![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What reaction forms most biological polymers? |
Condensation reactions. |
|
|
What reaction breaks down biological polymers? |
Hydrolysis reactions. |
|
|
Name 3 different monosaccharides. |
Glucose, fructose, galactose. |
|
|
What is the structure of alpha glucose? |
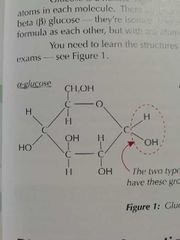
|
|
|
How is the structure of Beta glucose different to that of alpha glucose? |
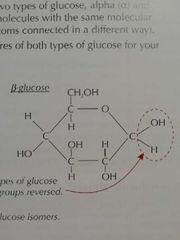
The H and OH group on carbon 1 is switched. |
|
|
What bond forms between two monosaccharides to form a disaccharide? |
A glycosidic bond. |
|
|
Draw the formation of a disaccharide. |

|
|
|
What is the test for non-reducing sugars? |
• Add dilute hydrochloric acid and boil. • Neutralise with sodium hydrogen carbonate. • Carry out the Benedict's test. |
|
|
What are the two types of starch? |
Amylose and amylopectin. |
|
|
How is amylose adapted to its function? |
It is coiled, making it compact for storage. Also insoluble so doesn't affect water potential. |
|
|
How is amylopectin adapted to its function? |
Is a branched chain, giving a larger surface area allowing for quicker hydrolysis. Also insoluble so doesn't affect water potential. |

