![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is "chemical kinetics" |
Study of the rates of chemical reactions |
|
|
How is the rate of reaction found |
· measure rate of formation of a product · or rate of removal of reactant Usual procedure: measure a property of reaction mixture,eg vol&👀 how varies w/ time |
|
|
Graph of amount of product v time is steepest @ start, then slows down until it finally stops. Why does this happen? |
· Steepest at start as reaction is at fastest · 1 reactant is being used up until none of it is left |
|
|
What does gradient @ any point of graph of amount/ concentration against time measure? |
Rate of reaction at that time |
|
|
Draw graph of how conc of reactant would change with time during a chem reaction |

|
|
|
Draw graph of how vol of gas produced would change with time during a chem reaction |
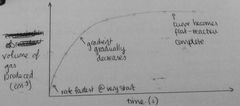
|
|
|
What's the technique used in recording of conc/ amount of product in the previous 2 graphs called |
Continuous monitoring |
|
|
How could we define rate of a chem reaction? |
· Amount product formed in given time (e.g. vol of gas (gas syringe) in t for reaction 2 finish) Rate = volume (cm^3)/ time(s)= ..cm^3s^-1 · Amount reactant used up in given time |
|
|
What factors affect rate of chem reaction? |
SA (only solids) Temp Pressure (gaseous reactants) Conc (reactions in solution) Catalyst |
|
|
How does conc affect rate of chem reaction? |
· ⬆ conc ⬆ rate · ⬆ particles per unit vol · So more frequent collisions |
|
|
How catalyst affects rate of chem reaction |
· catalysts provide alternate reaction pathway · w/ ⬇ Ea · ⬆ particles have E > Ea · ⬆ rate |
|
|
How does temp affect rate of chem reaction |
· ⬆ temp ⬆ rate · Particles more KE · ⬆ particles E > Ea · Particles move ⬆ fast so + likely to collide |
|
|
Give the meaning of the term catalyst |
Substance that speeds up reaction rate w/out being chemically changed |
|
|
We often measure reaction rate @ very start of reaction. What's this called? |
initial rates method |
|
|
What must be kept constant in investigation of effect of conc on rate at which thiosulfate ions in solution react with H+ ions to form sulphur precipitate? |
· Vol sodium thiosulfate sol. so depth of sol. in flask constant (to ensure cross is obscured when same quantity of S(s) has precipitated) · Vol & conc HCl · Temp |
|
|
Suggest why mixture in flask should be poured into container of sat. sodium carbonate solution after each experiment |
reaction produce SO2 cause breathing problems, esp for asthmatics SO2 is acidic oxide that reacts w/ alkaline sodium carb sol to form sodium sulfite Sodium sulfite ionic, stays in solution |
|
|
Draw enthalpy profile for exo reaction |

|
|
|
Draw enthalpy profile for endo reaction |
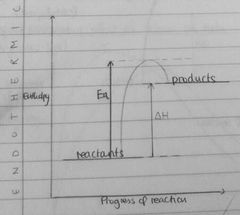
|
|
|
What do all reactions need to take place |
Reactions only take place when collisions take place with sufficient energy, known as activation energy |
|
|
Define activation energy |
Minimum energy needed in a collision for a reaction to happen |
|
|
Draw enthalpy profile for exo reaction w/ & w/out catalyst |

|
|
|
Draw enthalpy profile for exo reaction showing progress via an intermediate |
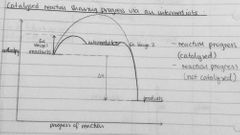
|
|
|
Draw an energy distribution curve (i.e Maxwell-Boltzmann) |
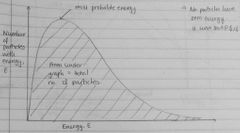
|
|
|
Do any particles have zero energy? So, where does the curve start? |
Origin |
|
|
Draw energy distribution curve for two diff temps, explain from graph why ⬆ temp ⬆ rate of reaction |
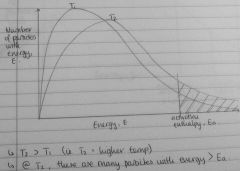
|
|
|
Explain the effect of a catalyst on reaction rate, starting by drawing a maxwell-boltzmann distribution |

A catalyst speeds up reaction rate as provides alternate reaction pathway with lower Ea Graph shows many more particles have E > Ea w/ catalyst than w/out · as area under graph = no of particles & is larger |
|
|
What's heterogeneous catalysis |
Catalyst is in a diff phase (state) to the reactants or products E.g. for C2H4(g) + H2(g) -(Ni catalyst)-> C2H6(g) |
|
|
What is the use of heterogeneous catalysts in industry? |
Easy to separate from the products |
|
|
What's homogeneous catalysis |
The catalyst is in the same phase as reactants and products |
|
|
What's the use of a solid heterogeneous catalyst for industrial reactions in the gas phase? |

(Provides surface for reaction) ·gas molecules briefly held onto surfaceof solid ·where atoms of catalyst help them to react · then product molecules break free & are carried away in the flow of gas |
|
|
Outline experiment to demonstrate that manganese(IV) oxide isn't used up in decomposition of H2O2 |
· weigh mass of manganese (IV) oxide · filter manganese(IV) oxide from water · Leave filtrate to dry · reweigh remaining solid |
|
|
How are catalysts economically beneficial in industrial reactions |
· makes reaction ⬆ productive by ⬆ yield of desired product & ⬇ waste · (can use lower temps for same reaction) · can often be recovered at end of reaction |
|
|
How does pressure affect rate of chem reaction |
⬆ pressure ⬆ rate ⬆ particles per unit volume So more frequent collisions |
|
|
How does SA affect reaction rate |
⬆ SA, ⬆ rate ⬆ rate of collision between reactant particles |

