![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is electric current |
Electric current is the flow of electric charge |
|
|
Current will only flow around a closed circuit if there is a..... |
Potential difference |
|
|
In a single closed loop is the current the same everywhere in the circuit? |
Yes |
|
|
Is potential difference the same thing as voltage ? |
Yes |
|
|
What is potential difference / voltage? |
The driving force that pushes the charge round |
|
|
What is resistance |
Anything thay slows the current of a circuit down |
|
|
The___ the resistance across a component the___ the current that flows through it (for a_____) |
The greater the resistance across a component the smaller the current that flows through it (for a given potential difference across the component) |
|
|
Unit for current |
Amperes (A) |
|
|
Unit for charge |
Cololmbs (c) |
|
|
Unit of resistance |
Ohms ♎ |
|
|
Unit of potential difference |
Volt ( V) |
|
|
What is the rate of flow of charge |
Current |
|
|
Equation for charge |

Q=It |
|
|
Triangle for charge current and time |

|
|
|
What happens when a bigger current flows |
More charges passes around the circuit |
|
|
Cell |

|
|
|
Battery |

|
|
|
Switch open |
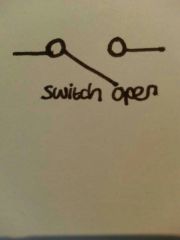
|
|
|
Resistor |

|
|
|
Variable resistor |

|
|
|
Ammeter |

|
|
|
LDR |

|
|
|
Thermistor |

|
|
|
Diode |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Voltmeter |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Fuse |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
LED |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Filament lamp / bulb |

|
|
|
Closed switch |

|
|
|
What is the equation linking potential difference current and resistance |

|
|
|
Ohmic conductors have a ..... |
Constant resistance |
|
|
What does the voltmeter measure |
The potential difference in volts across the wire |
|
|
How must the voltmeter be placed |
In parrallel |
|
|
What does the term 'I -V characteristics ' mean ? |
Refers to a graph showing how the current flowing through a component changes as the potential difference across it increases |
|
|
What happens to the current when a the temperature is constant |
At constant temperature the current flowing through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it |
|
|
Give 2 examples of ohmic conductors |
wire
Resistor |
|
|
Method for experiment investigating factors affecting resistance |

