate Tx: Atropine 2g up to 10 (titrate to drying secretions) 2-PAM: 1-2 g bolus then gtt Diazepam: 10-20mg (sz prophylaxis)
|
|
|
Nerve agents |
VX (not volatile) can be absorbed dermally Sarin (volatile) Tabin (ages quickly |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker antidote |
Calcium chloride Glucagon |
|
|
Treatment of hypermagnesemia |
Calcium gluconate |
|
|
Causes of miosis tox |
Opioids organophosphates, phenothiazines, clonidine |
|
|
Lead pipe rigidity |
Neuromuscular malignant syndrome |
|
|
Clonus /hyperreflexia cause |
Serotonin toxicity |
|
|
Flushing / warm dry skin |
Anticholinergic toxicity |
|
|
Warm, moist skin |
Sympathomimetic toxicity |
|
|
Anticholinergic /anti muscarinic agents |
Jimsonweed, atropine, benztropine, antihistamines, TCA |
|
|
Anticholinergic tx |
Supportive and benzo. cooling as needed. Foley for urinary retention. |
|
|
CCB and BB OD tx |
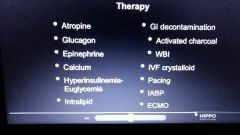
|
|
|
Dig presentation |
Hypomag, hyperK yellow green vision, halo around lights, n/v and pain, agitation legargy, psychosis, Bradycardia, VT, bidirectional VT. |