|
|
|
What happens to the resistance of a filament lamp when an electrical charge flows through |
Some energy is transferred to the thermal energy store of the filament that's designed to heat up Resistance increases with temperature So as more current flows through the filament lamp it heats up more and the resistance increases |
|
|
What happens to the resistance of a diode |
Resistance depends on direction of current
They let current flow in one direction but have a very high resistance if current is reversed |
|
|
Method for experiment investigating factors affecting resistance |
|
|
|
Factors affecting resistance |
Length of wire Whether components are in series or parallel |
|
|
What does the ammeter measure |
The current in (amps) flowing through the wire |
|
|
How must the ammeter be placed |
In series |
|
|
Ohmic conductors have a ..... |
Constant resistance |
|
|
What does the voltmeter measure |
The potential difference in volts across the wire |
|
|
How must the voltmeter be placed |
In parrallel |
|
|
What does the term 'I -V characteristics ' mean ? |
Refers to a graph showing how the current flowing through a component changes as the potential difference across it increases |
|
|
Practical for investigating IV characteristics of a component |
|
|
|
What Iv characteristics do non linear components ( such as diodes and filament lamps ) have? |
Curved line |
|
|
Iv characteristics of an ohmic conductor |
|
|
|
Iv characteristics of a filament lamp |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What happens to the current when a the temperature is constant |
At constant temperature the current flowing through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it |
|
|
Give 2 examples of ohmic conductors |
wire
Resistor |
|
|
Give to examples of components who's resistance changes |
Diode
Filament lamp |
|
|
What happens to the resistance of a filament lamp when an electrical charge flows through |
Some energy is transferred to the thermal energy store of the filament that's designed to heat up Resistance increases with temperature So as more current flows through the filament lamp it heats up more and the resistance increases |
|
|
What happens to the resistance of a diode |
Resistance depends on direction of current
They let current flow in one direction but have a very high resistance if current is reversed |
|
|
Method for experiment investigating factors affecting resistance |
|
|
|
Factors affecting resistance |
Length of wire Whether components are in series or parallel |
|
|
What does the ammeter measure |
The current in (amps) flowing through the wire |
|
|
How must the ammeter be placed |
In series |
|
|
Ohmic conductors have a ..... |
Constant resistance |
|
|
What does the voltmeter measure |
The potential difference in volts across the wire |
|
|
How must the voltmeter be placed |
In parrallel |
|
|
What does the term 'I -V characteristics ' mean ? |
Refers to a graph showing how the current flowing through a component changes as the potential difference across it increases |
|
|
Practical for investigating IV characteristics of a component |
|
|
|
What Iv characteristics do non linear components ( such as diodes and filament lamps ) have? |
Curved line |
|
|
Iv characteristics of an ohmic conductor |
|
|
|
Iv characteristics of a filament lamp |
|
|
|
Iv characteristics of a diode |
|
|
|
What is a light dependant resistor |
A resistor that is dependant on light intensity |
|
|
What happens to the resistance of an LDR in bright light |
Resistance falls |
|
|
What happens to the current when a the temperature is constant |
At constant temperature the current flowing through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it |
|
|
What happens to the LDR's resistance in darkness |
The resistance is highest |
|
|
What are LDRs used in |
Automatic night lights Outdoor lighting Burglar detectors |
|
|
LDR resistance light intensity graph |
|
|
|
What is a thermistor |
A temperature dependant resistor |
|
|
Iv characteristics of a filament lamp |
|
|
|
Iv characteristics of a diode |
|
|
|
What are thermistors used in ? |
Car engine temperature sensors Electronic thermostats |
|
|
Thermistor graph for temperature and resistance |
|
|
|
What type of circuit are LDRs and Thermistors used in |
Sensing circuits |
|
|
Example of a fan sensing circuit |
|
|
|
LDR resistance light intensity graph |
|
|
|
What is a sensing circuit used for |
Turning on or increasing the power to components depending on the conditions they are in |
|
|
Describe the potential difference across the fan and and fixed resistor |
The resistance will be the same as they're connected in parallel |
|
|
Describe the potential difference between the thermistor and the loop made up of the fixed resistor and fan |
The potential difference is shared out according to their resistances the bigger a components resistance the more of the potential difference it takes |
|
|
What happens to the resistance of the thermistor as the room gets hotter |
It decreases and takes a smaller share of the potential difference from the power supply so the potential difference across fixed resistor and fan rises making the fan go faster |
|
|
Thermistor graph for temperature and resistance |
|
|
|
The greater the potential difference across a component ________ it gets |
The greater the potential difference across a component the more energy it gets |
|
|
Example of a fan sensing circuit |
|
|
|
How are the different components connected in a series circuit |
In a line end to end between the positive and negative of the power supply
(Apart from voltmeters always connected in parallel) |
|
|
What happens when you disconnect one component in a series circuit |
The circuit is broken and all components stop |
|
|
Example of a series circuit (voltmeters in parallel) |
|
|
|
Give to examples of components who's resistance changes |
Diode
Filament lamp |
|
|
What happens to the potential difference when more cells are in series and the cells are connected in the same way ? |
The potential difference is bigger |
|
|
In a series circuit is the potential difference supply shared ? |
Yes |
|
|
Describe the distribution of current in a series circuit |
It flows the same through all components |
|
|
Example of a series circuit (voltmeters in parallel) |
|
|
|
What happens to the potential difference when more cells are in series and the cells are connected in the same way ? |
The potential difference is bigger |
|
|
Method for experiment investigating factors affecting resistance |
|
|
|
Describe the distribution of current in a series circuit |
It flows the same through all components |
|
|
Switch closed |

|
|
|
Filament lamp / bulb |

|
|
|
Fuse |

|
|
|
LED |

|
|
|
Voltmeter |

|
|
|
Diode |

|

